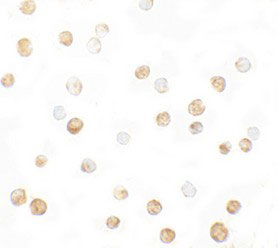
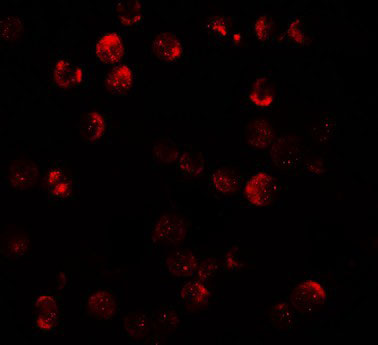
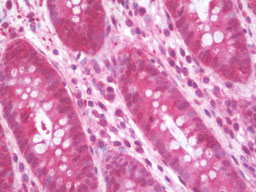
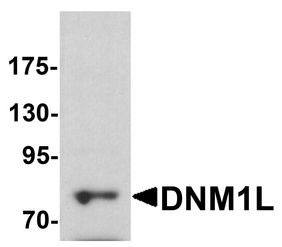
DNM1L / DRP1 Antibody (Internal)
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O00429 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 82kDa |
| Dilution | ICC (5 µg/ml), IF (20 µg/ml), IHC-P (10 µg/ml), WB (1-2 µg/ml) , |
| Gene ID | 10059 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Dynamin-1-like protein, 3.6.5.5, Dnm1p/Vps1p-like protein, DVLP, Dynamin family member proline-rich carboxyl-terminal domain less, Dymple, Dynamin-like protein, Dynamin-like protein 4, Dynamin-like protein IV, HdynIV, Dynamin-related protein 1, DNM1L, DLP1, DRP1 |
| Target/Specificity | DNM1L antibody is human and mouse reactive. At least four isoforms of DNM1L are known to exist; this antibody will detect the two longest isoforms. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Long term: -20°C; Short term: +4°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | DNM1L / DRP1 Antibody (Internal) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | DNM1L (HGNC:2973) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DLP1, DRP1 |
| Function | Functions in mitochondrial and peroxisomal division (PubMed:11514614, PubMed:12499366, PubMed:17301055, PubMed:17460227, PubMed:17553808, PubMed:18695047, PubMed:18838687, PubMed:19342591, PubMed:19411255, PubMed:19638400, PubMed:23283981, PubMed:23530241, PubMed:23921378, PubMed:26992161, PubMed:27145208, PubMed:27145933, PubMed:27301544, PubMed:27328748, PubMed:29478834, PubMed:32439975, PubMed:32484300, PubMed:9570752, PubMed:9786947). Mediates membrane fission through oligomerization into membrane-associated tubular structures that wrap around the scission site to constrict and sever the mitochondrial membrane through a GTP hydrolysis-dependent mechanism (PubMed:23530241, PubMed:23584531, PubMed:33850055). The specific recruitment at scission sites is mediated by membrane receptors like MFF, MIEF1 and MIEF2 for mitochondrial membranes (PubMed:23283981, PubMed:23921378, PubMed:29899447). While the recruitment by the membrane receptors is GTP-dependent, the following hydrolysis of GTP induces the dissociation from the receptors and allows DNM1L filaments to curl into closed rings that are probably sufficient to sever a double membrane (PubMed:29899447). Acts downstream of PINK1 to promote mitochondrial fission in a PRKN-dependent manner (PubMed:32484300). Plays an important role in mitochondrial fission during mitosis (PubMed:19411255, PubMed:26992161, PubMed:27301544, PubMed:27328748). Through its function in mitochondrial division, ensures the survival of at least some types of postmitotic neurons, including Purkinje cells, by suppressing oxidative damage (By similarity). Required for normal brain development, including that of cerebellum (PubMed:17460227, PubMed:26992161, PubMed:27145208, PubMed:27301544, PubMed:27328748). Facilitates developmentally regulated apoptosis during neural tube formation (By similarity). Required for a normal rate of cytochrome c release and caspase activation during apoptosis; this requirement may depend upon the cell type and the physiological apoptotic cues (By similarity). Required for formation of endocytic vesicles (PubMed:20688057, PubMed:23792689, PubMed:9570752). Proposed to regulate synaptic vesicle membrane dynamics through association with BCL2L1 isoform Bcl-X(L) which stimulates its GTPase activity in synaptic vesicles; the function may require its recruitment by MFF to clathrin-containing vesicles (PubMed:17015472, PubMed:23792689). Required for programmed necrosis execution (PubMed:22265414). Rhythmic control of its activity following phosphorylation at Ser-637 is essential for the circadian control of mitochondrial ATP production (PubMed:29478834). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Golgi apparatus. Endomembrane system; Peripheral membrane protein. Mitochondrion outer membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Peroxisome. Membrane, clathrin-coated pit {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35303}. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, synaptic vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35303}. Note=Mainly cytosolic. Recruited by RALA and RALBP1 to mitochondrion during mitosis (PubMed:21822277). Translocated to the mitochondrial membrane through O-GlcNAcylation and interaction with FIS1. Colocalized with MARCHF5 at mitochondrial membrane (PubMed:17606867). Localizes to mitochondria at sites of division (PubMed:15208300). Localizes to mitochondria following necrosis induction. Recruited to the mitochondrial outer membrane by interaction with MIEF1. Mitochondrial recruitment is inhibited by C11orf65/MFI (By similarity). Associated with peroxisomal membranes, partly recruited there by PEX11B. May also be associated with endoplasmic reticulum tubules and cytoplasmic vesicles and found to be perinuclear (PubMed:9422767, PubMed:9570752). In some cell types, localizes to the Golgi complex (By similarity). Binds to phospholipid membranes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K1M6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15208300, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17606867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21822277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9422767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9570752} |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed with highest levels found in skeletal muscles, heart, kidney and brain. Isoform 1 is brain-specific Isoform 2 and isoform 3 are predominantly expressed in testis and skeletal muscles respectively. Isoform 4 is weakly expressed in brain, heart and kidney. Isoform 5 is dominantly expressed in liver, heart and kidney. Isoform 6 is expressed in neurons |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Functions in mitochondrial and peroxisomal division. Mediates membrane fission through oligomerization into membrane- associated tubular structures that wrap around the scission site to constrict and sever the mitochondrial membrane through a GTP hydrolysis-dependent mechanism. Through its function in mitochondrial division, ensures the survival of at least some types of postmitotic neurons, including Purkinje cells, by suppressing oxidative damage. Required for normal brain development, including that of cerebellum. Facilitates developmentally regulated apoptosis during neural tube formation. Required for a normal rate of cytochrome c release and caspase activation during apoptosis; this requirement may depend upon the cell type and the physiological apoptotic cues. Also required for mitochondrial fission during mitosis. Required for formation of endocytic vesicles. Proposed to regulate synaptic vesicle membrane dynamics through association with BCL2L1 isoform Bcl-X(L) which stimulates its GTPase activity in synaptic vesicles; the function may require its recruitment by MFF to clathrin-containing vesicles. Required for programmed necrosis execution.
References
Shin H.-W.,et al.J. Biochem. 122:525-530(1997).
Hong Y.-R.,et al.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 249:697-703(1998).
Imoto M.,et al.J. Cell Sci. 111:1341-1349(1998).
Chen C.-H.,et al.DNA Cell Biol. 19:189-194(2000).
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.