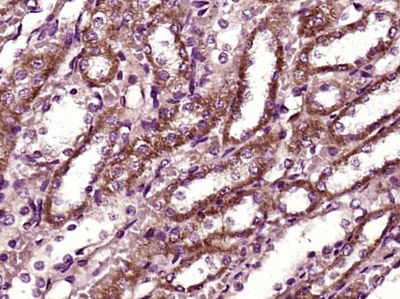
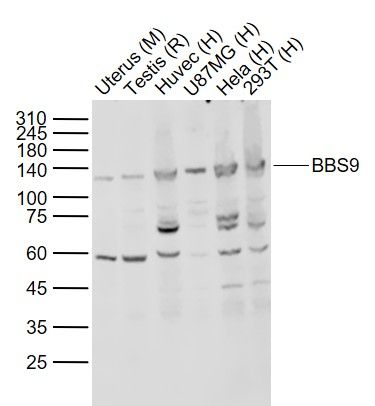
BBS9 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q3SYG4 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Pig, Dog |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 99 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human BBS9 |
| Epitope Specificity | 244-320/887 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, centrosome. Cell projection, cilium membrane. Cytoplasm. Note=Localizes to nonmembranous centriolar satellites in the cytoplasm. |
| SUBUNIT | Part of BBSome complex, that contains BBS1, BBS2, BBS4, BBS5, BBS7, BBS8, BBS9 and BBIP10. The BBSome complex binds to PCM1 and tubulin. |
| DISEASE | Defects in BBS9 are a cause of Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 9 (BBS9) [MIM:209900]. Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a genetically heterogeneous, autosomal recessive disorder characterized by usually severe pigmentary retinopathy, early onset obesity, polydactyly, hypogenitalism, renal malformation and mental retardation. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | BBS9 is an 887 amino acid protein that localizes to both the cytoplasm and the centrosome and exists as six alternatively spliced isoforms. Expressed in a wide variety of tissues, including liver, lung, heart, brain and skeletal muscle, BBS9 functions as a component of the multi-protein BBSome complex which is required for ciliogenesis and is regulated by GDP/GTP exchange factors. Defects in the gene encoding BBS9 are associated with the pathogenesis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 9 (BBS9), an autosomal recessive disorder that is characterized by severe pigmentary retinopathy, early onset obesity, polydactyly, hypogenitalism, renal malformation and mental retardation. Additionally, chromosomal aberrations involving the BBS9 gene may play a role in the formation of Wilms tumor 5 (WT5). |
| Gene ID | 27241 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Protein PTHB1, Bardet-Biedl syndrome 9 protein, Parathyroid hormone-responsive B1 gene protein, BBS9, PTHB1 |
| Target/Specificity | Widely expressed. Expressed in adult heart, skeletal muscle, lung, liver, kidney, placenta and brain, and in fetal kidney, lung, liver and brain. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |
| Name | BBS9 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | PTHB1 |
| Function | The BBSome complex is thought to function as a coat complex required for sorting of specific membrane proteins to the primary cilia. The BBSome complex is required for ciliogenesis but is dispensable for centriolar satellite function. This ciliogenic function is mediated in part by the Rab8 GDP/GTP exchange factor, which localizes to the basal body and contacts the BBSome. Rab8(GTP) enters the primary cilium and promotes extension of the ciliary membrane. Firstly the BBSome associates with the ciliary membrane and binds to RAB3IP/Rabin8, the guanosyl exchange factor (GEF) for Rab8 and then the Rab8-GTP localizes to the cilium and promotes docking and fusion of carrier vesicles to the base of the ciliary membrane. Required for proper BBSome complex assembly and its ciliary localization. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cell projection, cilium membrane. Cytoplasm Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriolar satellite |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed. Expressed in adult heart, skeletal muscle, lung, liver, kidney, placenta and brain, and in fetal kidney, lung, liver and brain. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.