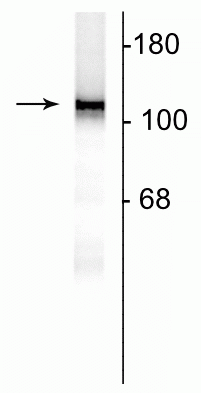
Anti-NMDA NR1 Subunit Antibody
Our Anti-NMDA NR1 Subunit primary antibody from PhosphoSolutions is mouse monoclonal. It detects hum
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P35439 |
| Reactivity | Bovine |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clone Names | R1JHL |
| Calculated MW | 105509 Da |
| Gene ID | 24408 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | GluN1 antibody, Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit zeta-1 antibody, Glutamate receptor ionotropic N methyl D aspartate 1 antibody, Glutamate receptor ionotropic N-methyl-D aspartate subunit 1 antibody, glutamate receptor ionotropic NMDA 1 antibody, Grin1 antibody, MRD8 antibody, N methyl D aspartate receptor antibody, N methyl D aspartate receptor channel subunit zeta 1 antibody, N methyl D aspartate receptor subunit NR1 antibody, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR1 antibody, NMD-R1 antibody, NMDA 1 antibody, NMDA R1 antibody, NMDAR1 antibody, NMDA receptor 1 antibody, NMDA1 antibody, NMDAR antibody, NMDZ1_HUMAN antibody, NR1 antibody |
| Target/Specificity | The ion channels activated by glutamate are typically divided into two classes. Glutamate receptors that are activated by kainate and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxalone propionic acid (AMPA) are known as kainate/AMPA receptors (K/AMPAR). Those that are sensitive to Nmethyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) are designated NMDA receptors (NMDAR). The NMDAR plays an essential role in memory, neuronal development and it has also been implicated in several disorders of the central nervous system including Alzheimer’s, epilepsy and ischemic neuronal cell death (Grosshans et al., 2002; Wenthold et al., 2003; Carroll and Zukin, 2002). The NMDA receptor is also one of the principal molecular targets for alcohol in the CNS (Lovinger et al., 1989; Alvestad et al., 2003; Snell et al., 1996). The NMDAR is also potentiated by protein phosphorylation (Lu et al., 1999). The rat NMDAR1 (NR1) was the first subunit of the NMDAR to be cloned. The NR1 protein can form NMDA activated channels when expressed in Xenopus oocytes but the currents in such channels are much smaller than those seen in situ. Channels with more physiological characteristics are produced when the NR1-subunit is combined with one or more of the NMDAR2 (NR2 A-D) subunits. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC~~1:100~500 |
| Format | Culture supernatant |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Anti-NMDA NR1 Subunit Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Shipping | Blue Ice |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The ion channels activated by glutamate are typically divided into two classes. Glutamate receptors that are activated by kainate and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxalone propionic acid (AMPA) are known as kainate/AMPA receptors (K/AMPAR). Those that are sensitive to Nmethyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) are designated NMDA receptors (NMDAR). The NMDAR plays an essential role in memory, neuronal development and it has also been implicated in several disorders of the central nervous system including Alzheimer’s, epilepsy and ischemic neuronal cell death (Grosshans et al., 2002; Wenthold et al., 2003; Carroll and Zukin, 2002). The NMDA receptor is also one of the principal molecular targets for alcohol in the CNS (Lovinger et al., 1989; Alvestad et al., 2003; Snell et al., 1996). The NMDAR is also potentiated by protein phosphorylation (Lu et al., 1999). The rat NMDAR1 (NR1) was the first subunit of the NMDAR to be cloned. The NR1 protein can form NMDA activated channels when expressed in Xenopus oocytes but the currents in such channels are much smaller than those seen in situ. Channels with more physiological characteristics are produced when the NR1-subunit is combined with one or more of the NMDAR2 (NR2 A-D) subunits.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.