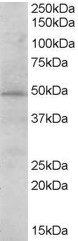
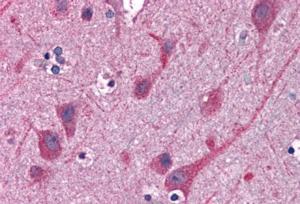
Goat Anti-STAP2 / BKS Antibody
Peptide-affinity purified goat antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UGK3 |
| Other Accession | NP_001013863, 55620 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Goat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 100ug/200ul |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 44894 Da |
| Gene ID | 55620 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Signal-transducing adaptor protein 2, STAP-2, Breast tumor kinase substrate, BRK substrate, STAP2, BKS |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC~~1:100~500 E~~N/A |
| Format | 0.5 mg IgG/ml in Tris saline (20mM Tris pH7.3, 150mM NaCl), 0.02% sodium azide, with 0.5% bovine serum albumin |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Goat Anti-STAP2 / BKS Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | STAP2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BKS |
| Function | Substrate of protein kinase PTK6. May play a regulatory role in the acute-phase response in systemic inflammation and may modulate STAT3 activity. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes the substrate of breast tumor kinase, an Src-type non-receptor tyrosine kinase. The encoded protein possesses domains and several tyrosine phosphorylation sites characteristic of adaptor proteins that mediate the interactions linking proteins involved in signal transduction pathways. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
References
An approach based on a genome-wide association study reveals candidate loci for narcolepsy. Shimada M, et al. Hum Genet, 2010 Oct. PMID 20677014.
Signal-transducing adaptor protein-2 regulates stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha-induced chemotaxis in T cells. Sekine Y, et al. J Immunol, 2009 Dec 15. PMID 19933863.
The protein content of an adaptor protein, STAP-2 is controlled by E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl. Sekine Y, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009 Jun 26. PMID 19401194.
STAP-2 is phosphorylated at tyrosine-250 by Brk and modulates Brk-mediated STAT3 activation. Ikeda O, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009 Jun 19. PMID 19393627.
STAP-2 negatively regulates both canonical and noncanonical NF-kappaB activation induced by Epstein-Barr virus-derived latent membrane protein 1. Ikeda O, et al. Mol Cell Biol, 2008 Aug. PMID 18573890.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.