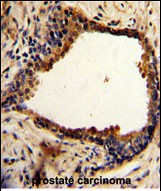
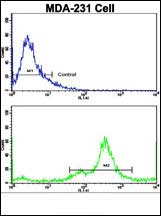
NDRG1 Antibody (N-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 2
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| FC, IHC-P, WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q92597 |
| Other Accession | Q6JE36, Q62433, Q4R4Q3, Q3SYX0 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Bovine, Monkey, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 42835 Da |
| Antigen Region | 12-40 aa |
| Gene ID | 10397 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Protein NDRG1, Differentiation-related gene 1 protein, DRG-1, N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 protein, Nickel-specific induction protein Cap43, Reducing agents and tunicamycin-responsive protein, RTP, Rit42, NDRG1, CAP43, DRG1, RTP |
| Target/Specificity | This NDRG1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 12-40 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human NDRG1. |
| Dilution | FC~~1:10~50 IHC-P~~1:50~100 WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | NDRG1 Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | NDRG1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CAP43, DRG1, RTP |
| Function | Stress-responsive protein involved in hormone responses, cell growth, and differentiation. Acts as a tumor suppressor in many cell types. Necessary but not sufficient for p53/TP53-mediated caspase activation and apoptosis. Has a role in cell trafficking, notably of the Schwann cell, and is necessary for the maintenance and development of the peripheral nerve myelin sheath. Required for vesicular recycling of CDH1 and TF. May also function in lipid trafficking. Protects cells from spindle disruption damage. Functions in p53/TP53-dependent mitotic spindle checkpoint. Regulates microtubule dynamics and maintains euploidy. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Nucleus. Cell membrane Note=Mainly cytoplasmic but differentially localized to other regions Associates with the plasma membrane in intestinal epithelia and lactating mammary gland. Translocated to the nucleus in a p53/TP53- dependent manner. In prostate epithelium and placental chorion, located in both the cytoplasm and in the nucleus. No nuclear localization in colon epithelium cells. In intestinal mucosa, prostate and renal cortex, located predominantly adjacent to adherens junctions Cytoplasmic with granular staining in proximal tubular cells of the kidney and salivary gland ducts. Recruits to the membrane of recycling/sorting and late endosomes via binding to phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. Associates with microtubules Colocalizes with TUBG1 in the centrosome. Cytoplasmic location increased with hypoxia. Phosphorylated form found associated with centromeres during S-phase of mitosis and with the plasma membrane |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitous; expressed most prominently in placental membranes and prostate, kidney, small intestine, and ovary tissues Also expressed in heart, brain, skeletal muscle, lung, liver and pancreas. Low levels in peripheral blood leukocytes and in tissues of the immune system. Expressed mainly in epithelial cells. Also found in Schwann cells of peripheral neurons. Reduced expression in adenocarcinomas compared to normal tissues. In colon, prostate and placental membranes, the cells that border the lumen show the highest expression. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
NDRG1 is a cytoplasmic protein involved in stress responses, hormone responses, cell growth, and differentiation. It is necessary for p53-mediated caspase activation and apoptosis.
References
Sugiyama,N., et.al., Mol. Cell Proteomics 6 (6), 1103-1109 (2007)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.