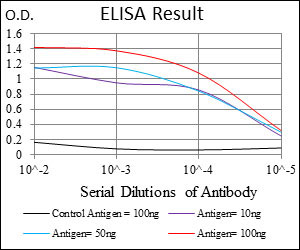
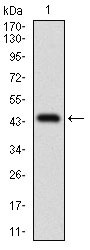
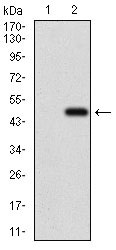
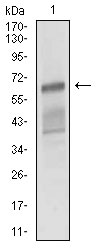
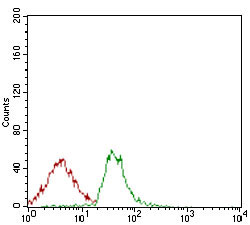
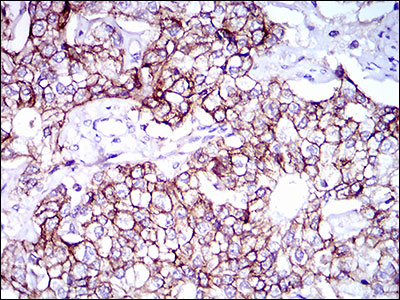
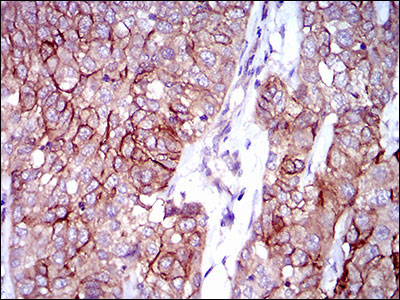
ALCAM Antibody
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, FC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q13740 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 4H9A5 |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Calculated MW | 65.1kDa |
| Description | This gene encodes activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM), also known as CD166 (cluster of differentiation 166), which is a member of a subfamily of immunoglobulin receptors with five immunoglobulin-like domains (VVC2C2C2) in the extracellular domain. This protein binds to T-cell differentiation antigene CD6, and is implicated in the processes of cell adhesion and migration. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found. |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ALCAM (AA: 48-216) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
| Gene ID | 214 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CD166 antigen, Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule, CD166, ALCAM, MEMD |
| Dilution | WB~~1/500 - 1/2000 IHC~~1/200 - 1/1000 FC~~1/200 - 1/400 E~~1/10000 |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | ALCAM Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ALCAM |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MEMD {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9502422} |
| Function | Cell adhesion molecule that mediates both heterotypic cell- cell contacts via its interaction with CD6, as well as homotypic cell- cell contacts (PubMed:15048703, PubMed:15496415, PubMed:16352806, PubMed:23169771, PubMed:24945728, PubMed:7760007). Promotes T-cell activation and proliferation via its interactions with CD6 (PubMed:15048703, PubMed:16352806, PubMed:24945728). Contributes to the formation and maturation of the immunological synapse via its interactions with CD6 (PubMed:15294938, PubMed:16352806). Mediates homotypic interactions with cells that express ALCAM (PubMed:15496415, PubMed:16352806). Acts as a ligand for the LILRB4 receptor, enhancing LILRB4-mediated inhibition of T cell proliferation (PubMed:29263213). Required for normal hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in the bone marrow (PubMed:24740813). Mediates attachment of dendritic cells onto endothelial cells via homotypic interaction (PubMed:23169771). Inhibits endothelial cell migration and promotes endothelial tube formation via homotypic interactions (PubMed:15496415, PubMed:23169771). Required for normal organization of the lymph vessel network. Required for normal hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in the bone marrow. Plays a role in hematopoiesis; required for normal numbers of hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Promotes in vitro osteoblast proliferation and differentiation (By similarity). Promotes neurite extension, axon growth and axon guidance; axons grow preferentially on surfaces that contain ALCAM. Mediates outgrowth and pathfinding for retinal ganglion cell axons (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61490}. Cell projection, dendrite {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61490}. Note=Detected at the immunological synapse, i.e, at the contact zone between antigen-presenting dendritic cells and T-cells (PubMed:15294938, PubMed:16352806). Colocalizes with CD6 and the TCR/CD3 complex at the immunological synapse (PubMed:15294938). |
| Tissue Location | Detected on hematopoietic stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood (PubMed:24740813). Detected on lymph vessel endothelial cells, skin and tonsil (PubMed:23169771). Detected on peripheral blood monocytes (PubMed:15048703). Detected on monocyte- derived dendritic cells (at protein level) (PubMed:16352806). Detected at low levels in spleen, placenta, liver (PubMed:9502422). Expressed by activated T-cells, B-cells, monocytes and thymic epithelial cells (PubMed:7760007). Isoform 1 and isoform 3 are detected in vein and artery endothelial cells, astrocytes, keratinocytes and artery smooth muscle cells (PubMed:15496415). Expressed by neurons in the brain Restricted expression in tumor cell lines. Detected in highly metastasizing melanoma cell lines (PubMed:9502422) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes a C2H2 zinc finger protein with transactivation and DNA-binding activities. It has been shown to have anti-proliferative properties, and thus thought to function as a tumor suppressor. In addition, overexpression of this gene during fetal development is believed to underlie the rare disorder, transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM). This gene is imprinted, with preferential expression of the paternal allele in many tissues, however, biallelic expression has been noted in peripheral blood leucocytes. A recent study reports that tissue-specific imprinting results from variable utilization of monoallelic and biallelic promoters. Many transcript variants differing in the 5' UTR and encoding two different isoforms, have been found for this gene. ;
References
1. Vascul Pharmacol. 2011 Mar-Jun;54(3-6):93-9. 2. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011 Apr;21(3):523-8.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.