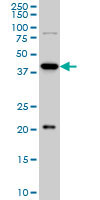
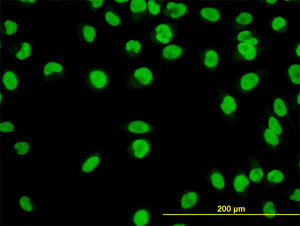
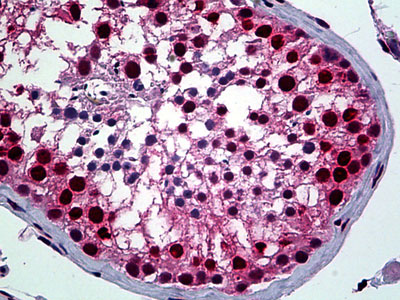
YY1 Antibody (clone 2C4)
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P25490 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 2C4 |
| Calculated MW | 45kDa |
| Dilution | IF (10 µg/ml), IHC-P (5 µg/ml), |
| Gene ID | 7528 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Transcriptional repressor protein YY1, Delta transcription factor, INO80 complex subunit S, NF-E1, Yin and yang 1, YY-1, YY1, INO80S |
| Target/Specificity | Human YY1 |
| Reconstitution & Storage | For long term storage -20°C is recommended. |
| Precautions | YY1 Antibody (clone 2C4) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | YY1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | INO80S |
| Function | Multifunctional transcription factor that exhibits positive and negative control on a large number of cellular and viral genes by binding to sites overlapping the transcription start site (PubMed:15329343, PubMed:17721549, PubMed:24326773, PubMed:25787250). Binds to the consensus sequence 5'-CCGCCATNTT-3'; some genes have been shown to contain a longer binding motif allowing enhanced binding; the initial CG dinucleotide can be methylated greatly reducing the binding affinity (PubMed:15329343, PubMed:17721549, PubMed:24326773, PubMed:25787250). The effect on transcription regulation is depending upon the context in which it binds and diverse mechanisms of action include direct activation or repression, indirect activation or repression via cofactor recruitment, or activation or repression by disruption of binding sites or conformational DNA changes (PubMed:15329343, PubMed:17721549, PubMed:24326773, PubMed:25787250). Its activity is regulated by transcription factors and cytoplasmic proteins that have been shown to abrogate or completely inhibit YY1- mediated activation or repression (PubMed:15329343, PubMed:17721549, PubMed:24326773, PubMed:25787250). For example, it acts as a repressor in absence of adenovirus E1A protein but as an activator in its presence (PubMed:1655281). Acts synergistically with the SMAD1 and SMAD4 in bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-mediated cardiac-specific gene expression (PubMed:15329343). Binds to SMAD binding elements (SBEs) (5'-GTCT/AGAC-3') within BMP response element (BMPRE) of cardiac activating regions (PubMed:15329343). May play an important role in development and differentiation. Proposed to recruit the PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex to target genes that are transcriptional repressed (PubMed:11158321). Involved in DNA repair (PubMed:18026119, PubMed:28575647). In vitro, binds to DNA recombination intermediate structures (Holliday junctions). Plays a role in regulating enhancer activation (PubMed:28575647). Recruits the PR-DUB complex to specific gene-regulatory regions (PubMed:20805357). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus matrix Note=Associated with the nuclear matrix. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Multifunctional transcription factor that exhibits positive and negative control on a large number of cellular and viral genes by binding to sites overlapping the transcription start site. Binds to the consensus sequence 5'-CCGCCATNTT-3'; some genes have been shown to contain a longer binding motif allowing enhanced binding; the initial CG dinucleotide can be methylated greatly reducing the binding affinity. The effect on transcription regulation is depending upon the context in which it binds and diverse mechanisms of action include direct activation or repression, indirect activation or repression via cofactor recruitment, or activation or repression by disruption of binding sites or conformational DNA changes. Its activity is regulated by transcription factors and cytoplasmic proteins that have been shown to abrogate or completely inhibit YY1-mediated activation or repression. For example, it acts as a repressor in absence of adenovirus E1A protein but as an activator in its presence. Acts synergistically with the SMAD1 and SMAD4 in bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-mediated cardiac-specific gene expression (PubMed:15329343). Binds to SMAD binding elements (SBEs) (5'- GTCT/AGAC-3') within BMP response element (BMPRE) of cardiac activating regions. May play an important role in development and differentiation. Proposed to recruit the PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex to target genes that are transcriptional repressed. Involved in DNA repair. In vitro, binds to DNA recombination intermediate structures (Holliday junctions).
References
Shi Y.,et al.Cell 67:377-388(1991).
Park K.,et al.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:9804-9808(1991).
Whitson R.H.,et al.Submitted (JUL-1992) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
McNeil S.,et al.J. Cell. Biochem. 68:500-510(1998).
Kalenik J.L.,et al.Nucleic Acids Res. 25:843-849(1997).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.