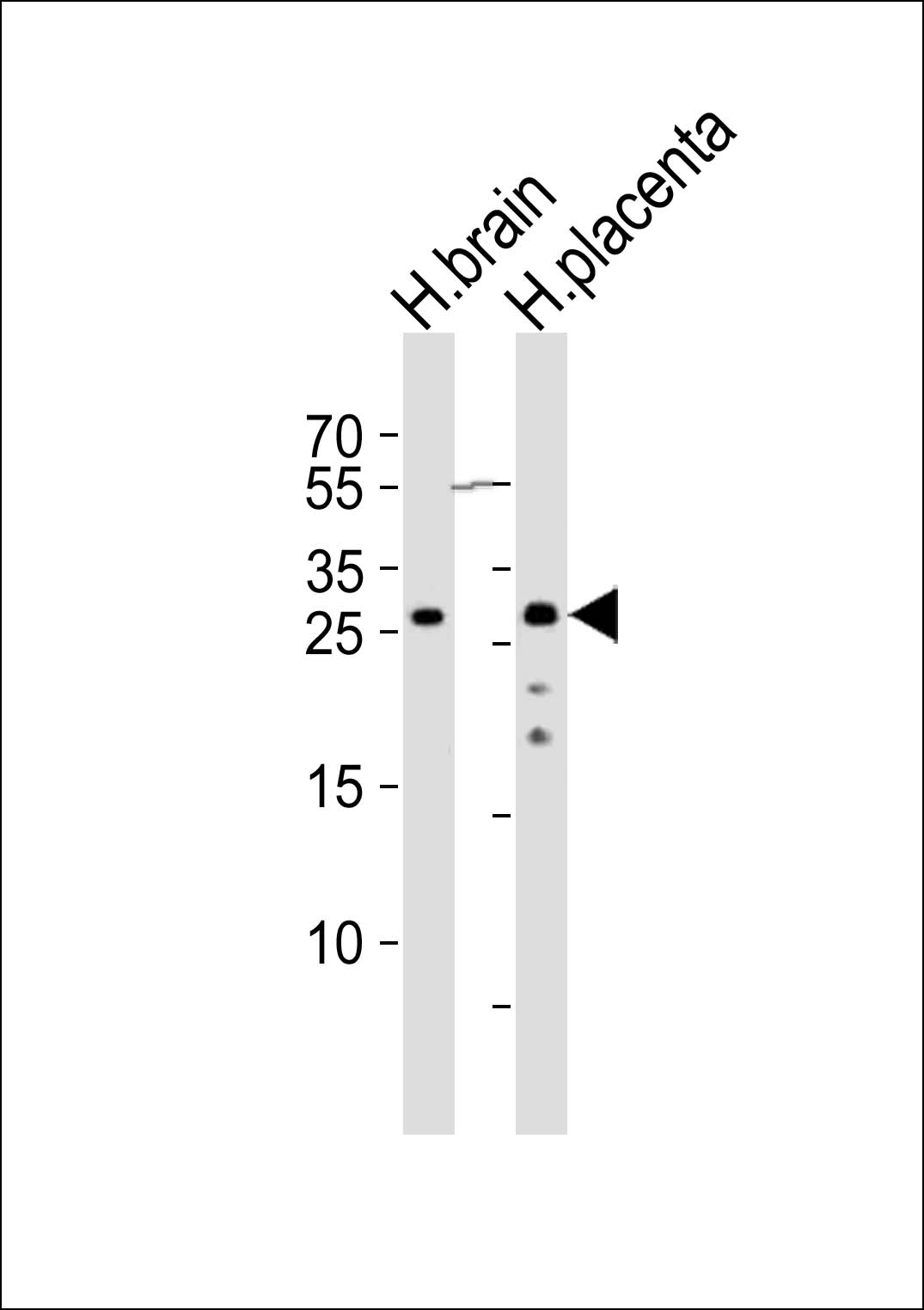
CHMP4A Antibody (C-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9BY43 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 25098 Da |
| Antigen Region | 205-239 aa |
| Gene ID | 29082 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Charged multivesicular body protein 4a, Chromatin-modifying protein 4a, CHMP4a, SNF7 homolog associated with Alix-2, SNF7-1, hSnf-1, Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 32-1, Vps32-1, hVps32-1, CHMP4A, C14orf123, SHAX2 |
| Target/Specificity | This CHMP4A antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 205-239 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CHMP4A. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | CHMP4A Antibody (C-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CHMP4A |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | C14orf123, SHAX2 |
| Function | Probable core component of the endosomal sorting required for transport complex III (ESCRT-III) which is involved in multivesicular bodies (MVBs) formation and sorting of endosomal cargo proteins into MVBs. MVBs contain intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that are generated by invagination and scission from the limiting membrane of the endosome and mostly are delivered to lysosomes enabling degradation of membrane proteins, such as stimulated growth factor receptors, lysosomal enzymes and lipids. The MVB pathway appears to require the sequential function of ESCRT-O, -I,-II and -III complexes. ESCRT-III proteins mostly dissociate from the invaginating membrane before the ILV is released. The ESCRT machinery also functions in topologically equivalent membrane fission events, such as the terminal stages of cytokinesis and the budding of enveloped viruses (HIV-1 and other lentiviruses). ESCRT-III proteins are believed to mediate the necessary vesicle extrusion and/or membrane fission activities, possibly in conjunction with the AAA ATPase VPS4. When overexpressed, membrane-assembled circular arrays of CHMP4A filaments can promote or stabilize negative curvature and outward budding. Via its interaction with PDCD6IP involved in HIV-1 p6- and p9-dependent virus release. CHMP4A/B/C are required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63 and syndecan (PubMed:22660413). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane. Late endosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein Note=Membrane-associated. Localizes to large vesicle-like structures Localizes to the midbody of dividing cells. Localized in two distinct rings on either side of the Fleming body |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed. Expressed at higher level in heart, kidney, liver and skeletal muscle. Also expressed in brain, placenta, lung and pancreas. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Probable core component of the endosomal sorting required for transport complex III (ESCRT-III) which is involved in multivesicular bodies (MVBs) formation and sorting of endosomal cargo proteins into MVBs. MVBs contain intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that are generated by invagination and scission from the limiting membrane of the endosome and mostly are delivered to lysosomes enabling degradation of membrane proteins, such as stimulated growth factor receptors, lysosomal enzymes and lipids. The MVB pathway appears to require the sequential function of ESCRT-O, -I,-II and -III complexes. ESCRT-III proteins mostly dissociate from the invaginating membrane before the ILV is released. The ESCRT machinery also functions in topologically equivalent membrane fission events, such as the terminal stages of cytokinesis and the budding of enveloped viruses (HIV-1 and other lentiviruses). ESCRT-III proteins are believed to mediate the necessary vesicle extrusion and/or membrane fission activities, possibly in conjunction with the AAA ATPase VPS4. When overexpressed, membrane-assembled circular arrays of CHMP4A filaments can promote or stabilize negative curvature and outward budding. Via its interaction with PDCD6IP involved in HIV-1 p6- and p9-dependent virus release.
References
Katoh K.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 278:39104-39113(2003).
Peck J.W.,et al.Biochem. J. 377:693-700(2004).
Li Y.,et al.Submitted (DEC-1999) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Zhang Q.-H.,et al.Genome Res. 10:1546-1560(2000).
Li W.B.,et al.Submitted (FEB-2003) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.