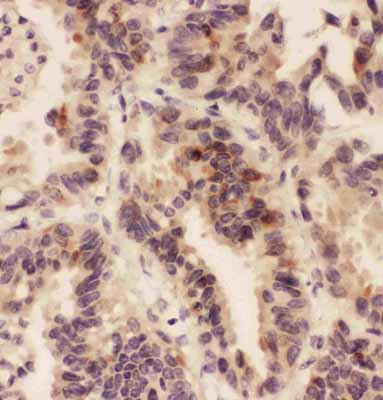
Anti-HSD11B1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P28845 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Rabbit IgG polyclonal antibody for Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1(HSD11B1) detection. Tested with WB, IHC-P in Human;Mouse;Rat. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 3290 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1, 1.1.1.146, 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1, 11-DH, 11-beta-HSD1, Short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 26C member 1, HSD11B1, HSD11, HSD11L, SDR26C1 |
| Calculated MW | 32401 MW KDa |
| Application Details | Immunohistochemistry(Paraffin-embedded Section), 0.5-1 µg/ml, Human, Rat, Mouse, By Heat Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Human, Rat, Mouse |
| Subcellular Localization | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Single-pass type II membrane protein . |
| Tissue Specificity | Widely expressed. Highest expression in liver. |
| Protein Name | Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1 |
| Contents | Each vial contains 5mg BSA, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg Thimerosal, 0.05mg NaN3. |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the N-terminus of human HSD11B1(16-33aa MAYYYYSANEEFRPEMLQ), different from the related mouse sequence by two amino acids, and from the related rat sequence by four amino acids. |
| Purification | Immunogen affinity purified. |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross reactivity with other proteins |
| Storage | At -20˚C for one year. After r˚Constitution, at 4˚C for one month. It˚Can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for a longer time.Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Name | HSD11B1 (HGNC:5208) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | HSD11, HSD11L, SDR26C1 |
| Function | Controls the reversible conversion of biologically active glucocorticoids such as cortisone to cortisol, and 11- dehydrocorticosterone to corticosterone in the presence of NADP(H) (PubMed:10497248, PubMed:12460758, PubMed:14973125, PubMed:15152005, PubMed:15280030, PubMed:17593962, PubMed:21453287, PubMed:27927697, PubMed:30902677). Participates in the corticosteroid receptor-mediated anti-inflammatory response, as well as metabolic and homeostatic processes (PubMed:10497248, PubMed:12414862, PubMed:15152005, PubMed:21453287). Plays a role in the secretion of aqueous humor in the eye, maintaining a normotensive, intraocular environment (PubMed:11481269). Bidirectional in vitro, predominantly functions as a reductase in vivo, thereby increasing the concentration of active glucocorticoids (PubMed:10497248, PubMed:11481269, PubMed:12414862, PubMed:12460758). It has broad substrate specificity, besides glucocorticoids, it accepts other steroid and sterol substrates (PubMed:15095019, PubMed:15152005, PubMed:17593962, PubMed:21453287). Interconverts 7-oxo- and 7-hydroxy-neurosteroids such as 7- oxopregnenolone and 7beta-hydroxypregnenolone, 7- oxodehydroepiandrosterone (3beta-hydroxy-5-androstene-7,17-dione) and 7beta-hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone (3beta,7beta-dihydroxyandrost-5-en- 17-one), among others (PubMed:17593962). Catalyzes the stereo-specific conversion of the major dietary oxysterol, 7-ketocholesterol (7- oxocholesterol), into the more polar 7-beta-hydroxycholesterol metabolite (PubMed:15095019, PubMed:15152005). 7-oxocholesterol is one of the most important oxysterols, it participates in several events such as induction of apoptosis, accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions, lipid peroxidation, and induction of foam cell formation (PubMed:15095019). Mediates the 7-oxo reduction of 7-oxolithocholate mainly to chenodeoxycholate, and to a lesser extent to ursodeoxycholate, both in its free form and when conjugated to glycine or taurine, providing a link between glucocorticoid activation and bile acid metabolism (PubMed:21453287). Catalyzes the synthesis of 7-beta- 25-dihydroxycholesterol from 7-oxo-25-hydroxycholesterol in vitro, which acts as a ligand for the G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 2 (EBI2) and may thereby regulate immune cell migration (PubMed:30902677). |
| Cellular Location | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed, highest expression in liver, lower in testis, ovary, lung, foreskin fibroblasts, and much lower in kidney (PubMed:1885595). Expressed in liver (at protein level) (PubMed:21453287). Expressed in the basal cells of the corneal epithelium and in the ciliary nonpigmented epithelium (both at mRNA and at protein level) (PubMed:11481269). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 is an NADPH-dependent enzyme highly expressed in key metabolic tissues including liver, adipose tissue, and the central nervous system. In these tissues, HSD11B1 reduces cortisone to the active hormone cortisol that activates glucocorticoid receptors. It is inhibited by carbenoxolone, a drug typically used in the treatment of peptic ulcers. Tannin et al.(1991) localized the HSD11B1 gene to chromosome 1. The localization was confirmed by isolating the gene from a chromosome 1-specific library using the cDNA as a probe. Schutte et al.(2000) mapped the HSD11B1 gene to 1q32-q41.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.