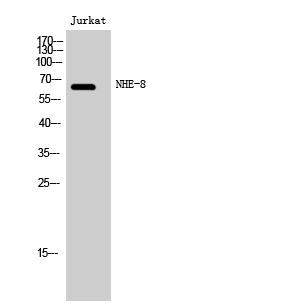
NHE-8 Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9Y2E8 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 65422 Da |
| Gene ID | 23315 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | SLC9A8; KIAA0939; NHE8; Sodium/hydrogen exchanger 8; Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 8; NHE-8; Solute carrier family 9 member 8 |
| Dilution | WB~~Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000.IHC-p:1:50-300 ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. IHC-P~~N/A |
| Format | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. |
| Storage Conditions | -20℃ |
| Name | SLC9A8 (HGNC:20728) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | KIAA0939, NHE8 |
| Function | Na(+)/H(+) antiporter. Mediates the electoneutral exchange of intracellular H(+) ions for extracellular Na(+) in 1:1 stoichiometry (PubMed:15522866). Acts as an Na(+)/H(+) exchanger in the trans-Golgi. Contributes to the regulation of pH regulation of Golgi apparatus, and consequently, in protein trafficking and endosomal morphology (PubMed:15522866, PubMed:20719963). In germ cells, plays a crucial role in acrosome biogenesis and sperm development, probably by playing a role in the fusion of the Golgi-derived vesicles that form the acrosomal cap (By similarity). Can also be active at the cell surface of specialized cells. In the small intestine, at the cell membrane, plays a major physiological role in transepithelial absorption of Na(+) and regulates intracellular pH homeostasis of intestinal epithelial cells (PubMed:34288721). Acts as an important regulator of mucosal integrity in the intestine and in the stomach, could mediate the pH fluctuation necessary for mucin exocytosis or assist membrane trafficking of other proteins (By similarity). Plays a role in photoreceptor survival and in the maintenance of intracellular pH homeostasis in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE cells) (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Golgi apparatus membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endosome, multivesicular body membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Apical cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, acrosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R4D1} Note=Intracellular versus plasma membrane-resident location may vary with cell type. Mainly localized to the mid- to trans-Golgi compartments but a proportion is also localized to multivesicular bodies (PubMed:15522866, PubMed:20719963). Localized at the apical membrane of polarized gastrointestinal epithelial cells (By similarity). Recruitment to the plasma membrane upon acid stimulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q4L208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15522866, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20719963} |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitous. Strongly expressed in skeletal muscle and kidney (PubMed:15522866). Detected throughout the entire gastrointestinal tract, with high expression detected in stomach, duodenum and ascending colon (PubMed:18209477) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Involved in pH regulation to eliminate acids generated by active metabolism or to counter adverse environmental conditions. Major proton extruding system driven by the inward sodium ion chemical gradient. Plays an important role in signal transduction.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.