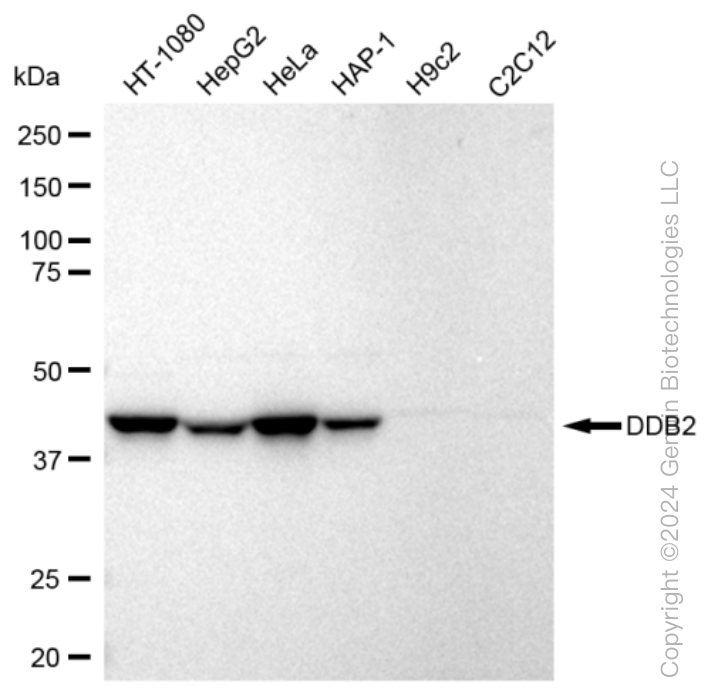
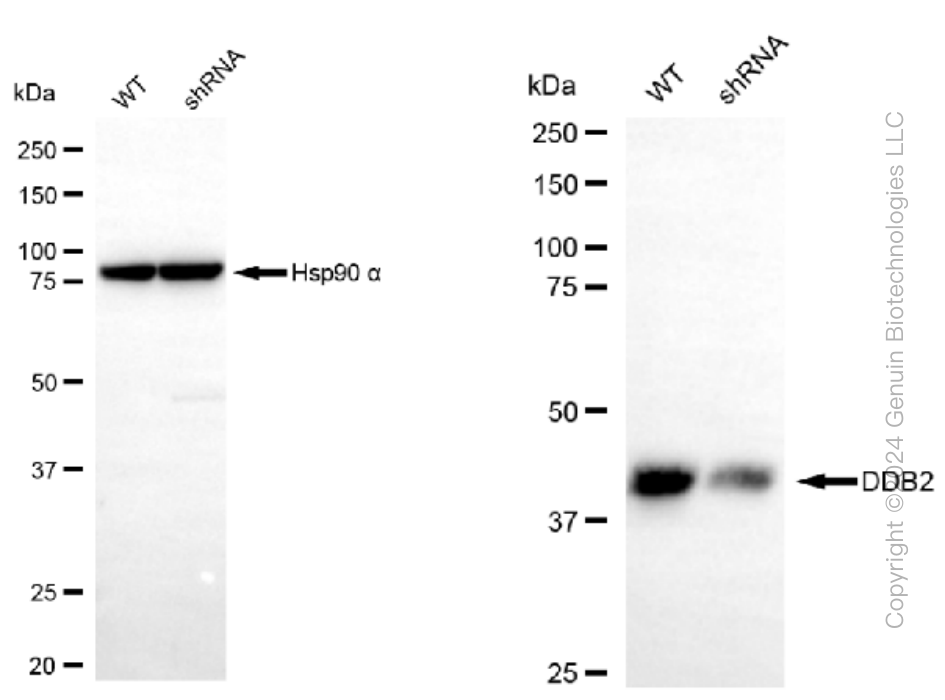
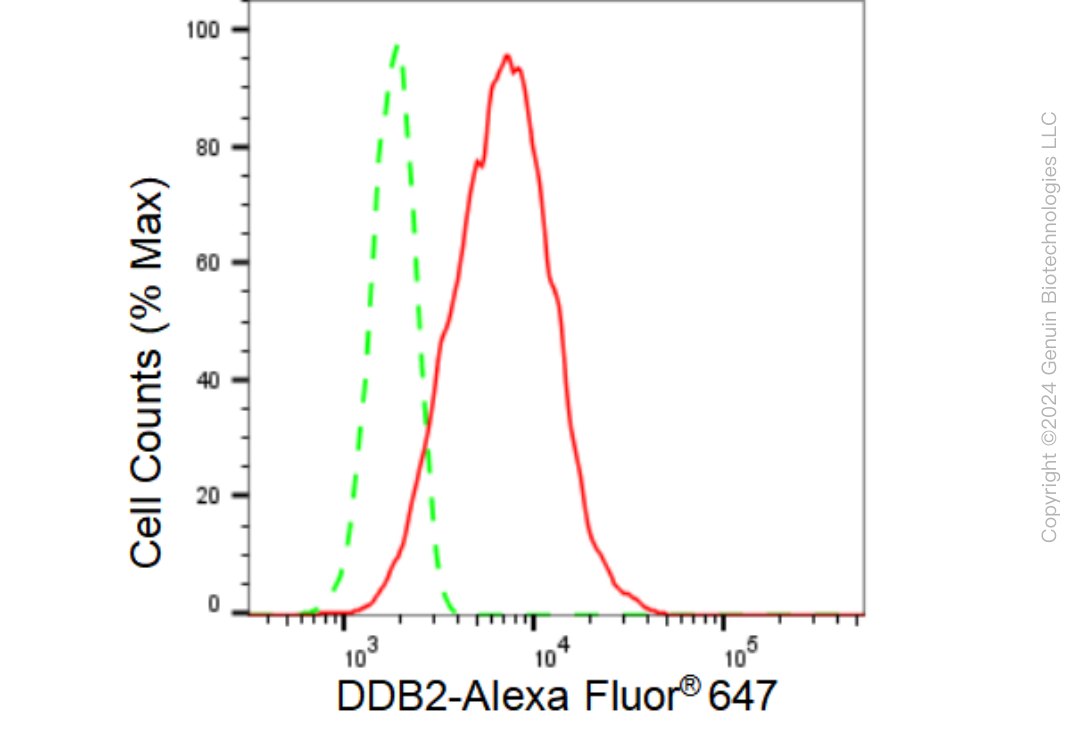
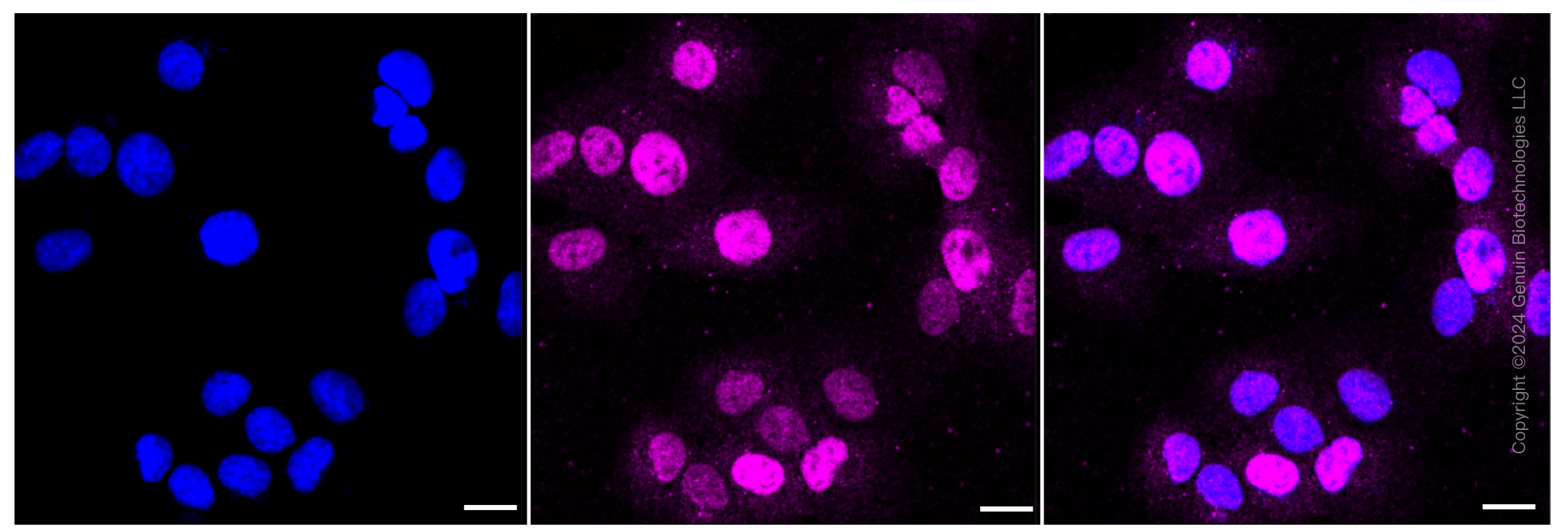
KD-Validated Anti-DDB2 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
Rabbit monoclonal antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, FC, ICC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q92466 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Clone Names | 23GB 2805 |
| Calculated MW | Predicted, 48 kDa , observed, 45 kDa |
| Gene Name | DDB2 |
| Aliases | DDB2; Damage Specific DNA Binding Protein 2; UV-Damaged DNA-Binding Protein 2; DDB P48 Subunit; UV-DDB2; DDBB; XPE; Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group E Protein; DNA Damage-Binding Protein 2; FLJ34321; Damage-Specific DNA Binding Protein 2 (48kD); Damage-Specific DNA Binding Protein 2, 48kDa; Damage-Specific DNA-Binding Protein 2; UV-DDB; DDBb |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human DDB2 |
| Gene ID | 1643 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | DNA damage-binding protein 2, DDB p48 subunit, DDBb, Damage-specific DNA-binding protein 2, UV-damaged DNA-binding protein 2, UV-DDB 2, DDB2 |
| Name | DDB2 |
|---|---|
| Function | Protein, which is both involved in DNA repair and protein ubiquitination, as part of the UV-DDB complex and DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) complexes, respectively (PubMed:10882109, PubMed:11278856, PubMed:11705987, PubMed:12732143, PubMed:15882621, PubMed:16473935, PubMed:18593899, PubMed:32789493, PubMed:9892649). Core component of the UV-DDB complex (UV-damaged DNA-binding protein complex), a complex that recognizes UV-induced DNA damage and recruit proteins of the nucleotide excision repair pathway (the NER pathway) to initiate DNA repair (PubMed:10882109, PubMed:11278856, PubMed:11705987, PubMed:12944386, PubMed:14751237, PubMed:16260596, PubMed:32789493). The UV-DDB complex preferentially binds to cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD), 6-4 photoproducts (6-4 PP), apurinic sites and short mismatches (PubMed:10882109, PubMed:11278856, PubMed:11705987, PubMed:12944386, PubMed:16260596). Also functions as the substrate recognition module for the DCX (DDB2-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex DDB2-CUL4-ROC1 (also known as CUL4-DDB-ROC1 and CUL4- DDB-RBX1) (PubMed:12732143, PubMed:15882621, PubMed:16473935, PubMed:18593899, PubMed:26572825). The DDB2-CUL4-ROC1 complex may ubiquitinate histone H2A, histone H3 and histone H4 at sites of UV- induced DNA damage (PubMed:16473935, PubMed:16678110). The ubiquitination of histones may facilitate their removal from the nucleosome and promote subsequent DNA repair (PubMed:16473935, PubMed:16678110). The DDB2-CUL4-ROC1 complex also ubiquitinates XPC, which may enhance DNA-binding by XPC and promote NER (PubMed:15882621). The DDB2-CUL4-ROC1 complex also ubiquitinates KAT7/HBO1 in response to DNA damage, leading to its degradation: recognizes KAT7/HBO1 following phosphorylation by ATR (PubMed:26572825). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Chromosome. Note=Accumulates at sites of DNA damage following UV irradiation. |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed; with highest levels in corneal endothelium and lowest levels in brain. Isoform D1 is highly expressed in brain and heart. Isoform D2, isoform D3 and isoform D4 are weakly expressed. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.