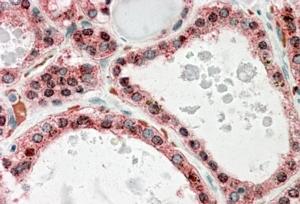
Goat Anti-KCNN2 Antibody
Peptide-affinity purified goat antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9H2S1 |
| Other Accession | NP_740721, 3781, 140492 (mouse), 54262 (rat) |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Mouse, Rat, Dog |
| Host | Goat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 100ug/200ul |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 63760 Da |
| Gene ID | 3781 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 2, SK2, SKCa 2, SKCa2, KCa2.2, KCNN2 |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC~~1:100~500 E~~N/A |
| Format | 0.5 mg IgG/ml in Tris saline (20mM Tris pH7.3, 150mM NaCl), 0.02% sodium azide, with 0.5% bovine serum albumin |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Goat Anti-KCNN2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | KCNN2 (HGNC:6291) |
|---|---|
| Function | Small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel that mediates the voltage-independent transmembrane transfer of potassium across the cell membrane through a constitutive interaction with calmodulin which binds the intracellular calcium allowing its opening (PubMed:10991935, PubMed:33242881, PubMed:9287325). The current is characterized by a voltage-independent activation, an intracellular calcium concentration increase-dependent activation and a single- channel conductance of about 3 picosiemens (PubMed:10991935). Also presents an inwardly rectifying current, thus reducing its already small outward conductance of potassium ions, which is particularly the case when the membrane potential displays positive values, above + 20 mV (PubMed:10991935). The inward rectification could be due to a blockade of the outward current by intracellular divalent cations such as calcium and magnesium and could also be due to an intrinsic property of the channel pore, independent of intracellular divalent ions. There are three positively charged amino acids in the S6 transmembrane domain, close to the pore, that collectively control the conductance and rectification through an electrostatic mechanism. Additionally, electrostatic contributions from these residues also play an important role in determining the intrinsic open probability of the channel in the absence of calcium, affecting the apparent calcium affinity for activation. Forms an heteromeric complex with calmodulin, which is constitutively associated in a calcium-independent manner. Channel opening is triggered when calcium binds the calmodulin resulting in a rotary movement leading to the formation of the dimeric complex to open the gate (By similarity). Plays a role in the repolarization phase of cardiac action potential (PubMed:13679367). |
| Cellular Location | Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere, Z line {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P58390} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in atrial myocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:13679367). Widely expressed. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Action potentials in vertebrate neurons are followed by an afterhyperpolarization (AHP) that may persist for several seconds and may have profound consequences for the firing pattern of the neuron. Each component of the AHP is kinetically distinct and is mediated by different calcium-activated potassium channels. The protein encoded by this gene is activated before membrane hyperpolarization and is thought to regulate neuronal excitability by contributing to the slow component of synaptic AHP. The encoded protein is an integral membrane protein that forms a voltage-independent calcium-activated channel with three other calmodulin-binding subunits. This gene is a member of the KCNN family of potassium channel genes. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.
References
Alpha-actinin2 cytoskeletal protein is required for the functional membrane localization of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel (SK2 channel). Lu L, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009 Oct 27. PMID 19815520.
Ablation of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel (SK2 channel) results in action potential prolongation in atrial myocytes and atrial fibrillation. Li N, et al. J Physiol, 2009 Mar 1. PMID 19139040.
Cell-cycle-dependent regulation of Ca2+-activated K+ channel in Jurkat T-lymphocyte. Morimoto T, et al. J Pharmacol Sci, 2007 May. PMID 17452806.
Molecular coupling of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel to L-type Ca2+ channels via alpha-actinin2. Lu L, et al. Circ Res, 2007 Jan 5. PMID 17110593.
Ca2+-activated K+ channels in human melanoma cells are up-regulated by hypoxia involving hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Tajima N, et al. J Physiol, 2006 Mar 1. PMID 16396931.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.