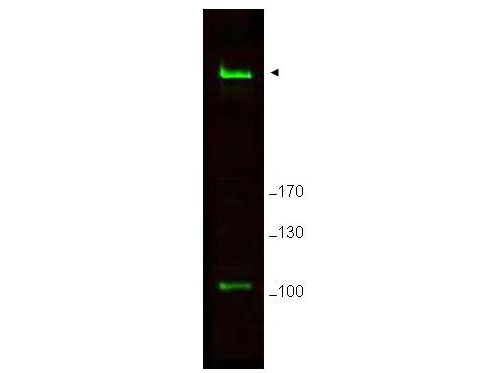
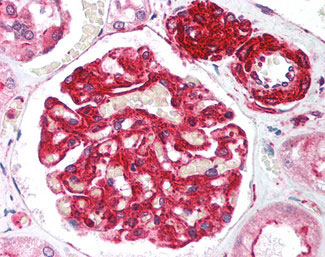
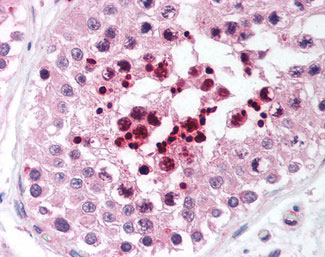
RIF1 Antibody (aa2406-2419)
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q5UIP0 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 274kDa |
| Dilution | ELISA (1:5000-1:40000), IHC-P (5 µg/ml), WB (1:500-1:3000) |
| Gene ID | 55183 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Telomere-associated protein RIF1, Rap1-interacting factor 1 homolog, RIF1 |
| Target/Specificity | Rif1 |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Store vial at -20 C prior to opening. Dilute only prior to immediate use. For extended storage aliquot contents and freeze at -20 C or below. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | RIF1 Antibody (aa2406-2419) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | RIF1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:15342490, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:23207} |
|---|---|
| Function | Key regulator of TP53BP1 that plays a key role in the repair of double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) in response to DNA damage: acts by promoting non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)-mediated repair of DSBs (PubMed:15342490, PubMed:28241136). In response to DNA damage, interacts with ATM-phosphorylated TP53BP1 (PubMed:23333306, PubMed:28241136). Interaction with TP53BP1 leads to dissociate the interaction between NUDT16L1/TIRR and TP53BP1, thereby unmasking the tandem Tudor-like domain of TP53BP1 and allowing recruitment to DNA DSBs (PubMed:28241136). Once recruited to DSBs, RIF1 and TP53BP1 act by promoting NHEJ-mediated repair of DSBs (PubMed:23333306). In the same time, RIF1 and TP53BP1 specifically counteract the function of BRCA1 by blocking DSBs resection via homologous recombination (HR) during G1 phase (PubMed:23333306). Also required for immunoglobulin class-switch recombination (CSR) during antibody genesis, a process that involves the generation of DNA DSBs (By similarity). Promotes NHEJ of dysfunctional telomeres (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Chromosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6PR54}. Chromosome, telomere. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Note=Following interaction with TP53BP1, recruited to sites of DNA damage, such as DSBs (By similarity). Exhibits ATM- and TP53BP1-dependent localization to uncapped or aberrant telomeres and to DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) (PubMed:15342490). Does not associate with normal telomere structures (PubMed:15342490, PubMed:15583028). Localizes to microtubules of the midzone of the mitotic spindle during anaphase, and to condensed chromosomes in telophase (PubMed:15583028) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6PR54, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15342490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15583028} |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in testis. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Required for checkpoint mediated arrest of cell cycle progression in response to DNA damage during S-phase (the intra-S- phase checkpoint). This checkpoint requires activation of at least 2 parallel pathways by the ATM kinase: one involves the MRN (MRE11A-RAD50-NBS1) complex, while the second requires CHEK2. RIF1 seems to act independently of both these pathways. Seems to play no role in either the G1/S or G2/M DNA damage checkpoints.
References
Silverman J.,et al.Genes Dev. 18:2108-2119(2004).
Hillier L.W.,et al.Nature 434:724-731(2005).
Xu L.,et al.J. Cell Biol. 167:819-830(2004).
Simonsson T.,et al.Submitted (MAR-2004) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Bechtel S.,et al.BMC Genomics 8:399-399(2007).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.