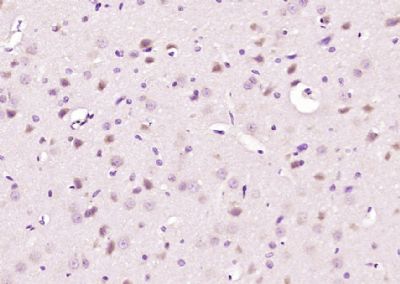
Nesprin 1 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q8NF91 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Dog, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 1010 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Nesprin 1 |
| Epitope Specificity | 51-150/8798 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Nucleus outer membrane. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere. The largest part of the protein is cytoplasmic, while its C-terminal part is associated with the nuclear envelope, most probably the outer nuclear membrane. In skeletal and smooth muscles, a significant amount is found in the sarcomeres. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the nesprin family. Contains 1 actin-binding domain. Contains 2 CH (calponin-homology) domains. Contains 12 HAT repeats. Contains 1 KASH domain. Contains 31 spectrin repeats. |
| DISEASE | Defects in SYNE1 are the cause of spinocerebellar ataxia autosomal recessive type 8 (SCAR8) [MIM:610743]; also known as autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia type 1 (ARCA1) or recessive ataxia of Beauce. Spinocerebellar ataxia is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of cerebellar disorders. Patients show progressive incoordination of gait and often poor coordination of hands, speech and eye movements, due to degeneration of the cerebellum with variable involvement of the brainstem and spinal cord. SCAR8 is an autosomal recessive form. Defects in SYNE1 are the cause of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy type 4 (EDMD4) [MIM:612998]. A degenerative myopathy characterized by weakness and atrophy of muscle without involvement of the nervous system, early contractures of the elbows, Achilles tendons and spine, and cardiomyopathy associated with cardiac conduction defects. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene encodes a spectrin repeat containing protein expressed in skeletal and smooth muscle, and peripheral blood lymphocytes, that localizes to the nuclear membrane. Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive spinocerebellar ataxia 8, also referred to as autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia type 1 or recessive ataxia of Beauce. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Gene ID | 23345 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Nesprin-1, Enaptin, KASH domain-containing protein 1, KASH1, Myocyte nuclear envelope protein 1, Myne-1, Nuclear envelope spectrin repeat protein 1, Synaptic nuclear envelope protein 1, Syne-1, SYNE1, C6orf98, KIAA0796, KIAA1262, KIAA1756, MYNE1 |
| Target/Specificity | Widely expressed. Highly expressed in skeletal and smooth muscles, heart, spleen, and peripheral blood leukocytes. |
| Dilution | IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4), 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |
| Name | SYNE1 (HGNC:17089) |
|---|---|
| Function | Multi-isomeric modular protein which forms a linking network between organelles and the actin cytoskeleton to maintain the subcellular spatial organization. As a component of the LINC (LInker of Nucleoskeleton and Cytoskeleton) complex involved in the connection between the nuclear lamina and the cytoskeleton. The nucleocytoplasmic interactions established by the LINC complex play an important role in the transmission of mechanical forces across the nuclear envelope and in nuclear movement and positioning. May be involved in nucleus- centrosome attachment and nuclear migration in neural progenitors implicating LINC complex association with SUN1/2 and probably association with cytoplasmic dynein-dynactin motor complexes; SYNE1 and SYNE2 may act redundantly. Required for centrosome migration to the apical cell surface during early ciliogenesis. May be involved in nuclear remodeling during sperm head formation in spermatogenesis; a probable SUN3:SYNE1/KASH1 LINC complex may tether spermatid nuclei to posterior cytoskeletal structures such as the manchette. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus outer membrane; Single-pass type IV membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side Nucleus. Nucleus envelope. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere. Note=The largest part of the protein is cytoplasmic, while its C-terminal part is associated with the nuclear envelope, most probably the outer nuclear membrane. In skeletal and smooth muscles, a significant amount is found in the sarcomeres. In myoblasts, relocalized from the nuclear envelope to the nucleus and cytoplasm during cell differentiation |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in HeLa, A431, A172 and HaCaT cells (at protein level). Widely expressed. Highly expressed in skeletal and smooth muscles, heart, spleen, peripheral blood leukocytes, pancreas, cerebellum, stomach, kidney and placenta. Isoform GSRP-56 is predominantly expressed in heart and skeletal muscle (at protein level). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.