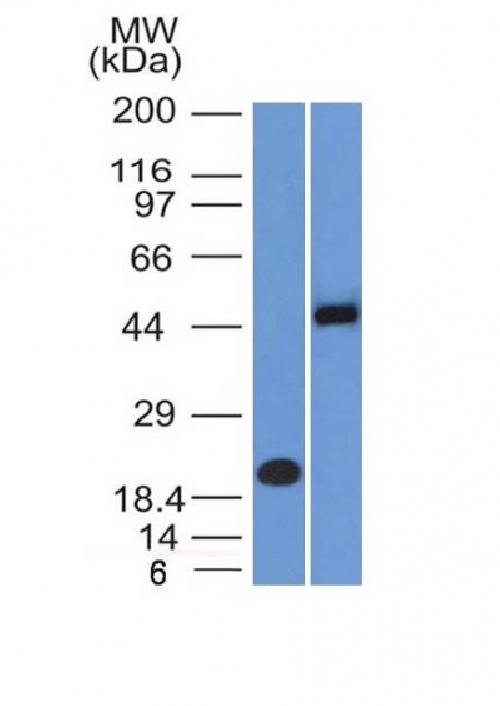
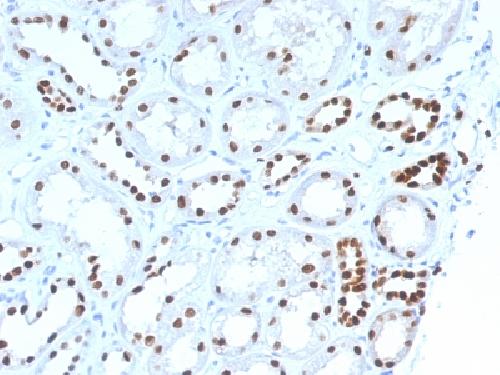
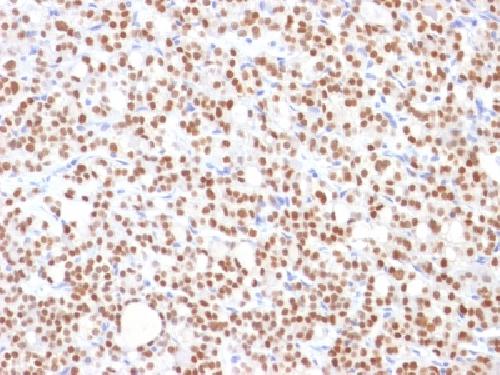
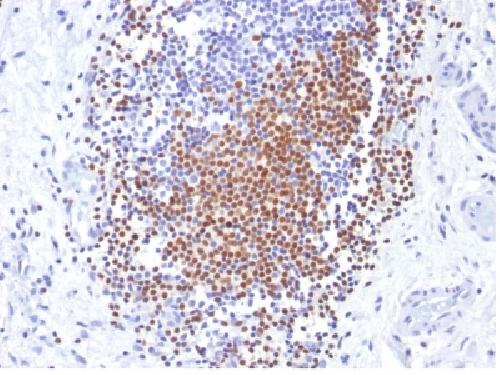
Anti-PAX8 (Renal Cell Marker) Antibody
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q06710 |
| Other Accession | 469728 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Clone Names | PAX8/1492 |
| Calculated MW | 48218 Da |
| Gene ID | 7849 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Paired box 8; Paired box gene 8; paired box homeotic gene 8; Paired box protein Pax-8; Paired domain gene 8; PAX8 |
| Application Note | Flow Cytometry (0.5-1ug/million cells); ,Immunofluorescence (1-2ug/ml); ,Western Blotting (0.5-1ug/ml); ,Immunohistology (Formalin-fixed) (1-2ug/ml for 30 minutes at RT),(Staining of formalin-fixed tissues requires boiling tissue sections in 10mM Tris buffer with 1mM EDTA, pH 9.0, for 10-20 min followed by cooling at RT for 20 minutes),Optimal dilution for a specific application should be determined. |
| Format | 200ug/ml of Ab purified from Bioreactor Concentrate by Protein A/G. Prepared in 10mM PBS with 0.05% BSA & 0.05% azide. Also available WITHOUT BSA & azide at 1.0mg/ml. |
| Storage | Store at 2 to 8°C.Antibody is stable for 24 months. |
| Precautions | Anti-PAX8 (Renal Cell Marker) Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PAX8 |
|---|---|
| Function | Transcription factor for the thyroid-specific expression of the genes exclusively expressed in the thyroid cell type, maintaining the functional differentiation of such cells. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the excretory system, thyroid gland and Wilms tumors |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Recognizes a protein of 62kDa, identified as PAX8. It is a member of the paired box (PAX) family of transcription factors. This nuclear protein is involved in thyroid follicular cell development and expression of thyroid-specific genes. Mutations in this gene have been associated with thyroid dysgenesis, thyroid follicular carcinomas, and atypical thyroid adenomas. PAX-8 is expressed in the thyroid (and associated carcinomas), non-ciliated mucosal cells of the fallopian tubes, and simple ovarian inclusion cysts, but not normal ovarian surface epithelial cells. PAX-8 is expressed in a high percentage of ovarian serous, endometrioid, and clear cell carcinomas, but only rarely in primary ovarian mucinous adenocarcinomas. PAX-8 expression is reported in renal tubules as well as renal cell carcinoma, nephroblastoma, and seminoma. PAX-8 antibody may be used as an additional immunohistochemical marker for renal epithelial tumors.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.