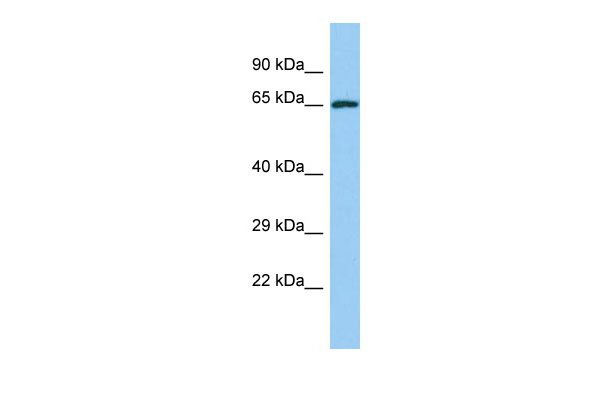
YTHDF2 Antibody - C-terminal region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9Y5A9 |
| Other Accession | NM_016258, NP_057342 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Horse, Bovine, Dog |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Horse, Bovine, Dog |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 62kDa |
| Gene ID | 51441 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | HGRG8, NY-REN-2 |
| Other Names | YTH domain-containing family protein 2, CLL-associated antigen KW-14, High-glucose-regulated protein 8, Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-2, YTHDF2, HGRG8 |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-YTHDF2 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | YTHDF2 Antibody - C-terminal region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | YTHDF2 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:24284625, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:31675} |
|---|---|
| Function | Specifically recognizes and binds N6-methyladenosine (m6A)- containing RNAs, and regulates their stability (PubMed:24284625, PubMed:26046440, PubMed:26318451, PubMed:32492408). M6A is a modification present at internal sites of mRNAs and some non-coding RNAs and plays a role in mRNA stability and processing (PubMed:22575960, PubMed:24284625, PubMed:25412658, PubMed:25412661, PubMed:32492408). Acts as a regulator of mRNA stability by promoting degradation of m6A-containing mRNAs via interaction with the CCR4-NOT and ribonuclease P/MRP complexes, depending on the context (PubMed:24284625, PubMed:26046440, PubMed:27558897, PubMed:30930054, PubMed:32492408). The YTHDF paralogs (YTHDF1, YTHDF2 and YTHDF3) share m6A-containing mRNAs targets and act redundantly to mediate mRNA degradation and cellular differentiation (PubMed:28106072, PubMed:32492408). M6A-containing mRNAs containing a binding site for RIDA/HRSP12 (5'-GGUUC-3') are preferentially degraded by endoribonucleolytic cleavage: cooperative binding of RIDA/HRSP12 and YTHDF2 to transcripts leads to recruitment of the ribonuclease P/MRP complex (PubMed:30930054). Other m6A-containing mRNAs undergo deadenylation via direct interaction between YTHDF2 and CNOT1, leading to recruitment of the CCR4-NOT and subsequent deadenylation of m6A- containing mRNAs (PubMed:27558897). Required maternally to regulate oocyte maturation: probably acts by binding to m6A-containing mRNAs, thereby regulating maternal transcript dosage during oocyte maturation, which is essential for the competence of oocytes to sustain early zygotic development (By similarity). Also required during spermatogenesis: regulates spermagonial adhesion by promoting degradation of m6A-containing transcripts coding for matrix metallopeptidases (By similarity). Also involved in hematopoietic stem cells specification by binding to m6A-containing mRNAs, leading to promote their degradation (PubMed:30065315). Also acts as a regulator of neural development by promoting m6A-dependent degradation of neural development-related mRNA targets (By similarity). Inhibits neural specification of induced pluripotent stem cells by binding to methylated neural-specific mRNAs and promoting their degradation, thereby restraining neural differentiation (PubMed:32169943). Regulates circadian regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism: acts by promoting m6A-dependent degradation of PPARA transcripts (PubMed:30428350). Regulates the innate immune response to infection by inhibiting the type I interferon response: acts by binding to m6A-containing IFNB transcripts and promoting their degradation (PubMed:30559377). May also act as a promoter of cap-independent mRNA translation following heat shock stress: upon stress, relocalizes to the nucleus and specifically binds mRNAs with some m6A methylation mark at their 5'-UTR, protecting demethylation of mRNAs by FTO, thereby promoting cap-independent mRNA translation (PubMed:26458103). Regulates mitotic entry by promoting the phase-specific m6A-dependent degradation of WEE1 transcripts (PubMed:32267835). Promotes formation of phase-separated membraneless compartments, such as P-bodies or stress granules, by undergoing liquid-liquid phase separation upon binding to mRNAs containing multiple m6A-modified residues: polymethylated mRNAs act as a multivalent scaffold for the binding of YTHDF proteins, juxtaposing their disordered regions and thereby leading to phase separation (PubMed:31292544, PubMed:31388144, PubMed:31642031, PubMed:32451507). The resulting mRNA-YTHDF complexes then partition into different endogenous phase-separated membraneless compartments, such as P-bodies, stress granules or neuronal RNA granules (PubMed:31292544). May also recognize and bind RNAs modified by C5-methylcytosine (m5C) and act as a regulator of rRNA processing (PubMed:31815440). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cytoplasm, P-body. Cytoplasm, Stress granule. Nucleus. Note=Localizes to the cytosol and relocates to the nucleus following heat shock stress (PubMed:26458103) Can partition into different structures: into P-bodies in unstressed cells, and into stress granules during stress (PubMed:31292544) |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and down-regulated during neural differentiation |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
References
Scanlan M.J.,et al.Int. J. Cancer 83:456-464(1999).
Roberts T.P.,et al.Submitted (OCT-1999) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Krackhardt A.M.,et al.Submitted (OCT-2001) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
Gregory S.G.,et al.Nature 441:315-321(2006).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.