Anti-Villin Antibody
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, FC |
|---|---|
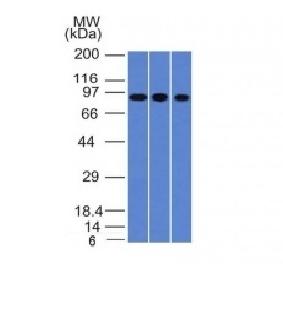
| Primary Accession | P09327 |
| Other Accession | 654595 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG1, kappa |
| Clone Names | VIL1/1325 |
| Calculated MW | 92695 Da |
| Gene ID | 7429 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | VIL1; Villin-1; Villin1 |
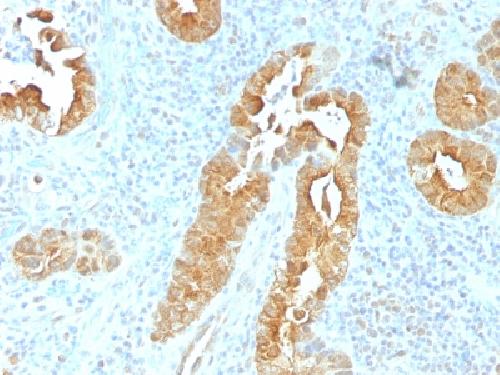
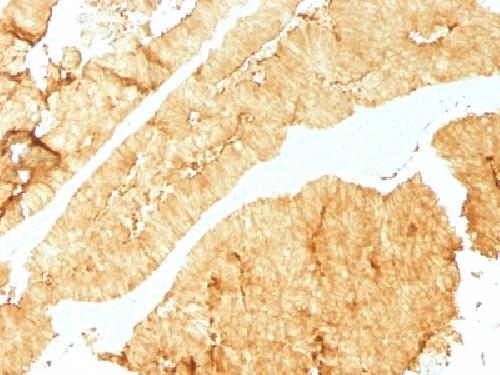
| Application Note | Flow Cytometry (0.5-1ug/million cells in 0.1ml); ,Immunofluorescence (1-2ug/ml); ,Western Blotting (1-2ug/ml for 60 minutes at RT);,Immunohistology (Formalin-fixed) (0.25-0.5ug/ml for 30 minutes at RT),(Staining of formalin-fixed tissues requires boiling tissue sections in 10mM citrate buffer, pH 6.0, for 10-20 min followed by cooling at RT for 20 minutes),Optimal dilution for a specific application should be determined. |
| Format | 200ug/ml of Ab purified from Bioreactor Concentrate by Protein A/G. Prepared in 10mM PBS with 0.05% BSA & 0.05% azide. Also available WITHOUT BSA & azide at 1.0mg/ml. |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | Anti-Villin Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | VIL1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | VIL |
| Function | Epithelial cell-specific Ca(2+)-regulated actin-modifying protein that modulates the reorganization of microvillar actin filaments. Plays a role in the actin nucleation, actin filament bundle assembly, actin filament capping and severing. Binds phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA); binds LPA with higher affinity than PIP2. Binding to LPA increases its phosphorylation by SRC and inhibits all actin-modifying activities. Binding to PIP2 inhibits actin-capping and -severing activities but enhances actin-bundling activity. Regulates the intestinal epithelial cell morphology, cell invasion, cell migration and apoptosis. Protects against apoptosis induced by dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) in the gastrointestinal epithelium. Appears to regulate cell death by maintaining mitochondrial integrity. Enhances hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced epithelial cell motility, chemotaxis and wound repair. Upon S.flexneri cell infection, its actin-severing activity enhances actin-based motility of the bacteria and plays a role during the dissemination. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell projection, lamellipodium. Cell projection, ruffle. Cell projection, microvillus Cell projection, filopodium tip. Cell projection, filopodium. Note=Relocalized in the tip of cellular protrusions and filipodial extensions upon infection with S.flexneri in primary intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) and in the tail-like structures forming the actin comets of S.flexneri. Redistributed to the leading edge of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced lamellipodia (By similarity). Rapidly redistributed to ruffles and lamellipodia structures in response to autotaxin, lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) treatment. |
| Tissue Location | Specifically expressed in epithelial cells. Major component of microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells and kidney proximal tubule cells. Expressed in canalicular microvilli of hepatocytes (at protein level). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Recognizes a protein of 95kDa, which is identified as villin. It is a major constituent in the microvilli, which compose the brush border of epithelial cells forming absorptive surfaces of the intestinal and renal proximal tubular epithelia. Anti-Villin labels the brush border area in the gastrointestinal mucosal epithelium and urogenital tract. Among neoplasms, villin is predominantly expressed in tumors of colorectal origin. Antibody to villin is useful in identifying malignant cells from primary and metastatic colorectal carcinomas. This antibody also labels Merkel cells of the skin.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.