Anti-Keratocan Picoband Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

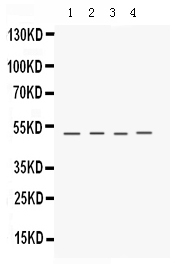
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O60938 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Rabbit IgG polyclonal antibody for Keratocan(KERA) detection. Tested with WB in Human;Mouse. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 11081 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Keratocan, KTN, Keratan sulfate proteoglycan keratocan, KERA, SLRR2B |
| Calculated MW | 40509 MW KDa |
| Application Details | Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Human, Mouse |
| Subcellular Localization | Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix . |
| Tissue Specificity | Cornea. Increased expression in the stroma of keratoconus corneas. Also detected in trachea, and in low levels, in intestine, skeletal muscle, ovary, lung and putamen. . |
| Protein Name | Keratocan |
| Contents | Each vial contains 5mg BSA, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg NaN3. |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the C-terminus of human Keratocan (77-109aa YLQNNLIETIPEKPFENATQLRWINLNKNKITN), different from the related mouse sequence by two amino acids. |
| Purification | Immunogen affinity purified. |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross reactivity with other proteins |
| Storage | At -20˚C for one year. After r˚Constitution, at 4˚C for one month. It˚Can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for a longer time.Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Name | KERA |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | SLRR2B |
| Function | May be important in developing and maintaining corneal transparency and for the structure of the stromal matrix. |
| Cellular Location | Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix |
| Tissue Location | Cornea (at protein level) (PubMed:10802664, PubMed:11683372). Increased expression in the stroma of keratoconus corneas (PubMed:11683372). Also detected in trachea, and in low levels, in intestine, skeletal muscle, ovary, lung and putamen (PubMed:10802664). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Keratocan (KTN), also known as keratan sulfate proteoglycan keratocan, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KERA gene. It is mapped to 12q22. The protein encoded by this gene is a keratan sulfate proteoglycan that is involved in corneal transparency. Defects in this gene are a cause of autosomal recessive cornea plana 2 (CNA2). Keratan sulfate proteoglycans (KSPGs) are members of the small leucine-rich proteoglycan (SLRP) family. KSPGs, particularly keratocan, lumican and mimecan, are important to the transparency of the cornea.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.