Vesicular Monoamine Transporter 2, C-Terminus Antibody
Affinity purified sheep polyclonal antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q05940 |
| Reactivity | Rat |
| Host | Sheep |
| Clonality | polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 57 KDa |
| Gene ID | 6571 |
|---|---|
| Gene Name | VMAT2 |
| Other Names | Synaptic vesicular amine transporter, Monoamine transporter, Solute carrier family 18 member 2, Vesicular amine transporter 2, VAT2, SLC18A2, SVMT, VMAT2 |
| Target/Specificity | Synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acid residues from the intracellular C-terminal region conjugated to KLH. |
| Dilution | WB~~ 1:1000 |
| Format | Prepared from sheep serum by affinity purification using a column to which the peptide immunogen was coupled. |
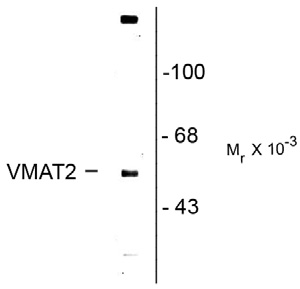
| Antibody Specificity | Specific for the ~57k VMAT2 protein in Western blots of rat caudate lysate. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Vesicular Monoamine Transporter 2, C-Terminus Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Shipping | Blue Ice |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Vesicular neurotransmitter transporters sequester the transmitters into synaptic vesicles (Erickson et al., 1996). The vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) is responsible for catecholamine and serotonin storage in central synapses. Antibodies specific for VMAT have been used to monitor expression of the transporter during development and in aging and can be effectively used as a marker for monoamine terminals (Haycock et al., 2003; Witkovsky et al., 2005).
References
Erickson JD, Schafer MKH, Bonner TI, Eiden LE, Weihe E (1996) Distinct pharmacological properties and distribution in neurons and endocrine cells of two isoforms of the human vesicular monoamine transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5166-5171.
Giros B, El Mestikawy S, Godinot N, Zheng K, Han H, Yang-Feng T, Caron MG (1991) Cloning, pharmacological characterization, and chromosome assignment of the human dopamine transporter. J Pharmacol Exptl Ther 56:2139-2142.
Haycock JW, Becker L, Ang, L, Furukawa Y, Hornykiewicz O, Kish SJ (2003) Marked disparity between age-related changes in dopamine and other presynaptic dopaminergic markers in human striatum. J Neurochem 87:574-585.
Witkovsky P, Arango-Gonzalez B, Haycock JW, Kohler K (2004) Rat retinal dopaminergic neurons: Differential maturation of somatodendritic and axonal compartments. J Comp Neurol 481:352-362.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.