CD-14 Antibody (NT)
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, IF, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P08571 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 40076 Da |
| Gene ID | 929 |
|---|---|
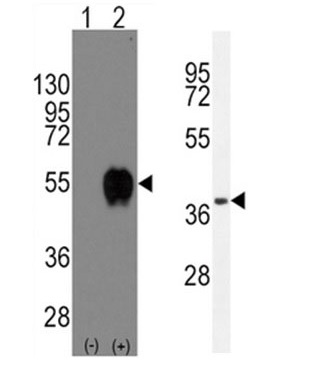
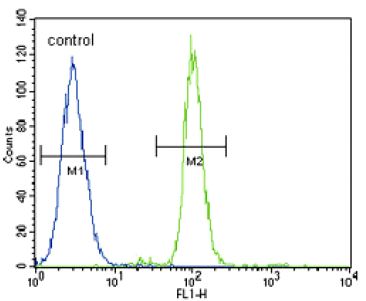
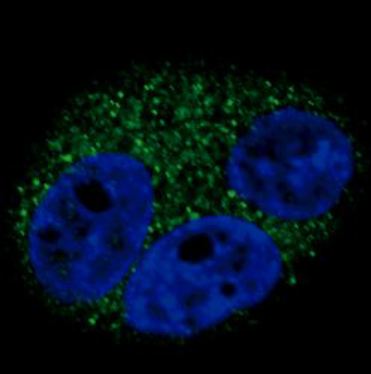
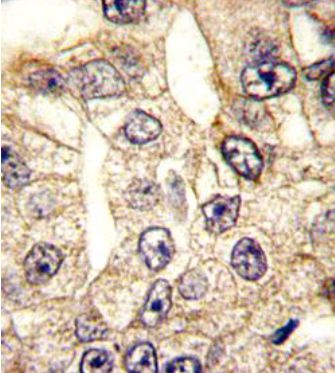
| Positive Control | Western blot: 293 cell lysate, IHC: human lung carcinoma, FACS: A549 cells, IF: A549 cells |
| Application & Usage | Western blot: ~1:1000, IHC: ~1:10–1:50, IF: ~1:10–1:50, FACS: ~1:10-1:50. |
| Other Names | CD14; Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14; Myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein; CD_antigen=CD14; Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, urinary form; Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, membrane-bound form. |
| Target/Specificity | CD-14 |
| Antibody Form | Liquid |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Formulation | 100 µl of antibody in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | -20 °C |
| Background Descriptions | |
| Precautions | CD-14 Antibody (NT) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CD14 |
|---|---|
| Function | Coreceptor for bacterial lipopolysaccharide (PubMed:1698311, PubMed:23264655). In concert with LBP, binds to monomeric lipopolysaccharide and delivers it to the LY96/TLR4 complex, thereby mediating the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (PubMed:20133493, PubMed:22265692, PubMed:23264655). Acts via MyD88, TIRAP and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response (PubMed:8612135). Acts as a coreceptor for TLR2:TLR6 heterodimer in response to diacylated lipopeptides and for TLR2:TLR1 heterodimer in response to triacylated lipopeptides, these clusters trigger signaling from the cell surface and subsequently are targeted to the Golgi in a lipid-raft dependent pathway (PubMed:16880211). Binds electronegative LDL (LDL(-)) and mediates the cytokine release induced by LDL(-) (PubMed:23880187). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor, GPI-anchor. Secreted. Membrane raft. Golgi apparatus. Note=Secreted forms may arise by cleavage of the GPI anchor. |
| Tissue Location | Detected on macrophages (at protein level) (PubMed:1698311). Expressed strongly on the surface of monocytes and weakly on the surface of granulocytes; also expressed by most tissue macrophages. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) elicits the secretion of mediators and cytokines produced by activated macrophages and monocytes. CD14 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein found on the surfaces of monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. CD14 functions as a receptor for LPS, resulting in the secretion of various proteins. An important component in the LPS activation of monocytes through the CD14 receptor is the “adapter molecule,” lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP). There are two forms of CD14, a membrane-associated form (mCD14), and a soluble form (sCD14). mCD14 responds to LPS alone and facilitates the secretion of proteins, while cells not expressing mCD14 fail to respond to LPS. The cells that lack mCD14 respond to LPS/LBP in the presence of sCD14.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.