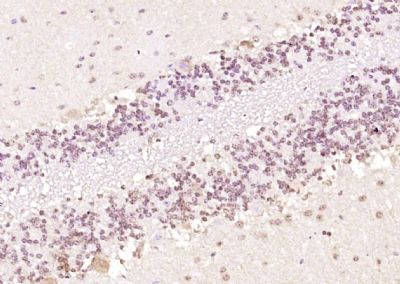
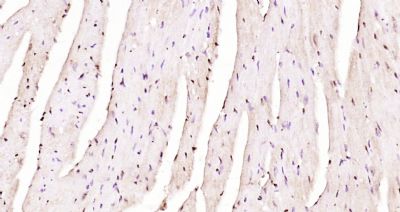
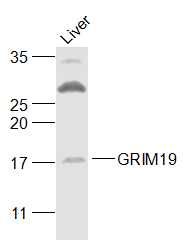
GRIM19 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9P0J0 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Pig |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 16 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human GRIM19 |
| Epitope Specificity | 51-144/144 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Mitochondrion inner membrane; Single-pass membrane protein; Matrix side. Nucleus. Note=May be translocated into the nucleus upon IFN/RA treatment. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the complex I NDUFA13 subunit family. |
| SUBUNIT | Complex I is composed of 45 different subunits. Interacts with CARD15, but not with CARD4. Interacts with STAT3, but not with STAT1, STAT2 and STAT5A. Interacts with HHV-8 IRF1, in the nucleus, with HPV-16 E6 and SV40 LT. Interacts with OLFM4. |
| DISEASE | Defects in NDUFA13 may be a cause of susceptibility to Hurthle cell thyroid carcinoma (HCTC) [MIM:607464]. Hurthle cell thyroid carcinoma accounts for approximately 3% of all thyroid cancers. Although they are classified as variants of follicular neoplasms, they are more often multifocal and somewhat more aggressive and are less likely to take up iodine than are other follicular neoplasms. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | A novel gene, Genes associated with Retinoid IFN induced Mortality (GRIM) GRIM19 gene was identified. Antisense expression of GRIM19 confers a strong resistance against IFN/RA induced death by reducing the intracellular levels of GRIM19 protein. Overexpression of GRIM19 enhances cell death in response to IFN/RA. GRIM19 is primarily a nuclear protein whose expression is induced by the IFN/RA combination. These data indicate that GRIM19 is a novel cell death regulatory molecule. |
| Gene ID | 51079 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 13, Cell death regulatory protein GRIM-19, Complex I-B16.6, CI-B16.6, Gene associated with retinoic and interferon-induced mortality 19 protein, GRIM-19, Gene associated with retinoic and IFN-induced mortality 19 protein, NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase B16.6 subunit, NDUFA13, GRIM19 |
| Target/Specificity | Widely expressed, with highest expression in heart, skeletal muscle, liver, kidney and placenta. In intestinal mucosa, down-regulated in areas involved in Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:25,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |
| Name | NDUFA13 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | GRIM19 |
| Function | Accessory subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), that is believed not to be involved in catalysis (PubMed:27626371). Complex I functions in the transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme is believed to be ubiquinone (PubMed:27626371). Involved in the interferon/all-trans-retinoic acid (IFN/RA) induced cell death. This apoptotic activity is inhibited by interaction with viral IRF1. Prevents the transactivation of STAT3 target genes. May play a role in CARD15-mediated innate mucosal responses and serve to regulate intestinal epithelial cell responses to microbes (PubMed:15753091). |
| Cellular Location | Mitochondrion inner membrane; Single-pass membrane protein; Matrix side. Nucleus Note=Localizes mainly in the mitochondrion (PubMed:12628925). May be translocated into the nucleus upon IFN/RA treatment |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed, with highest expression in heart, skeletal muscle, liver, kidney and placenta. In intestinal mucosa, down-regulated in areas involved in Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.