Anti-TIA1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

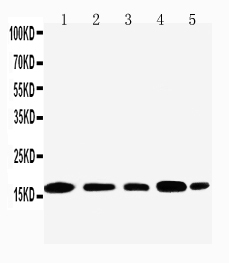
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P31483 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Rabbit IgG polyclonal antibody for Nucleolysin TIA-1 isoform p40(TIA1) detection. Tested with WB in Human;Mouse. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 7072 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Nucleolysin TIA-1 isoform p40, RNA-binding protein TIA-1, T-cell-restricted intracellular antigen-1, TIA-1, p40-TIA-1, TIA1 |
| Calculated MW | 42963 MW KDa |
| Application Details | Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Human, Mouse |
| Subcellular Localization | Cytoplasmic granule. Nucleus. Accumulates in cytoplasmic stress granules (SG) following cellular damage. |
| Protein Name | Nucleolysin TIA-1 isoform p40 |
| Contents | Each vial contains 5mg BSA, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg Thimerosal, 0.05mg NaN3. |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the N-terminus of human TIA1(98-110aa STQRSQDHFHVFV), identical to the related mouse sequence. |
| Purification | Immunogen affinity purified. |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross reactivity with other proteins |
| Storage | At -20˚C for one year. After r˚Constitution, at 4˚C for one month. It˚Can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for a longer time.Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Name | TIA1 |
|---|---|
| Function | RNA-binding protein involved in the regulation of alternative pre-RNA splicing and mRNA translation by binding to uridine-rich (U- rich) RNA sequences (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:12486009, PubMed:17488725, PubMed:8576255). Binds to U-rich sequences immediately downstream from a 5' splice sites in a uridine-rich small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (U snRNP)-dependent fashion, thereby modulating alternative pre-RNA splicing (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:8576255). Preferably binds to the U- rich IAS1 sequence in a U1 snRNP-dependent manner; this binding is optimal if a 5' splice site is adjacent to IAS1 (By similarity). Activates the use of heterologous 5' splice sites; the activation depends on the intron sequence downstream from the 5' splice site, with a preference for a downstream U-rich sequence (PubMed:11106748). By interacting with SNRPC/U1-C, promotes recruitment and binding of spliceosomal U1 snRNP to 5' splice sites followed by U-rich sequences, thereby facilitating atypical 5' splice site recognition by U1 snRNP (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:12486009, PubMed:17488725). Activates splicing of alternative exons with weak 5' splice sites followed by a U-rich stretch on its own pre-mRNA and on TIAR mRNA (By similarity). Acts as a modulator of alternative splicing for the apoptotic FAS receptor, thereby promoting apoptosis (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:17488725, PubMed:1934064). Binds to the 5' splice site region of FAS intron 5 to promote accumulation of transcripts that include exon 6 at the expense of transcripts in which exon 6 is skipped, thereby leading to the transcription of a membrane-bound apoptotic FAS receptor, which promotes apoptosis (PubMed:11106748, PubMed:17488725, PubMed:1934064). Binds to a conserved AU-rich cis element in COL2A1 intron 2 and modulates alternative splicing of COL2A1 exon 2 (PubMed:17580305). Also binds to the equivalent AT-rich element in COL2A1 genomic DNA, and may thereby be involved in the regulation of transcription (PubMed:17580305). Binds specifically to a polypyrimidine-rich controlling element (PCE) located between the weak 5' splice site and the intronic splicing silencer of CFTR mRNA to promote exon 9 inclusion, thereby antagonizing PTB1 and its role in exon skipping of CFTR exon 9 (PubMed:14966131). Involved in the repression of mRNA translation by binding to AU-rich elements (AREs) located in mRNA 3' untranslated regions (3' UTRs), including target ARE-bearing mRNAs encoding TNF and PTGS2 (By similarity). Also participates in the cellular response to environmental stress, by acting downstream of the stress-induced phosphorylation of EIF2S1/EIF2A to promote the recruitment of untranslated mRNAs to cytoplasmic stress granules (SGs), leading to stress-induced translational arrest (PubMed:10613902). Formation and recruitment to SGs is regulated by Zn(2+) (By similarity). Possesses nucleolytic activity against cytotoxic lymphocyte target cells (PubMed:1934064). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm Cytoplasm, Stress granule Note=Accumulates in cytoplasmic stress granules (SG) following cellular damage (PubMed:10613902, PubMed:15371533). Recruitment to SG is induced by Zn(2+) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15371533} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in heart, small intestine, kidney, liver, lung, skeletal muscle, testes, pancreas, and ovary (at protein level) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
TIA1, also called WDM, encodes an RNA-binding protein involved in splicing regulation and translational repression. The product encoded by this gene is a member of a RNA-binding protein family and possesses nucleolytic activity against cytotoxic lymphocyte(CTL) target cells. By in situ hybridization, this gene is mapped to chromosome 2p13.3. It has been suggested that this protein may be involved in the induction of apoptosis as it preferentially recognizes poly(A) homopolymers and induces DNA fragmentation in CTL targets. The major granule-associated species is a 15-kDa protein that is though to be derived from the carboxyl terminus of the 40-kDa product by proteolytic processing.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.