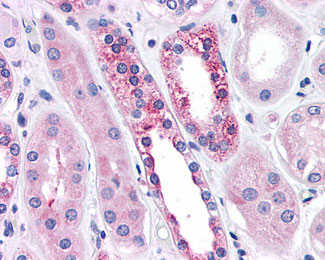
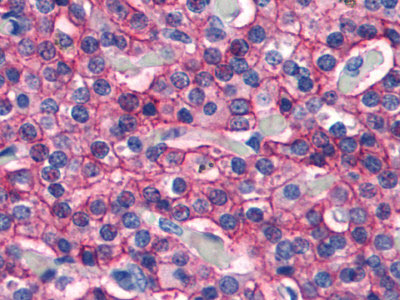
CASR/Calcium Sensing Receptor Antibody (N-Terminus)
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P41180 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Hamster, Monkey, Pig, Chicken, Horse, Bovine, Dog |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 121kDa |
| Dilution | IHC-P (4-8 µg/ml) |
| Gene ID | 846 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor, CaSR, Parathyroid cell calcium-sensing receptor 1, PCaR1, CASR, GPRC2A, PCAR1 |
| Target/Specificity | Human CASR. BLAST analysis of the peptide immunogen showed no homology with other human proteins. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Long term: -70°C; Short term: +4°C |
| Precautions | CASR/Calcium Sensing Receptor Antibody (N-Terminus) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CASR {ECO:0000303|PubMed:16740594, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:1514} |
|---|---|
| Function | G-protein-coupled receptor that senses changes in the extracellular concentration of calcium ions and plays a key role in maintaining calcium homeostasis (PubMed:17555508, PubMed:19789209, PubMed:21566075, PubMed:22114145, PubMed:22789683, PubMed:23966241, PubMed:25104082, PubMed:25292184, PubMed:25766501, PubMed:26386835, PubMed:32817431, PubMed:33603117, PubMed:34194040, PubMed:34467854, PubMed:7759551, PubMed:8636323, PubMed:8702647, PubMed:8878438). Senses fluctuations in the circulating calcium concentration: activated by elevated circulating calcium, leading to decreased parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion in parathyroid glands (By similarity). In kidneys, acts as a key regulator of renal tubular calcium resorption (By similarity). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G-proteins) and modulates the activity of downstream effectors (PubMed:38632411). CASR is coupled with different G(q)/G(11), G(i)/G(o)- or G(s)-classes of G-proteins depending on the context (PubMed:38632411). In the parathyroid and kidney, CASR signals through G(q)/G(11) and G(i)/G(o) G-proteins: G(q)/G(11) coupling activates phospholipase C-beta, releasing diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) second messengers, while G(i)/G(o) coupling mediates inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity (PubMed:38632411, PubMed:7759551). The G-protein- coupled receptor activity is activated by a co-agonist mechanism: aromatic amino acids, such as Trp or Phe, act concertedly with divalent cations, such as calcium or magnesium, to achieve full receptor activation (PubMed:27386547, PubMed:27434672, PubMed:32817431, PubMed:33603117, PubMed:34194040). Acts as an activator of the NLRP3 inflammasome via G(i)/G(o)-mediated signaling: down-regulation of cyclic AMP (cAMP) relieving NLRP3 inhibition by cAMP (PubMed:32843625). Acts as a regulator of proton-sensing receptor GPR68 in a seesaw manner: CASR-mediated signaling inhibits GPR68 signaling in response to extracellular calcium, while GPR68 inhibits CASR in presence of extracellular protons (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the temporal lobe, frontal lobe, parietal lobe, hippocampus, and cerebellum. Also found in kidney, lung, liver, heart, skeletal muscle, placenta. |
| Volume | 50 µl |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Senses changes in the extracellular concentration of calcium ions. The activity of this receptor is mediated by a G- protein that activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system.
References
Pearce S.H.S.,et al.Submitted (DEC-1994) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Garrett J.E.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 270:12919-12925(1995).
Aida K.,et al.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 214:524-529(1995).
Freichel M.,et al.Endocrinology 137:3842-3848(1996).
Aida K.,et al.J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80:2594-2598(1995).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.