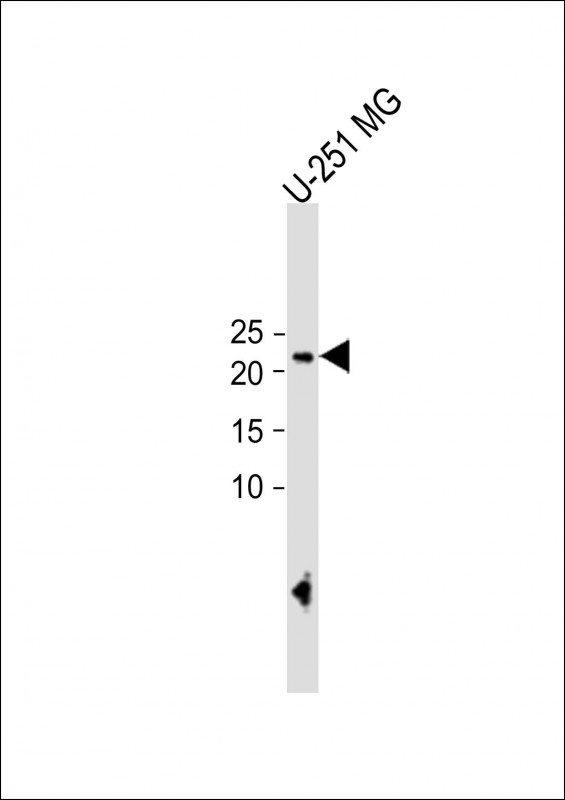
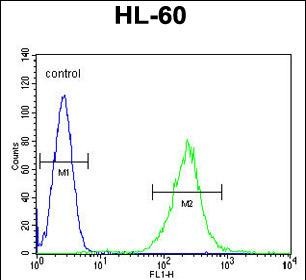
ECAT1 Antibody (N-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 2
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, FC, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q587J8 |
| Other Accession | NP_001017361 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 24306 Da |
| Antigen Region | 20-48 aa |
| Gene ID | 154288 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | KHDC3-like protein, ES cell-associated transcript 1 protein, KHDC3L, C6orf221, ECAT1 |
| Target/Specificity | This ECAT1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 20-48 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ECAT1. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 FC~~1:10~50 IHC-P~~1:10~50 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | ECAT1 Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | KHDC3L {ECO:0000303|PubMed:31609975, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:33699} |
|---|---|
| Function | Component of the subcortical maternal complex (SCMC), a multiprotein complex that plays a key role in early embryonic development (By similarity). The SCMC complex is a structural constituent of cytoplasmic lattices, which consist in fibrous structures found in the cytoplasm of oocytes and preimplantation embryos (By similarity). They are required to store maternal proteins critical for embryonic development, such as proteins that control epigenetic reprogramming of the preimplantation embryo, and prevent their degradation or activation (By similarity). KHDC3 ensures proper spindle assembly by regulating the localization of AURKA via RHOA signaling and of PLK1 via a RHOA-independent process (By similarity). Required for the localization of MAD2L1 to kinetochores to enable spindle assembly checkpoint function (By similarity). As part of the OOEP-KHDC3 scaffold, recruits BLM and TRIM25 to DNA replication forks, thereby promoting the ubiquitination of BLM by TRIM25, enhancing BLM retainment at replication forks and therefore promoting stalled replication fork restart (By similarity). Regulates homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair via recruitment of RAD51 to sites of DNA double-strand breaks, and sustainment of PARP1 activity, which in turn modulates downstream ATM or ATR activation (PubMed:31609975). Activation of ATM or ATR in response to DNA double-strand breaks may be cell-type specific (By similarity). Its role in DNA double-strand break repair is independent of its role in restarting stalled replication forks (By similarity). Promotes neural stem cell neurogenesis and neuronal differentiation in the hippocampus (By similarity). May regulate normal development of learning, memory and anxiety (By similarity). Capable of binding RNA (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CWU5}. Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Nucleus. Mitochondrion {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CWU5}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CWU5} Chromosome. Note=Core component of cytoplasmic lattices in oocytes (By similarity). Expressed in the subcortex of oocytes (By similarity). Located throughout the cell cortex of ovulated eggs in a complex with NLRP5 (By similarity). After fertilization, restricted to the apical cortex and excluded from regions of cell-cell contact (By similarity). Localized to centrosomes during interphase and mitosis (By similarity). Localizes to sites of DNA double-strand break repair (PubMed:31609975) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CWU5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31609975} |
| Tissue Location | Expression appears to be maximal in germinal vesicle oocytes, it tails off through metaphase II oocytes and is undetectable following the completion of the oocyte to embryo transition. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
References
Pierre, A., et al. Genomics 90(5):583-594(2007) Mitsui, K., et al. Cell 113(5):631-642(2003)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.