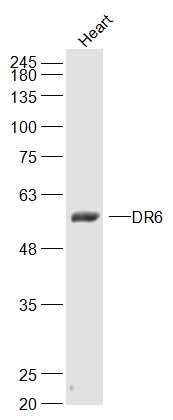
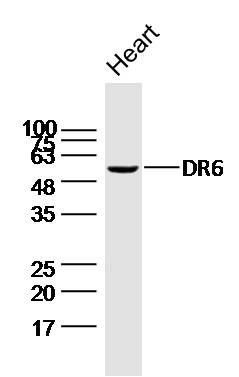
DR6 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 1
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O75509 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Dog, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 52/68 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human DR6/CD358 |
| Epitope Specificity | 101-200/655 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein (Probable). |
| SIMILARITY | Contains 1 death domain. Contains 4 TNFR-Cys repeats. |
| SUBUNIT | Associates with TRADD. Interacts with N-APP (By similarity). |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | May activate NF-kappa-B and promote apoptosis. May activate JNK and be involved in T-cell differentiation. Required for both normal cell body death and axonal pruning. Trophic-factor deprivation triggers the cleavage of surface APP by beta-secretase to release sAPP-beta which is further cleaved to release an N-terminal fragment of APP (N-APP). N-APP binds TNFRSF21 triggering caspase activation and degeneration of both neuronal cell bodies (via caspase-3) and axons (via caspase-6). Tissue specificity: Highly expressed in heart, brain, placenta, pancreas, lymph node, thymus and prostate. Detected at lower levels in lung, skeletal muscle, kidney, testis, uterus, small intestine, colon, spleen, bone marrow and fetal liver. Very low levels were found in adult liver and peripheral blood leukocytes. |
| Gene ID | 27242 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 21, Death receptor 6, CD358, TNFRSF21, DR6 |
| Target/Specificity | Highly expressed in heart, brain, placenta, pancreas, lymph node, thymus and prostate. Detected at lower levels in lung, skeletal muscle, kidney, testis, uterus, small intestine, colon, spleen, bone marrow and fetal liver. Very low levels were found in adult liver and peripheral blood leukocytes. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |
| Name | TNFRSF21 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DR6 |
| Function | Promotes apoptosis, possibly via a pathway that involves the activation of NF-kappa-B. Can also promote apoptosis mediated by BAX and by the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm. Trophic-factor deprivation triggers the cleavage of surface APP by beta-secretase to release sAPP-beta which is further cleaved to release an N-terminal fragment of APP (N-APP). Negatively regulates oligodendrocyte survival, maturation and myelination. Plays a role in signaling cascades triggered by stimulation of T-cell receptors, in the adaptive immune response and in the regulation of T-cell differentiation and proliferation. Negatively regulates T-cell responses and the release of cytokines such as IL4, IL5, IL10, IL13 and IFNG by Th2 cells. Negatively regulates the production of IgG, IgM and IgM in response to antigens. May inhibit the activation of JNK in response to T-cell stimulation. Also acts as a regulator of pyroptosis: recruits CASP8 in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS) and subsequent oxidation, leading to activation of GSDMC (PubMed:34012073). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein Note=Endocytosed following oxidation in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS). |
| Tissue Location | Detected in fetal spinal cord and in brain neurons, with higher levels in brain from Alzheimer disease patients (at protein level). Highly expressed in heart, brain, placenta, pancreas, lymph node, thymus and prostate. Detected at lower levels in lung, skeletal muscle, kidney, testis, uterus, small intestine, colon, spleen, bone marrow and fetal liver. Very low levels were found in adult liver and peripheral blood leukocytes. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.