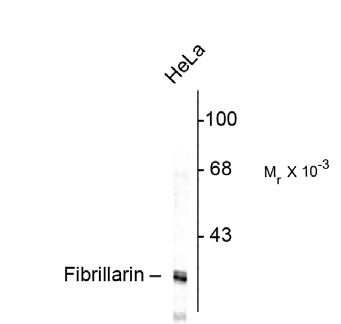
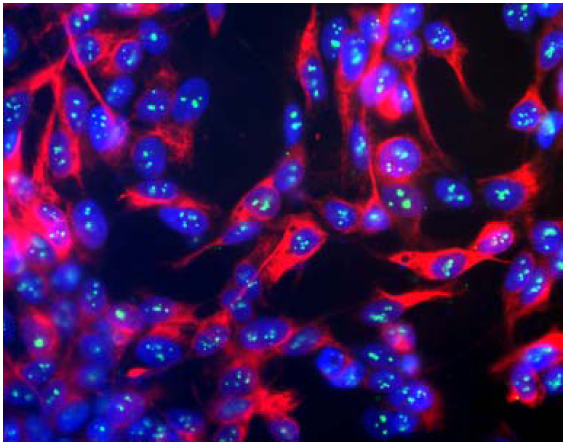
Fibrillarin (Nop1p) Antibody
Mouse monoclonal antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P15646 |
| Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clone Names | 38F3 |
| Calculated MW | 34 KDa |
| Gene ID | 851548 |
|---|---|
| Gene Name | NOP1 |
| Other Names | rRNA 2'-O-methyltransferase fibrillarin, 211-, Histone-glutamine methyltransferase, U3 small nucleolar RNA-associated protein NOP1, Nucleolar protein 1, U3 snoRNA-associated protein NOP1, NOP1, LOT3 |
| Target/Specificity | Yeast nuclear preparations. |
| Dilution | WB~~ 1:1000 IF~~ 1:500 |
| Format | Total IgG fraction |
| Antibody Specificity | Specific for the ~34kDa Fibrillarin /Nop1p protein. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Fibrillarin (Nop1p) Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Shipping | Blue Ice |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Nop1p was originally identified as a nucleolar protein of bakers yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The Nop1p protein is 327 amino acids in size (34.5kDa), is essential for yeast viability, and is localized in the nucleoli (1). The systematic name for S. cerevisiae Nop1 is YDL014W, and it is now known to be part of the small subunit processome complex, involved in the processing of pre-18S ribosomal RNA. Nop1p is the yeast homologue of a protein found in all eukaryotes and archea generally called fibrillarin (2). Fibrillarin/Nop1p is extraordinarily conserved, so that the yeast and human proteins are 67% identical, and the human protein can functionally replace the yeast protein. Patients with the autoimmune disease scleroderma often have strong circulating autoantibodies to a ~34kDa protein which was subsequently found to be fibrillarin. Recent studies show that knock-out of the fibrillarin gene in mice results in embryonic lethality, although mice with only one functional fibrillarin/Nop1p gene were viable (3). This antibody is becoming widely used as a convenient marker for nucleoli in a wide variety of species (e.g. 4-6).
References
1. Ochs RL, Lischwe MA, Spohn WH, Busch H. Fibrillarin: a new protein of the nucleolus identified by autoimmune sera. Biol Cell 54:123-133 (1985).
2. Aris JP and Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a yeast nucleolar protein that is similar to a rat liver nucleolar protein. J. Cell Biol. 107:17-31 (1988).
3. Newton K, Petfalski E, Tollervey D, Caceres JF. Fibrillarin is essential for early development and required for accumulation of an intron-encoded small nucleolar RNA in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 23:8519-8527 (2003).
4. Tyagi S and Alsmadi O. Imaging native beta-actin mRNA in motile fibroblasts. Biophys J. 87:4153-62 (2004).
5. Paeschke1 K, Simonsson T, Postberg J, Rhodes D, Lipps H-J. Telomere end-binding proteins control the formation of G-quadruplex DNA structures in vivo Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 12, 847-854 (2005).
6. Vermaak D, Henikoff S, Malik HS. Positive selection drives the evolution of rhino, a member of the heterochromatin protein 1 family in Drosophila. PLoS Genetics 1:96-108 (2005).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.