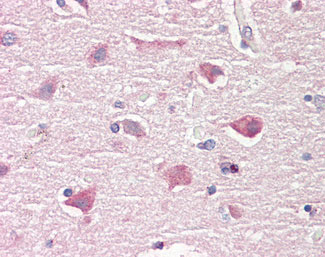
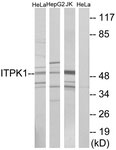
ITPK1 Antibody (aa81-130)
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q13572 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 46kDa |
| Dilution | ELISA (1:10000), IHC-P (10 µg/ml), WB (1:500-1:1000) |
| Gene ID | 3705 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Inositol-tetrakisphosphate 1-kinase, 2.7.1.134, Inositol 1, 3, 4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase, Inositol-triphosphate 5/6-kinase, Ins(1, 3, 4)P(3) 5/6-kinase, 2.7.1.159, ITPK1 |
| Target/Specificity | ITPK1 Antibody detects endogenous levels of total ITPK1 protein. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Store at -20°C for up to one year. |
| Precautions | ITPK1 Antibody (aa81-130) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ITPK1 (HGNC:6177) |
|---|---|
| Function | Kinase that can phosphorylate various inositol polyphosphate such as Ins(3,4,5,6)P4 or Ins(1,3,4)P3 (PubMed:11042108, PubMed:8662638). Phosphorylates Ins(3,4,5,6)P4 at position 1 to form Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5 (PubMed:11042108). This reaction is thought to have regulatory importance, since Ins(3,4,5,6)P4 is an inhibitor of plasma membrane Ca(2+)-activated Cl(-) channels, while Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5 is not. Also phosphorylates Ins(1,3,4)P3 on O-5 and O-6 to form Ins(1,3,4,6)P4, an essential molecule in the hexakisphosphate (InsP6) pathway (PubMed:11042108, PubMed:8662638). Also acts as an inositol polyphosphate phosphatase that dephosphorylates Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 and Ins(1,3,4,6)P4 to Ins(1,3,4)P3, and Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5 to Ins(3,4,5,6)P4 (PubMed:11909533, PubMed:17616525). May also act as an isomerase that interconverts the inositol tetrakisphosphate isomers Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 and Ins(1,3,4,6)P4 in the presence of ADP and magnesium (PubMed:11909533). Probably acts as the rate-limiting enzyme of the InsP6 pathway. Modifies TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by interfering with the activation of TNFRSF1A-associated death domain (PubMed:11909533, PubMed:12925536, PubMed:17616525). Plays an important role in MLKL-mediated necroptosis. Produces highly phosphorylated inositol phosphates such as inositolhexakisphosphate (InsP6) which bind to MLKL mediating the release of an N-terminal auto-inhibitory region leading to its activation. Essential for activated phospho-MLKL to oligomerize and localize to the cell membrane during necroptosis (PubMed:17616525). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in brain > heart > skeletal muscle = kidney = pancreas = liver = placenta > lung. In brain, it is expressed in cerebellum, cerebral cortex, medulla, spinal cord, occipital lobe, frontal lobe, temporal lobe and putamen. |
| Volume | 250 µl |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Kinase that can phosphorylate various inositol polyphosphate such as Ins(3,4,5,6)P4 or Ins(1,3,4)P3. Phosphorylates Ins(3,4,5,6)P4 at position 1 to form Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5. This reaction is thought to have regulatory importance, since Ins(3,4,5,6)P4 is an inhibitor of plasma membrane Ca(2+)-activated Cl(-) channels, while Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5 is not. Also phosphorylates Ins(1,3,4)P3 on O-5 and O-6 to form Ins(1,3,4,6)P4, an essential molecule in the hexakisphosphate (InsP6) pathway. Also acts as an inositol polyphosphate phosphatase that dephosphorylate Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 and Ins(1,3,4,6)P4 to Ins(1,3,4)P3, and Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5 to Ins(3,4,5,6)P4. May also act as an isomerase that interconverts the inositol tetrakisphosphate isomers Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 and Ins(1,3,4,6)P4 in the presence of ADP and magnesium. Probably acts as the rate-limiting enzyme of the InsP6 pathway. Modifies TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by interfering with the activation of TNFRSF1A-associated death domain.
References
Wilson M.P.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 271:11904-11910(1996).
Yang X.,et al.Biochem. J. 351:551-555(2000).
Wilson M.P.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 276:40998-41004(2001).
Ho M.W.Y.,et al.Curr. Biol. 12:477-482(2002).
Sun Y.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 277:45759-45764(2002).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.