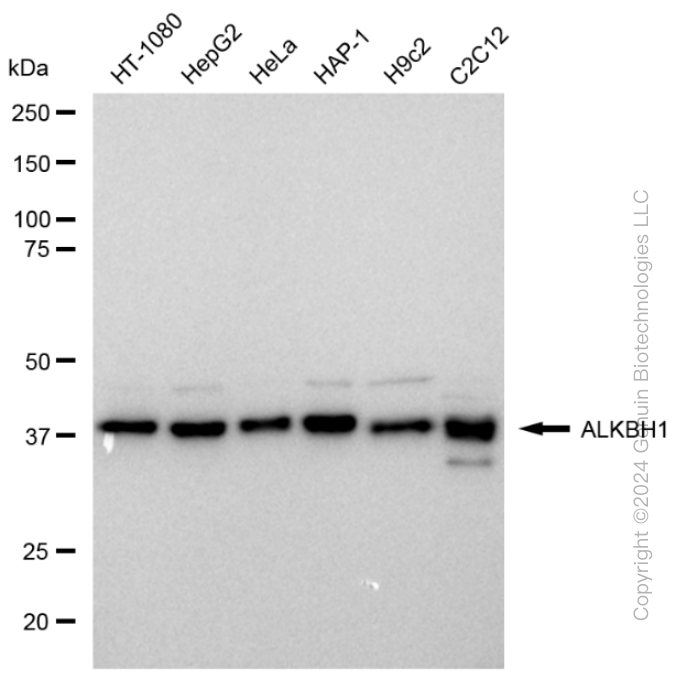
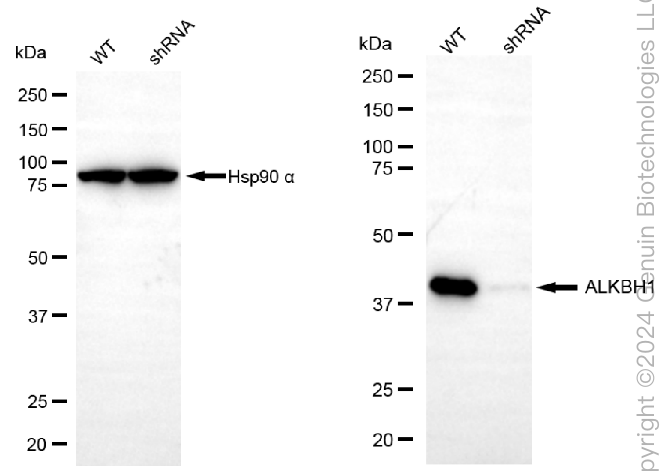
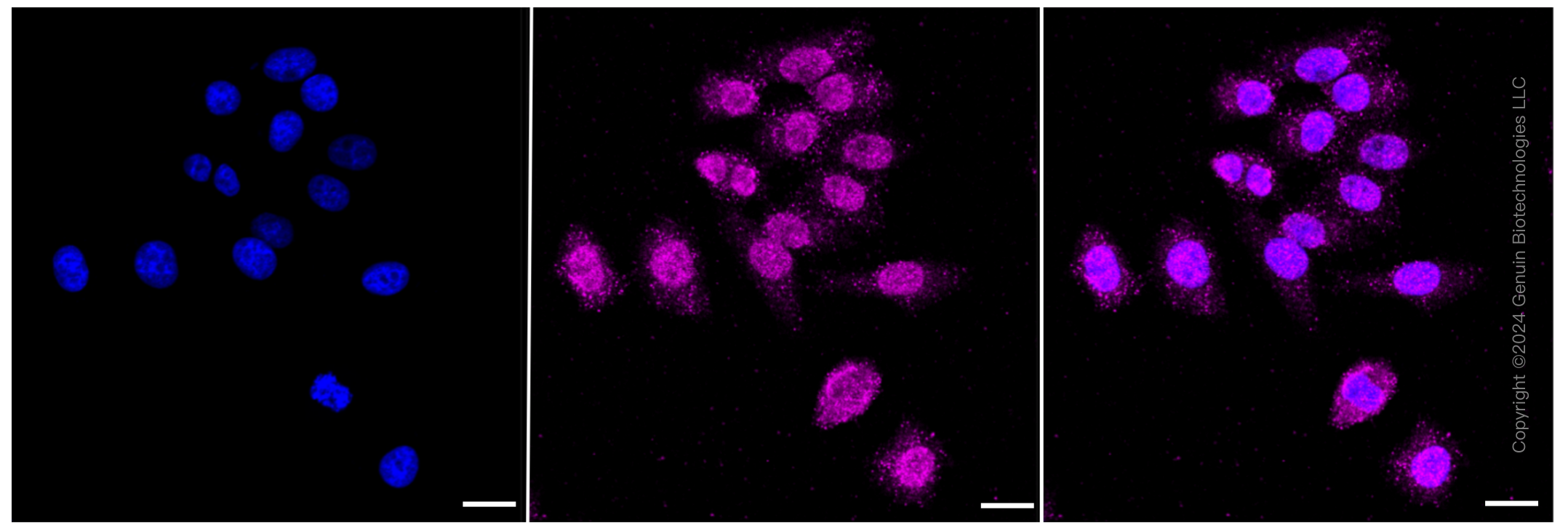
KD-Validated Anti-ALKBH1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody
Rabbit monoclonal antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, ICC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q13686 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Human, Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Clone Names | 23GB1385 |
| Calculated MW | Predicted, 44 kDa; Observed, 43 kDa |
| Gene Name | ALKBH1 |
| Aliases | ALKBH1; AlkB Homolog 1, Histone H2A Dioxygenase; ABH; ALKBH; HABH; Alpha-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenase ABH1; Alkylated DNA Repair Protein AlkB Homolog 1; DNA N6-Methyl Adenine Demethylase ALKBH1; MRNA N(3)-Methylcytidine Demethylase; DNA Oxidative Demethylase ALKBH1; Nucleic Acid Dioxygenase ALKBH1; DNA 6mA Demethylase; DNA Lyase ABH1; AlkB; ABH1; AlkB, Alkylation Repair Homolog 1 (E. Coli); AlkB, Alkylation Repair Homolog (E. Coli); TRNA N1-Methyl Adenine Demethylase; AlkB, Alkylation Repair Homolog 1; Alkylation Repair, AlkB Homolog; DNA Demethylase ALKBH1; EC 1.14.11.51; EC 1.14.11.33; EC 1.14.11.-; EC 4.2.99.18; ALKB |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from ALKBH1 |
| Gene ID | 8846 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Nucleic acid dioxygenase ALKBH1, 1.14.11.-, Alkylated DNA repair protein alkB homolog 1, Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase ABH1, DNA 6mA demethylase, 1.14.11.-, ALKBH1 (HGNC:17911) |
| Name | ALKBH1 (HGNC:17911) |
|---|---|
| Function | Dioxygenase that acts on nucleic acids, such as DNA and tRNA (PubMed:18603530, PubMed:27497299, PubMed:27745969). Requires molecular oxygen, alpha-ketoglutarate and iron (PubMed:18603530, PubMed:27497299). A number of activities have been described for this dioxygenase, but recent results suggest that it mainly acts on tRNAs and mediates their demethylation or oxidation depending on the context and subcellular compartment (PubMed:27497299, PubMed:27745969). Mainly acts as a tRNA demethylase by removing N(1)-methyladenine from various tRNAs, with a preference for N(1)-methyladenine at position 58 (m1A58) present on a stem loop structure of tRNAs (PubMed:27745969). Acts as a regulator of translation initiation and elongation in response to glucose deprivation: regulates both translation initiation, by mediating demethylation of tRNA(Met), and translation elongation, N(1)- methyladenine-containing tRNAs being preferentially recruited to polysomes to promote translation elongation (PubMed:27745969). In mitochondrion, specifically interacts with mt-tRNA(Met) and mediates oxidation of mt-tRNA(Met) methylated at cytosine(34) to form 5- formylcytosine (f(5)c) at this position (PubMed:27497299). mt-tRNA(Met) containing the f(5)c modification at the wobble position enables recognition of the AUA codon in addition to the AUG codon, expanding codon recognition in mitochondrial translation (PubMed:27497299). Specifically demethylates DNA methylated on the 6th position of adenine (N(6)-methyladenosine) DNA (PubMed:30017583, PubMed:30392959). N(6)- methyladenosine (m6A) DNA is present at some L1 elements in embryonic stem cells and probably promotes their silencing (By similarity). Demethylates mRNAs containing N(3)-methylcytidine modification (PubMed:31188562). Also able to repair alkylated single-stranded DNA by oxidative demethylation, but with low activity (PubMed:18603530). Also has DNA lyase activity and introduces double-stranded breaks at abasic sites: cleaves both single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA at abasic sites, with the greatest activity towards double-stranded DNA with two abasic sites (PubMed:19959401). DNA lyase activity does not require alpha-ketoglutarate and iron and leads to the formation of an irreversible covalent protein-DNA adduct with the 5' DNA product (PubMed:19959401, PubMed:23577621). DNA lyase activity is not required during base excision repair and class switch recombination of the immunoglobulin heavy chain during B lymphocyte activation. May play a role in placental trophoblast lineage differentiation (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Mitochondrion. Note=Mainly localizes in euchromatin, largely excluded from heterochromatin and nucleoli (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P0CB42} |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitous. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.