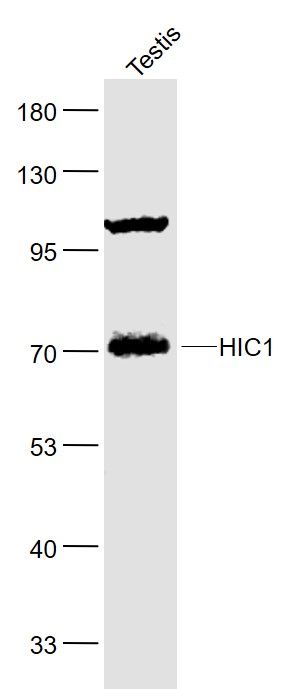
HIC1 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q14526 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Pig, Dog, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 76 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human HIC1 |
| Epitope Specificity | 501-650/733 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Nucleus. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family. Hic subfamily.Contains 1 BTB (POZ) domain.Contains 5 C2H2-type zinc fingers. |
| SUBUNIT | Self-associates. Interacts with HIC2. Interacts with CTBP1 and CTBP2. Interacts with TCF7L2 and ARID1A. Interacts with MTA1 and MBD3; indicative for an association with the NuRD complex. |
| Post-translational modifications | Acetylated on several residues, including Lys-333. Lys-333 is deacetylated by SIRT1.Sumoylated on Lys-333 by a PIAS family member, which enhances interaction with MTA1, positively regulates transcriptional repression activity and is enhanced by HDAC4. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | Hypermethylated in cancer (HIC-1) was originally identified as a target of p53-induced gene expression. HIC-1 is deleted in the genetic disorder Miller-Dieker syndrome (MDS), and the expression of HIC-1 is also frequently suppressed in leukemia and various cancers due to the hypermethylation of specific DNA regions and the resulting transcriptional silencing. These and other studies indicate that HIC-1 acts as a putative tumor suppressor protein that mediates transcriptional repression. HIC-1 is ubiquitously expressed in adult tissues and its structure is defined by five zinc fingers and an N-terminal broad complex POZ (or BTB) domain. In several BTB/POZ containing proteins, including BCL-6 and the promyelocytic leukemia zinc-finger (PLZF) oncoprotein, this domain interacts with the SMRT/N-CoR-mSin3A HDAC complex and is directly involved in repressing and silencing gene transcription. When this domain is deleted, as with the oncogenic PLZF-RAR chimera of promyelocytic leukemias, this transcriptional repression is attenuated. Conversely, HIC-1 does not interact with components of the HDAC complex, suggesting that HIC-1-induced transcriptional repression is unassociated with the POZ/BTB domain. |
| Gene ID | 3090 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Hypermethylated in cancer 1 protein, Hic-1, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 29, HIC1, ZBTB29 |
| Target/Specificity | Ubiquitously expressed with highest levels found in lung, colon, prostate, thymus, testis and ovary. Expression is absent or decreased in many tumor cells. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |
| Name | HIC1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ZBTB29 |
| Function | Transcriptional repressor (PubMed:12052894, PubMed:15231840). Recognizes and binds to the consensus sequence '5- [CG]NG[CG]GGGCA[CA]CC-3' (PubMed:15231840). May act as a tumor suppressor (PubMed:20154726). Involved in development of head, face, limbs and ventral body wall (By similarity). Involved in down- regulation of SIRT1 and thereby is involved in regulation of p53/TP53- dependent apoptotic DNA-damage responses (PubMed:16269335). The specific target gene promoter association seems to be depend on corepressors, such as CTBP1 or CTBP2 and MTA1 (PubMed:12052894, PubMed:20547755). In cooperation with MTA1 (indicative for an association with the NuRD complex) represses transcription from CCND1/cyclin-D1 and CDKN1C/p57Kip2 specifically in quiescent cells (PubMed:20547755). Involved in regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway probably by association with TCF7L2 and preventing TCF7L2 and CTNNB1 association with promoters of TCF-responsive genes (PubMed:16724116). Seems to repress transcription from E2F1 and ATOH1 which involves ARID1A, indicative for the participation of a distinct SWI/SNF-type chromatin-remodeling complex (PubMed:18347096, PubMed:19486893). Probably represses transcription of ACKR3, FGFBP1 and EFNA1 (PubMed:16690027, PubMed:19525223, PubMed:20154726). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed with highest levels found in lung, colon, prostate, thymus, testis and ovary. Expression is absent or decreased in many tumor cells |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.