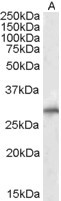
Goat Anti-SIAH1 Antibody
Peptide-affinity purified goat antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IP, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q8IUQ4 |
| Other Accession | NP_001006611, 6477, 20437 (mouse) |
| Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Predicted | Mouse, Dog |
| Host | Goat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 100ug/200ul |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 31123 Da |
| Gene ID | 6477 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SIAH1, 6.3.2.-, Seven in absentia homolog 1, Siah-1, Siah-1a, SIAH1, HUMSIAH |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IP~~N/A E~~N/A |
| Format | 0.5 mg IgG/ml in Tris saline (20mM Tris pH7.3, 150mM NaCl), 0.02% sodium azide, with 0.5% bovine serum albumin |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Goat Anti-SIAH1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SIAH1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | HUMSIAH |
| Function | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:14506261, PubMed:14645235, PubMed:14654780, PubMed:15064394, PubMed:16085652, PubMed:19224863, PubMed:20508617, PubMed:22483617, PubMed:28546513, PubMed:32430360, PubMed:33591310, PubMed:9334332, PubMed:9858595). E3 ubiquitin ligases accept ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates (PubMed:14506261, PubMed:14645235, PubMed:14654780, PubMed:15064394, PubMed:16085652, PubMed:19224863, PubMed:20508617, PubMed:22483617, PubMed:9334332, PubMed:9858595). Mediates E3 ubiquitin ligase activity either through direct binding to substrates or by functioning as the essential RING domain subunit of larger E3 complexes (PubMed:14506261, PubMed:14645235, PubMed:14654780, PubMed:15064394, PubMed:16085652, PubMed:19224863, PubMed:20508617, PubMed:22483617, PubMed:9334332, PubMed:9858595). Triggers the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of many substrates, including proteins involved in transcription regulation (ELL2, MYB, POU2AF1, PML and RBBP8), a cell surface receptor (DCC), the cell-surface receptor-type tyrosine kinase FLT3, the cytoplasmic signal transduction molecules (KLF10/TIEG1 and NUMB), an antiapoptotic protein (BAG1), a microtubule motor protein (KIF22), a protein involved in synaptic vesicle function in neurons (SYP), a structural protein (CTNNB1) and SNCAIP (PubMed:10747903, PubMed:11146551, PubMed:11389839, PubMed:11389840, PubMed:11483517, PubMed:11483518, PubMed:11752454, PubMed:12072443). Confers constitutive instability to HIPK2 through proteasomal degradation (PubMed:18536714, PubMed:33591310). It is thereby involved in many cellular processes such as apoptosis, tumor suppression, cell cycle, axon guidance, transcription regulation, spermatogenesis and TNF-alpha signaling (PubMed:14506261, PubMed:14645235, PubMed:14654780, PubMed:15064394, PubMed:16085652, PubMed:19224863, PubMed:20508617, PubMed:22483617, PubMed:9334332, PubMed:9858595). Has some overlapping function with SIAH2 (PubMed:14506261, PubMed:14645235, PubMed:14654780, PubMed:15064394, PubMed:16085652, PubMed:19224863, PubMed:20508617, PubMed:22483617, PubMed:9334332, PubMed:9858595). Induces apoptosis in cooperation with PEG3 (By similarity). Upon nitric oxid (NO) generation that follows apoptotic stimulation, interacts with S-nitrosylated GAPDH, mediating the translocation of GAPDH to the nucleus (By similarity). GAPDH acts as a stabilizer of SIAH1, facilitating the degradation of nuclear proteins (By similarity). Mediates ubiquitination and degradation of EGLN2 and EGLN3 in response to the unfolded protein response (UPR), leading to their degradation and subsequent stabilization of ATF4 (By similarity). Also part of the Wnt signaling pathway in which it mediates the Wnt-induced ubiquitin- mediated proteasomal degradation of AXIN1 (PubMed:28546513, PubMed:32430360). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=Predominantly cytoplasmic. Partially nuclear |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed at a low level. Down-regulated in advanced hepatocellular carcinomas. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the seven in absentia homolog (SIAH) family. The protein is an E3 ligase and is involved in ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of specific proteins. The activity of this ubiquitin ligase has been implicated in the development of certain forms of Parkinson's disease, the regulation of the cellular response to hypoxia and induction of apoptosis. Alternative splicing results in several additional transcript variants, some encoding different isoforms and others that have not been fully characterized.
References
SIAH-1 interacts with mammalian polyhomeotic homologues HPH2 and affects its stability via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Wu H, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2010 Jul 2. PMID 20471960.
E2F1 represses beta-catenin/TCF activity by direct up-regulation of Siah1. Xie W, et al. J Cell Mol Med, 2009 Aug. PMID 20187294.
Direct ubiquitination of beta-catenin by Siah-1 and regulation by the exchange factor TBL1. Dimitrova YN, et al. J Biol Chem, 2010 Apr 30. PMID 20181957.
Distinct expression patterns of the E3 ligase SIAH-1 and its partner Kid/KIF22 in normal tissues and in the breast tumoral processes. Bruzzoni-Giovanelli H, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2010 Feb 9. PMID 20144232.
The expression of SIAH1 is downregulated and associated with Bim and apoptosis in human breast cancer tissues and cells. Wen YY, et al. Mol Carcinog, 2010 May. PMID 20082325.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.