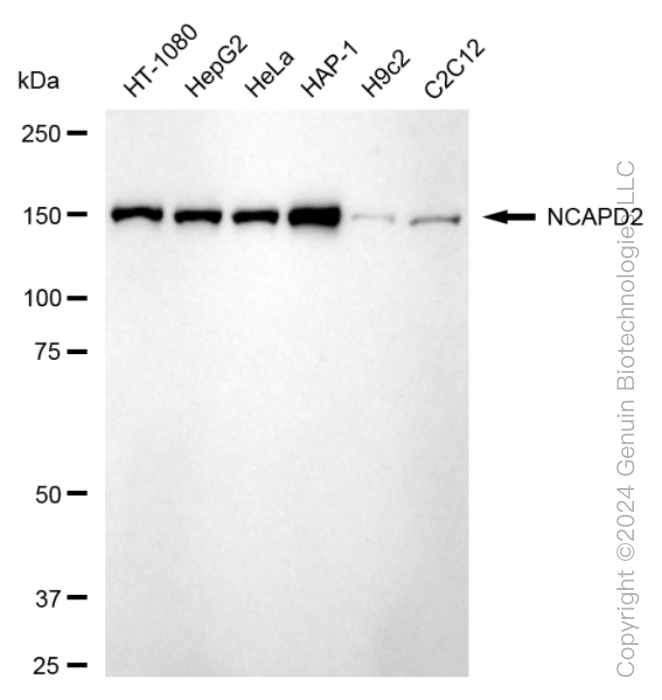
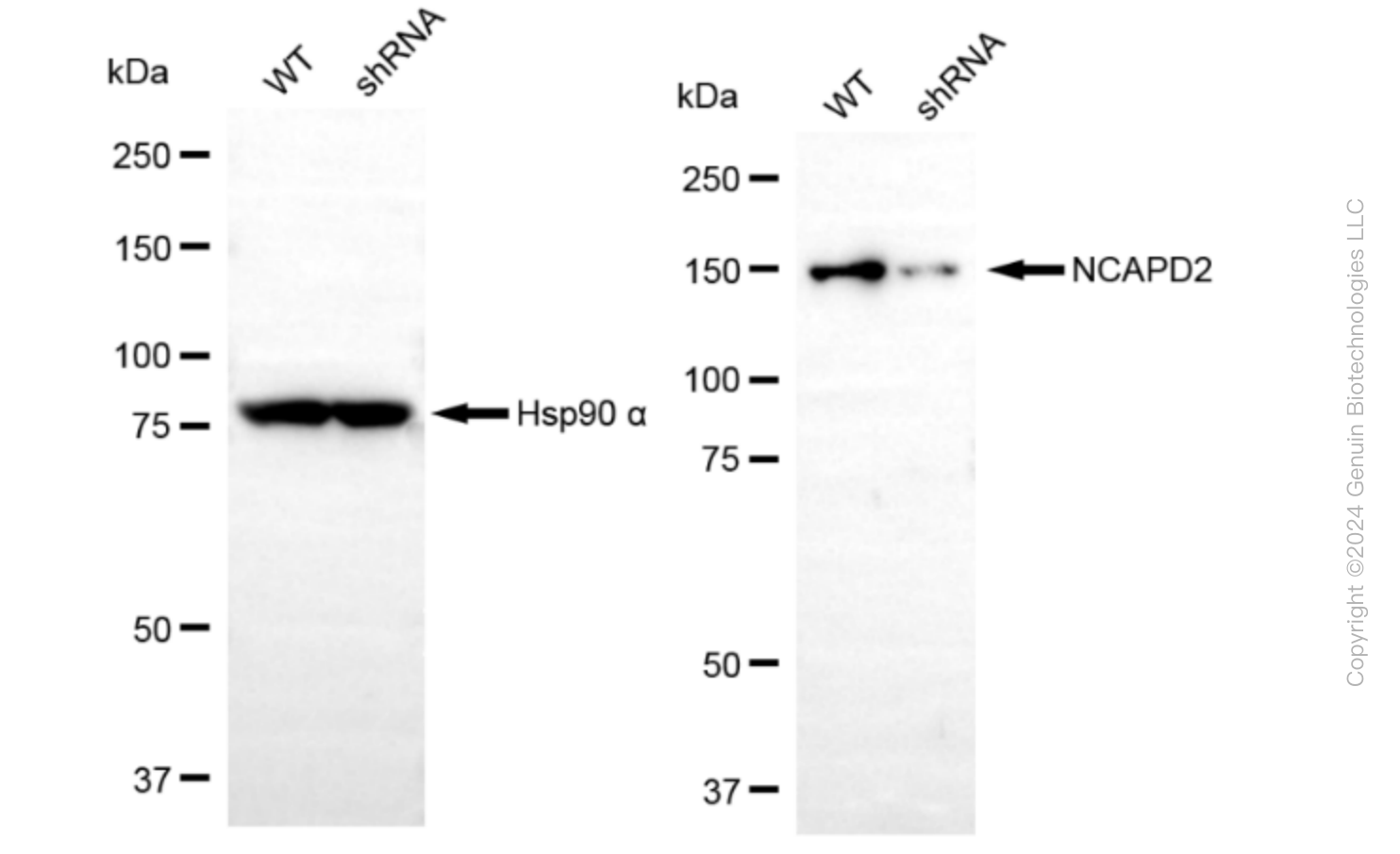
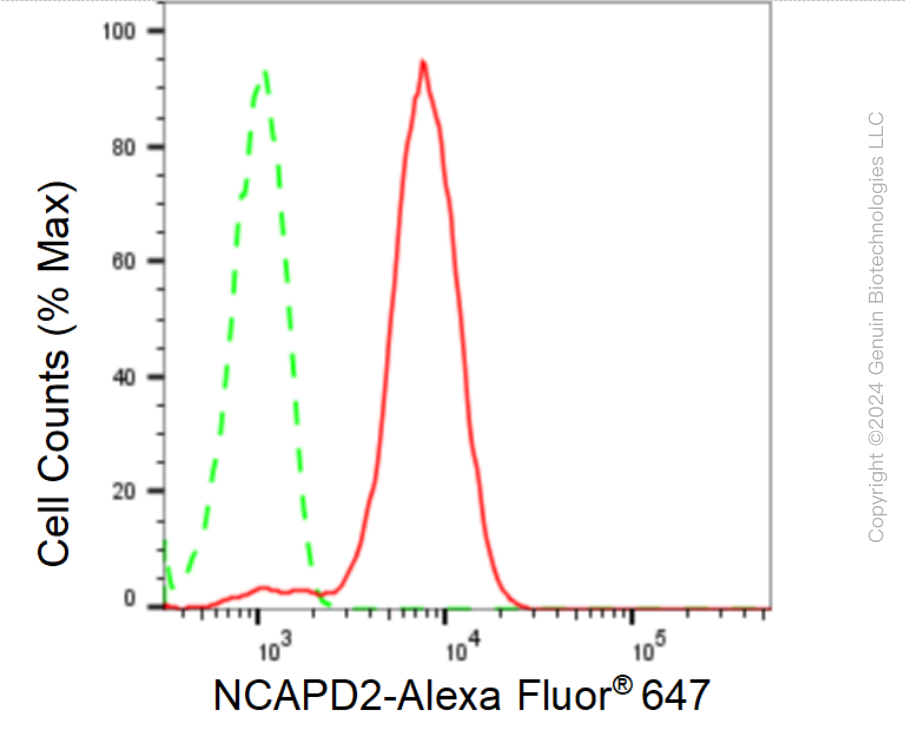
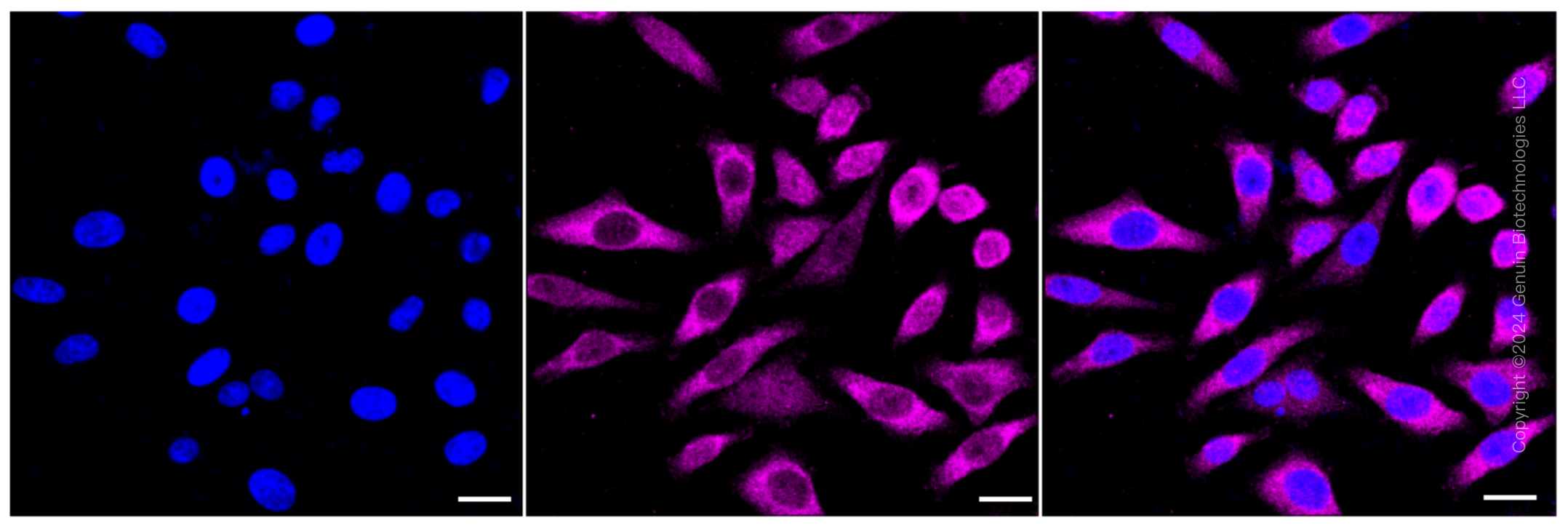
KD-Validated Anti-Non-SMC Condensin I Complex Subunit D2 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
Rabbit monoclonal antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, FC, ICC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q15021 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Clone Names | 24GB75 |
| Calculated MW | Predicted, 157 kDa , observed , 150 kDa |
| Gene Name | NCAPD2 |
| Aliases | Non-SMC Condensin I Complex Subunit D2; HCAP-D2; CNAP1; KIAA0159; CAP-D2; Chromosome Condensation-Related SMC-Associated Protein 1; Chromosome-Associated Protein D2; Condensin Complex Subunit 1; XCAP-D2 Homolog; Chromosome Condensation Related SMC Associated Protein 1; Non-SMC Condensin I Complex, Subunit D2; MCPH21; CAPD2 |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CNAP1 |
| Gene ID | 9918 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Condensin complex subunit 1, Chromosome condensation-related SMC-associated protein 1, Chromosome-associated protein D2, hCAP-D2, Non-SMC condensin I complex subunit D2, XCAP-D2 homolog, NCAPD2 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:27737959, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:24305} |
| Name | NCAPD2 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:27737959, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:24305} |
|---|---|
| Function | Regulatory subunit of the condensin complex, a complex required for conversion of interphase chromatin into mitotic-like condense chromosomes. The condensin complex probably introduces positive supercoils into relaxed DNA in the presence of type I topoisomerases and converts nicked DNA into positive knotted forms in the presence of type II topoisomerases. May target the condensin complex to DNA via its C-terminal domain (PubMed:11136719). May promote the resolution of double-strand DNA catenanes (intertwines) between sister chromatids. Condensin-mediated compaction likely increases tension in catenated sister chromatids, providing directionality for type II topoisomerase-mediated strand exchanges toward chromatid decatenation. Required for decatenation of non-centromeric ultrafine DNA bridges during anaphase. Early in neurogenesis, may play an essential role to ensure accurate mitotic chromosome condensation in neuron stem cells, ultimately affecting neuron pool and cortex size (PubMed:27737959). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Chromosome. Note=In interphase cells, the majority of the condensin complex is found in the cytoplasm, while a minority of the complex is associated with chromatin. A subpopulation of the complex however remains associated with chromosome foci in interphase cells. During mitosis, most of the condensin complex is associated with the chromatin. At the onset of prophase, the regulatory subunits of the complex are phosphorylated by CDK1, leading to condensin's association with chromosome arms and to chromosome condensation. Dissociation from chromosomes is observed in late telophase |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.