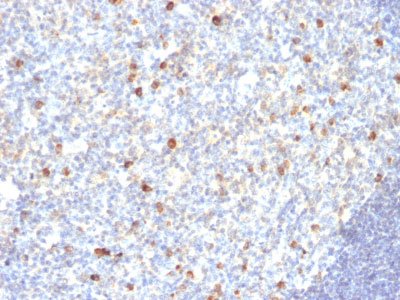
IgM (Immunoglobulin Mu Heavy Chain) (B-Cell Marker) Antibody - With BSA and Azide
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone SPM188 ]
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IHC, IF, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P01871 |
| Other Accession | 3507, 510635, P20769 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG1, kappa |
| Clone Names | SPM188 |
| Calculated MW | 50-75kDa |
| Other Names | Ig mu chain C region, IGHM |
|---|---|
| Application Note | IHC~~1:100~500 IF~~1:50~200 FC~~1:10~50 |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | IgM (Immunoglobulin Mu Heavy Chain) (B-Cell Marker) Antibody - With BSA and Azide is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | IGHM {ECO:0000303|PubMed:11340299, ECO:0000303|Ref.14} |
|---|---|
| Function | Constant region of immunoglobulin heavy chains. Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are membrane-bound or secreted glycoproteins produced by B lymphocytes. In the recognition phase of humoral immunity, the membrane-bound immunoglobulins serve as receptors which, upon binding of a specific antigen, trigger the clonal expansion and differentiation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulins- secreting plasma cells. Secreted immunoglobulins mediate the effector phase of humoral immunity, which results in the elimination of bound antigens (PubMed:20176268, PubMed:22158414). The antigen binding site is formed by the variable domain of one heavy chain, together with that of its associated light chain. Thus, each immunoglobulin has two antigen binding sites with remarkable affinity for a particular antigen. The variable domains are assembled by a process called V-(D)-J rearrangement and can then be subjected to somatic hypermutations which, after exposure to antigen and selection, allow affinity maturation for a particular antigen (PubMed:17576170, PubMed:20176268). |
| Cellular Location | [Isoform 1]: Secreted. Note=During differentiation, B-lymphocytes switch from expression of membrane-bound IgM to secretion of IgM. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Recognizes a protein of 75kDa, identified as mu heavy chain of human immunoglobulins. It does not cross-react with alpha (IgA), gamma (IgG), epsilon (IgE), or delta (IgD), heavy chains, T-cells, monocytes, granulocytes, or erythrocytes. Monomeric IgM is expressed as a membrane bound antibody on the surface of B cells and as a pentamer when secreted by plasma cells. IgM antibody is prominent in early immune responses to most antigens. Aberrant levels are associated with immune deficiency states, hereditary deficiencies, myeloma, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia, chronic infection and hepatocellular disease. This MAb is useful in the identification of leukemias, plasmacytomas, and certain non-Hodgkin s lymphomas. The most common feature of these malignancies is the restricted expression of a single heavy chain class. Demonstration of clonality in lymphoid infiltrates indicates that the infiltrate is clonal and therefore malignant.
References
Baryshnikov AIu. Gematol Transfuziol. 1990 Aug;35(8):4-7. | Martinova T.et al., In: Problems medical biotechnology and immunological infection diseases. Vol 11, 182-186, 1996. | Baryshnikov A, and Tonevitsky A, Monoclonal antibodies in laboratory and clinic. Thesis p212, 1997. |
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.