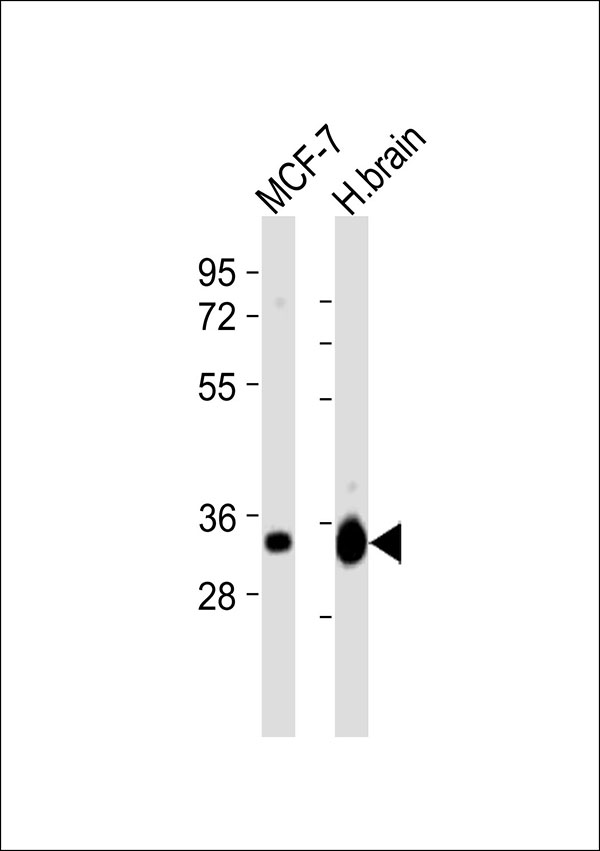
EB3 Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 2
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UPY8 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 32 KDa |
| Antigen Region | 221 - 280 aa |
| Gene ID | 22924 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 3, EB1 protein family member 3, EBF3, End-binding protein 3, EB3, RP3, MAPRE3 |
| Target/Specificity | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the C-term region of human EB3. The exact sequence is proprietary. |
| Dilution | WB~~ 1:8000 |
| Format | 0.01M PBS, pH 7.2, 0.09% (W/V) Sodium azide, Glycerol 50% |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C.Stable for 12 months from date of receipt |
| Name | MAPRE3 |
|---|---|
| Function | Plus-end tracking protein (+TIP) that binds to the plus-end of microtubules and regulates the dynamics of the microtubule cytoskeleton (PubMed:19255245, PubMed:28814570). Promotes microtubule growth (PubMed:19255245, PubMed:28814570). May be involved in spindle function by stabilizing microtubules and anchoring them at centrosomes (PubMed:19255245, PubMed:28814570). Also acts as a regulator of minus- end microtubule organization: interacts with the complex formed by AKAP9 and PDE4DIP, leading to recruit CAMSAP2 to the Golgi apparatus, thereby tethering non-centrosomal minus-end microtubules to the Golgi, an important step for polarized cell movement (PubMed:28814570). Promotes elongation of CAMSAP2-decorated microtubule stretches on the minus-end of microtubules (PubMed:28814570). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Note=Associated with the microtubule network. Detected at the plus end of microtubules |
| Tissue Location | Predominantly expressed in brain and muscle. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Binds to the plus end of microtubules and regulates the dynamics of the microtubule cytoskeleton. Promotes microtubule growth. May be involved in spindle function by stabilizing microtubules and anchoring them at centrosomes. May play a role in cell migration (By similarity).
References
Nakagawa H.,et al.Oncogene 19:210-216(2000).
Su L.-K.,et al.Genomics 71:142-149(2001).
Halleck A.,et al.Submitted (JUN-2004) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Hillier L.W.,et al.Nature 434:724-731(2005).
Mural R.J.,et al.Submitted (SEP-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.