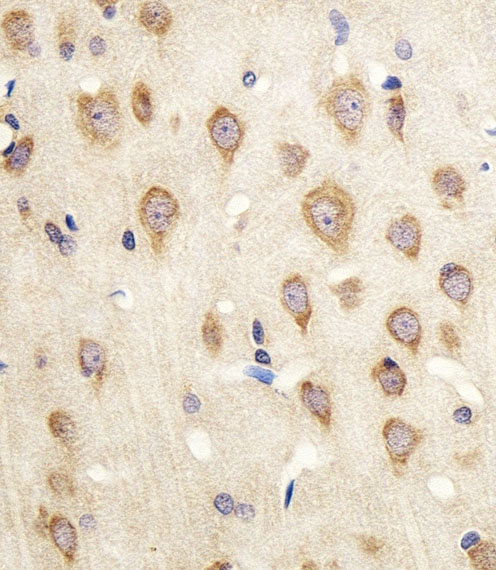
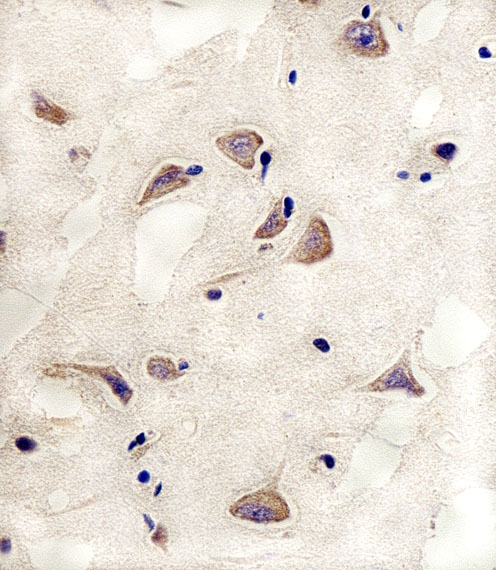
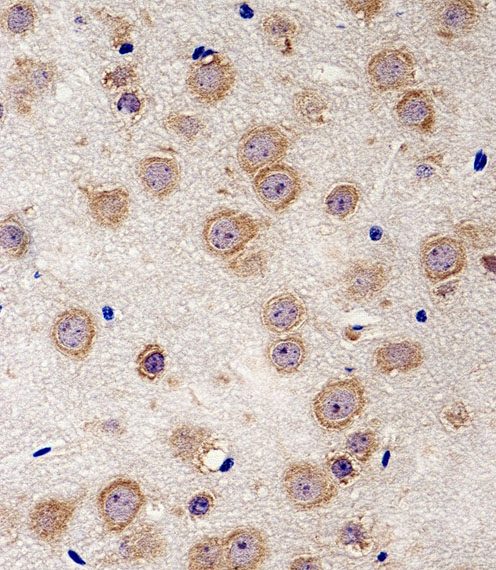
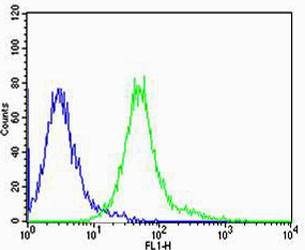
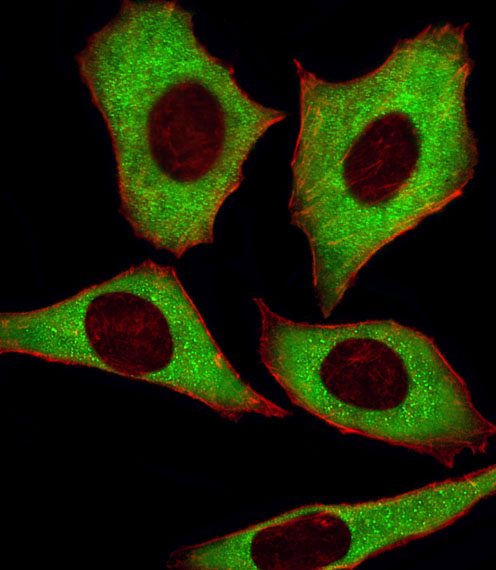
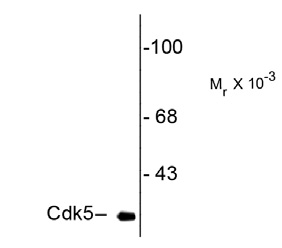
Cdk5 Antibody
Mouse monoclonal antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IHC, IF, WB, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q03114 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Clone Names | 1H3 |
| Calculated MW | 28 KDa |
| Gene ID | 140908 |
|---|---|
| Gene Name | CDK5 |
| Other Names | Cyclin-dependent-like kinase 5, Cell division protein kinase 5, Serine/threonine-protein kinase PSSALRE, Tau protein kinase II catalytic subunit, TPKII catalytic subunit, Cdk5, Cdkn5 |
| Target/Specificity | Purified rat Cdk5. |
| Dilution | IHC~~1:500 IF~~1:500 WB~~ 1:1000 FC~~1:500 |
| Format | Protein G purified culture supernatant. |
| Antibody Specificity | The antibody is specific for the ~ 28kDa Cdk5 protein in Western blots of rat striatal lysate. The antibody shows no cross reactivity with the Cdk5 cofactor p35 or its degradation product p25. This monoclonal also works well for immunocytochemistry using primary cultured rat neurons and for immunohistochemistry on mouse brain tissue. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Cdk5 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Shipping | Blue Ice |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The neuronal protein kinase, Cdk5 has been implicated in a vast array of normal neuronal functions including regulation of neurotransmitter synthesis (Kansy J et al., 2004), the presynaptic vesicle cycle (Nguyen, C. & Bibb, JA 2003), neurotransmitter receptor trafficking and dopamine neurotransmission (Bibb, JA et al. 1999). At the same time Cdk5 has been implicated in a plethora of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, epilepsy, schizophrenia, and drug addiction. Detection of Cdk5 in normal samples as well as tissue undergoing neurodegeneration may advance studies in these areas. Moreover, this antibody may allow more accurate postmortem evaluations of Cdk5 protein expression, and thus serve as a valuable new reagent for neuropathology.
References
Kansy, J. et al. Identification of tyrosine hydroxylase as a physiological substrate of Cdk5. J. Neurochem. 91, 374-384 (2004).
Nguyen, C. & Bibb, J. A. Cdk5 and the mystery of synaptic vesicle endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 163, 697- 699 (2003).
Bibb, J. A. et al. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 by Cdk5 modulates dopamine signaling in neurons. Nature 402, 669-671 (1999).
Lagace, D. C. et al. Cdk5 is essential for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 18567–18571 (2008).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.