AKR1C2 Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

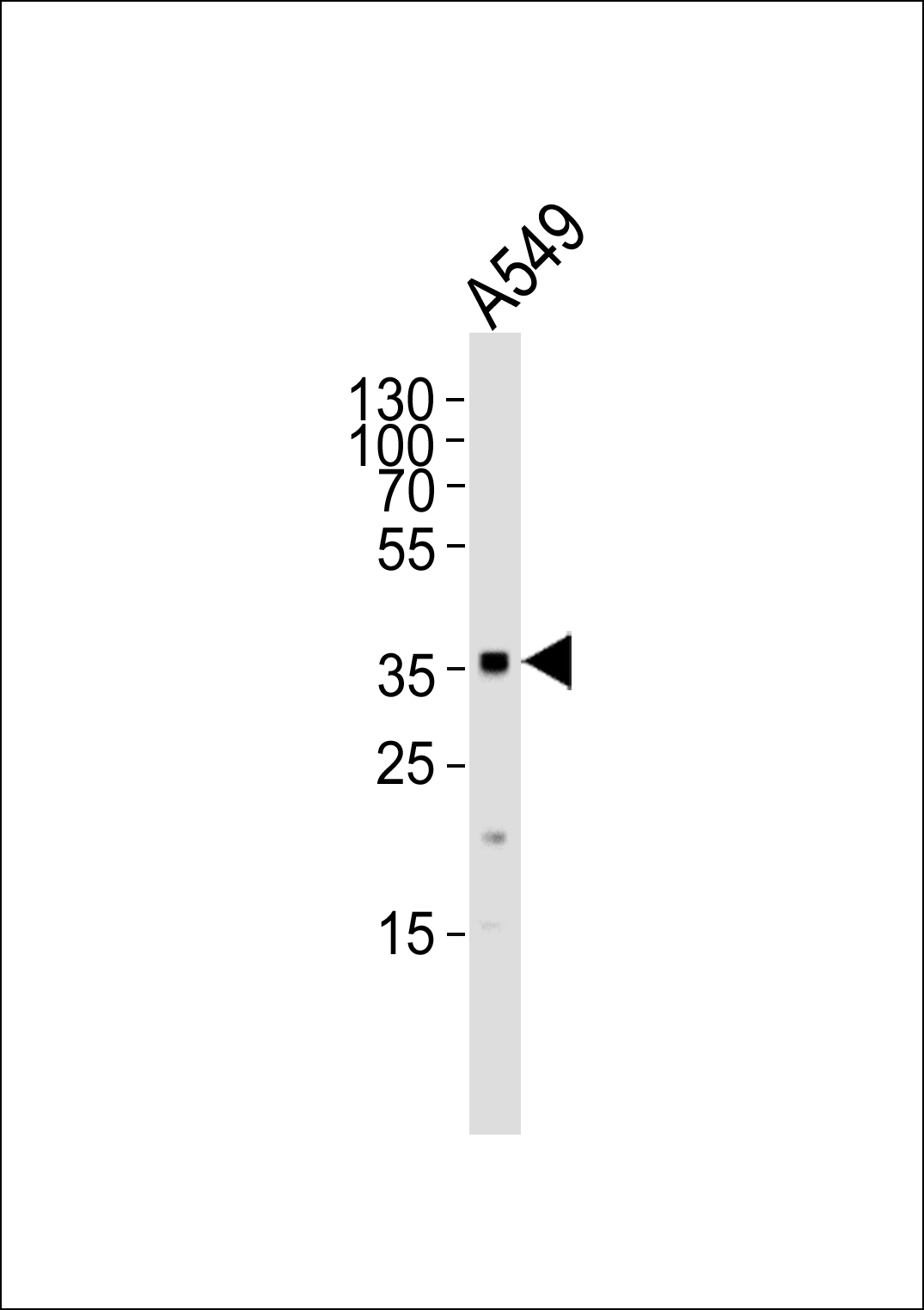
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P52895 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 38,16 KDa |
| Antigen Region | 34-63 aa |
| Gene ID | 1646 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C2, 1---, 3-alpha-HSD3, Chlordecone reductase homolog HAKRD, Dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 2, DD-2, DD2, Dihydrodiol dehydrogenase/bile acid-binding protein, DD/BABP, Trans-1, 2-dihydrobenzene-1, 2-diol dehydrogenase, Type III 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, AKR1C2, DDH2 |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 |
| Format | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline (without Mg2+ and Ca2+), pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
| Storage Conditions | -20℃ |
| Name | AKR1C2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DDH2 |
| Function | Cytosolic aldo-keto reductase that catalyzes the NADH and NADPH-dependent reduction of ketosteroids to hydroxysteroids (PubMed:19218247). Most probably acts as a reductase in vivo since the oxidase activity measured in vitro is inhibited by physiological concentrations of NADPH (PubMed:14672942). Displays a broad positional specificity acting on positions 3, 17 and 20 of steroids and regulates the metabolism of hormones like estrogens and androgens (PubMed:10998348). Works in concert with the 5-alpha/5-beta-steroid reductases to convert steroid hormones into the 3-alpha/5-alpha and 3- alpha/5-beta-tetrahydrosteroids. Catalyzes the inactivation of the most potent androgen 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone (5-alpha-DHT) to 5-alpha- androstane-3-alpha,17-beta-diol (3-alpha-diol) (PubMed:15929998, PubMed:17034817, PubMed:17442338, PubMed:8573067). Also specifically able to produce 17beta-hydroxy-5alpha-androstan-3-one/5alphaDHT (PubMed:10998348). May also reduce conjugated steroids such as 5alpha- dihydrotestosterone sulfate (PubMed:19218247). Displays affinity for bile acids (PubMed:8486699). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in fetal testes. Expressed in fetal and adult adrenal glands. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Works in concert with the 5-alpha/5-beta-steroid reductases to convert steroid hormones into the 3-alpha/5-alpha and 3-alpha/5-beta-tetrahydrosteroids. Catalyzes the inactivation of the most potent androgen 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone (5-alpha- DHT) to 5-alpha-androstane-3-alpha,17-beta-diol (3-alpha-diol). Has a high bile-binding ability.
References
Qin K.-N.,et al.J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 46:673-679(1993).
Ciaccio P.J.,et al.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1186:129-132(1994).
Qin K.-N.,et al.Gene 149:357-361(1994).
Dufort I.,et al.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 228:474-479(1996).
Shiraishi H.,et al.Biochem. J. 334:399-405(1998).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.