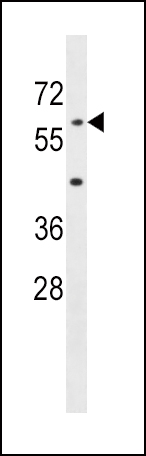
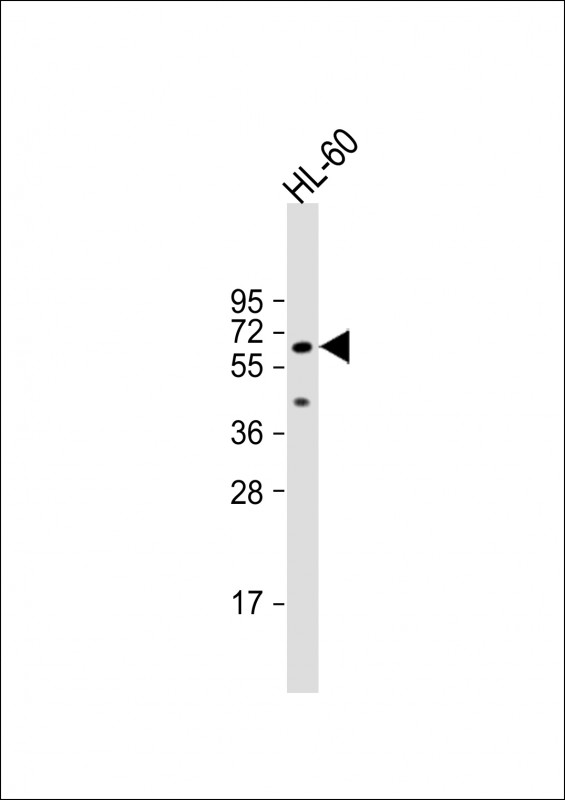
AOAH Antibody (Center)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P28039 |
| Other Accession | NP_001628.1, NP_001170977.1 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 65105 Da |
| Antigen Region | 168-197 aa |
| Gene ID | 313 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Acyloxyacyl hydrolase, Acyloxyacyl hydrolase small subunit, Acyloxyacyl hydrolase large subunit, AOAH |
| Target/Specificity | This AOAH antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 168-197 amino acids from the Central region of human AOAH. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | AOAH Antibody (Center) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | AOAH {ECO:0000303|PubMed:1883828} |
|---|---|
| Function | Removes the secondary (acyloxyacyl-linked) fatty acyl chains from the lipid A region of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (PubMed:1883828, PubMed:29343645, PubMed:8089145). By breaking down LPS, terminates the host response to bacterial infection and prevents prolonged and damaging inflammatory responses (By similarity). In peritoneal macrophages, seems to be important for recovery from a state of immune tolerance following infection by Gram-negative bacteria (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Secreted. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Note=Detected in urine {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35298} |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This locus encodes both the light and heavy subunits of acyloxyacyl hydrolase. The encoded enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of acyloxylacyl-linked fatty acyl chains from bacterial lipopolysaccharides, effectively detoxifying these molecules. The encoded protein may play a role in modulating host inflammatory response to gram-negative bacteria. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.
References
Rose, J.E., et al. Mol. Med. 16 (7-8), 247-253 (2010) :
Pelak, K., et al. J. Infect. Dis. 201(8):1141-1149(2010)
Barnes, K.C., et al. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 118(1):70-77(2006)
Coulthard, M.G., et al. Infect. Immun. 64(5):1510-1515(1996)
Staab, J.F., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 269(38):23736-23742(1994)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.