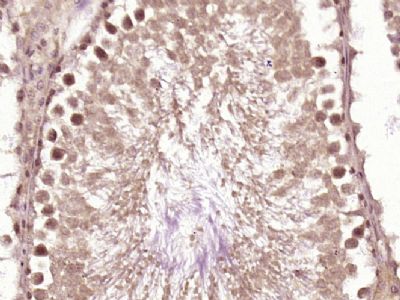
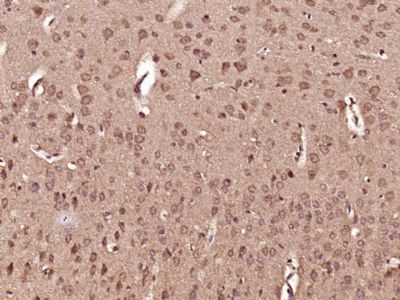
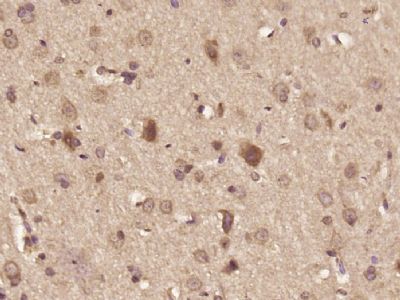
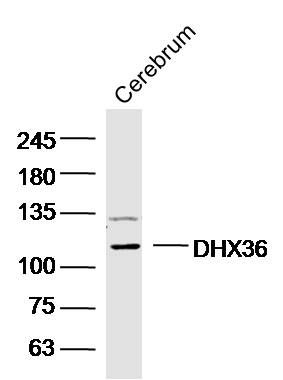
DHX36 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9H2U1 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 115 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human DHX36 |
| Epitope Specificity | 151-250/1008 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Isoform 1 preferentially localized to the nucleus and isoform 2 localized to the cytoplasm. However, partitioning of cellular localization between the nucleus and cytoplasm is not exclusive, as isoform 1 was also detected in the cytoplasm. Both isoforms were excluded from nucleoli. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the DEAD box helicase family. DEAH subfamily. Contains 1 helicase ATP-binding domain. Contains 1 helicase C-terminal domain. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene is a member of the DEAH-box family of RNA-dependent NTPases which are named after the conserved amino acid sequence Asp-Glu-Ala-His in motif II. The protein encoded by this gene has been shown to enhance the deadenylation and decay of mRNAs with 3'-UTR AU-rich elements (ARE-mRNA). The protein has also been shown to resolve into single strands the highly stable tetramolecular DNA configuration (G4) that can form spontaneously in guanine-rich regions of DNA. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Gene ID | 170506 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | ATP-dependent DNA/RNA helicase DHX36, 3.6.4.12, 3.6.4.13, DEAD/H box polypeptide 36, DEAH-box protein 36, G4-resolvase-1, G4R1, MLE-like protein 1, RNA helicase associated with AU-rich element protein, DHX36 (HGNC:14410) |
| Target/Specificity | Highly expressed in testis. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |
| Name | DHX36 (HGNC:14410) |
|---|---|
| Function | Multifunctional ATP-dependent helicase that unwinds G- quadruplex (G4) structures (PubMed:16150737, PubMed:18854321, PubMed:20472641, PubMed:21586581). Plays a role in many biological processes such as genomic integrity, gene expression regulations and as a sensor to initiate antiviral responses (PubMed:14731398, PubMed:18279852, PubMed:21993297, PubMed:22238380, PubMed:25579584). G4 structures correspond to helical structures containing guanine tetrads (By similarity). Binds with high affinity to and unwinds G4 structures that are formed in nucleic acids (G4-DNA and G4-RNA) (PubMed:16150737, PubMed:18842585, PubMed:20472641, PubMed:21586581, PubMed:24369427, PubMed:26195789). Plays a role in genomic integrity (PubMed:22238380). Converts the G4-RNA structure present in telomerase RNA template component (TREC) into a double-stranded RNA to promote P1 helix formation that acts as a template boundary ensuring accurate reverse transcription (PubMed:20472641, PubMed:21149580, PubMed:21846770, PubMed:22238380, PubMed:24151078, PubMed:25579584). Plays a role in transcriptional regulation (PubMed:21586581, PubMed:21993297). Resolves G4-DNA structures in promoters of genes, such as YY1, KIT/c-kit and ALPL and positively regulates their expression (PubMed:21993297). Plays a role in post-transcriptional regulation (PubMed:27940037). Unwinds a G4-RNA structure located in the 3'-UTR polyadenylation site of the pre- mRNA TP53 and stimulates TP53 pre-mRNA 3'-end processing in response to ultraviolet (UV)-induced DNA damage (PubMed:27940037). Binds to the precursor-microRNA-134 (pre-miR-134) terminal loop and regulates its transport into the synapto-dendritic compartment (By similarity). Involved in the pre-miR-134-dependent inhibition of target gene expression and the control of dendritic spine size (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of cytoplasmic mRNA translation and mRNA stability (PubMed:24369427, PubMed:26489465). Binds to both G4-RNA structures and alternative non-quadruplex-forming sequence within the 3'-UTR of the PITX1 mRNA regulating negatively PITX1 protein expression (PubMed:24369427). Binds to both G4-RNA structure in the 5'-UTR and AU- rich elements (AREs) localized in the 3'-UTR of NKX2-5 mRNA to either stimulate protein translation or induce mRNA decay in an ELAVL1- dependent manner, respectively (PubMed:26489465). Also binds to ARE sequences present in several mRNAs mediating exosome-mediated 3'-5' mRNA degradation (PubMed:14731398, PubMed:18279852). Involved in cytoplasmic urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) mRNA decay (PubMed:14731398). Component of a multi-helicase-TICAM1 complex that acts as a cytoplasmic sensor of viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and plays a role in the activation of a cascade of antiviral responses including the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines via the adapter molecule TICAM1 (By similarity). Required for early embryonic development and hematopoiesis. Involved in the regulation of cardioblast differentiation and proliferation during heart development. Involved in spermatogonia differentiation. May play a role in ossification (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytosol {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VHK9}. Cytoplasm, Stress granule. Nucleus speckle. Chromosome, telomere. Mitochondrion {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VHK9}. Perikaryon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D4A2Z8}. Cell projection, dendrite {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D4A2Z8}. Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D4A2Z8}. Note=Predominantly localized in the nucleus (PubMed:18279852). Colocalizes with SRSF2 in nuclear speckles (PubMed:18279852). Colocalizes with DDX5 in nucleolar caps upon transcription inhibition (PubMed:18279852). Accumulates and colocalized with TIA1 in cytoplasmic stress granules (SGs) in an arsenite-, heat shock- and RNA-binding-dependent manner (PubMed:18854321). Shuttles into and out of SGs in an ATPase-dependent manner (PubMed:18854321) Colocalizes in the cytosol with the multi-helicase-TICAM1 complex that translocates to the mitochondria upon poly(I:C) RNA ligand stimulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VHK9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18279852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18854321} [Isoform 2]: Nucleus. Cytoplasm Note=Preferentially localized in the cytoplasm (PubMed:14731398) Excluded from nucleoli (PubMed:14731398) |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in testis. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.