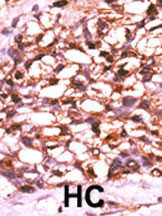
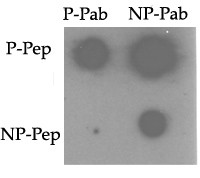
Phospho-TNIK(S764) Antibody
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 3
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, DB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UKE5 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 154943 Da |
| Gene ID | 23043 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | TRAF2 and NCK-interacting protein kinase, TNIK, KIAA0551 |
| Target/Specificity | This TNIK Antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to amino acid residues surrounding S764 of human TNIK. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 IHC-P~~1:50~100 DB~~1:500 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Phospho-TNIK(S764) Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | TNIK (HGNC:30765) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | KIAA0551 |
| Function | Serine/threonine kinase that acts as an essential activator of the Wnt signaling pathway. Recruited to promoters of Wnt target genes and required to activate their expression. May act by phosphorylating TCF4/TCF7L2. Appears to act upstream of the JUN N- terminal pathway. May play a role in the response to environmental stress. Part of a signaling complex composed of NEDD4, RAP2A and TNIK which regulates neuronal dendrite extension and arborization during development. More generally, it may play a role in cytoskeletal rearrangements and regulate cell spreading. Phosphorylates SMAD1 on Thr-322. Activator of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. MAP4Ks act in parallel to and are partially redundant with STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST2 in the phosphorylation and activation of LATS1/2, and establish MAP4Ks as components of the expanded Hippo pathway (PubMed:26437443). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Recycling endosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Note=Associated with recycling endosomes and the cytoskeletal fraction upon RAP2A overexpression |
| Tissue Location | Expressed ubiquitously. Highest levels observed in heart, brain and skeletal muscle. Expressed in normal colonic epithelia and colorectal cancer tissues. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
TNIK is a stress-activated serine/threonine kinase that may play a role in the response to environmental stress. This protein appears to act upstream of the JUN N-terminal pathway, and may play a role in cytoskeletal regulation.
References
Taira, K., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 279(47):49488-49496 (2004).
Fu, C.A., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 274(43):30729-30737 (1999).
Yonekura, H., et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 27(13):2591-2600 (1999).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.