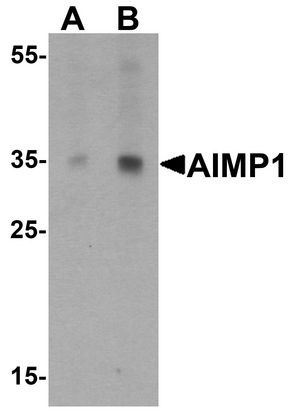
AIMP1 / EMAP II Antibody (C-Terminus)
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q12904 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 34kDa |
| Dilution | IHC-P (10 µg/ml), WB (0.5-1 µg/ml), |
| Gene ID | 9255 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Aminoacyl tRNA synthase complex-interacting multifunctional protein 1, Multisynthase complex auxiliary component p43, Endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide 2, EMAP-2, Endothelial monocyte-activating polypeptide II, EMAP-II, Small inducible cytokine subfamily E member 1, AIMP1, EMAP2, SCYE1 |
| Target/Specificity | AIMP1 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. At least two isoforms of AIMP1 are known to exist; this antibody will recognize both isoforms. AIMP1 antibody is predicted to not cross-react with AIMP2. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Long term: -20°C; Short term: +4°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | AIMP1 / EMAP II Antibody (C-Terminus) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | AIMP1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | EMAP2, SCYE1 |
| Function | Non-catalytic component of the multisynthase complex. Stimulates the catalytic activity of cytoplasmic arginyl-tRNA synthase (PubMed:10358004). Binds tRNA. Possesses inflammatory cytokine activity (PubMed:11306575). Negatively regulates TGF-beta signaling through stabilization of SMURF2 by binding to SMURF2 and inhibiting its SMAD7- mediated degradation (By similarity). Involved in glucose homeostasis through induction of glucagon secretion at low glucose levels (By similarity). Promotes dermal fibroblast proliferation and wound repair (PubMed:16472771). Regulates KDELR1-mediated retention of HSP90B1/gp96 in the endoplasmic reticulum (By similarity). Plays a role in angiogenesis by inducing endothelial cell migration at low concentrations and endothelian cell apoptosis at high concentrations (PubMed:12237313). Induces maturation of dendritic cells and monocyte cell adhesion (PubMed:11818442). Modulates endothelial cell responses by degrading HIF-1A through interaction with PSMA7 (PubMed:19362550). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Secreted. Endoplasmic reticulum {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31230}. Golgi apparatus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31230}. Note=Enriched in secretory vesicles of pancreatic alpha cells and secreted from the pancreas in response to low glucose levels (By similarity). Secreted in response to hypoxia (PubMed:10850427). Also secreted in response to both apoptotic and necrotic cell death. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31230, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10850427} |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Non-catalytic component of the multisynthase complex. Stimulates the catalytic activity of cytoplasmic arginyl-tRNA synthase. Binds tRNA. Possesses inflammatory cytokine activity. Negatively regulates TGF-beta signaling through stabilization of SMURF2 by binding to SMURF2 and inhibiting its SMAD7-mediated degradation. Involved in glucose homeostasis through induction of glucagon secretion at low glucose levels. Promotes dermal fibroblast proliferation and wound repair. Regulates KDELR1- mediated retention of HSP90B1/gp96 in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plays a role in angiogenesis by inducing endothelial cell migration at low concentrations and endothelian cell apoptosis at high concentrations. Induces maturation of dendritic cells and monocyte cell adhesion. Modulates endothelial cell responses by degrading HIF-1A through interaction with PSMA7.
References
Kao J.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 269:25106-25119(1994).
Halleck A.,et al.Submitted (JUN-2004) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
Park S.G.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 274:16673-16676(1999).
Barnett G.,et al.Cancer Res. 60:2850-2857(2000).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.