Cryopyrin Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

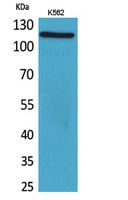
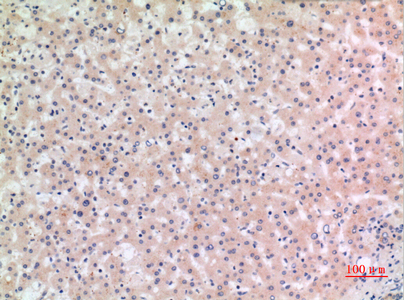
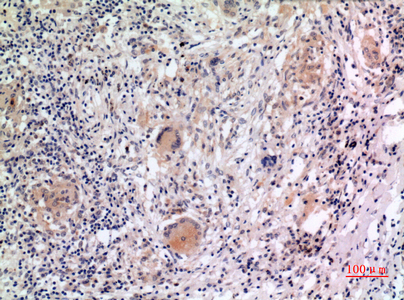
Application
| WB, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q96P20 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 118173 Da |
| Gene ID | 114548 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | NLRP3; C1orf7; CIAS1; NALP3; PYPAF1; NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3; Angiotensin/vasopressin receptor AII/AVP-like; Caterpiller protein 1.1CLR1.1; Cold autoinflammatory syndrome 1 protein; Cryopyrin; PYRIN-containing APAF1-like protein 1 |
| Dilution | WB~~Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. IHC-p: 1/100-1/300. ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. IHC-P~~N/A |
| Format | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. |
| Storage Conditions | -20℃ |
| Name | NLRP3 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:17907925, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:16400} |
|---|---|
| Function | Sensor component of the NLRP3 inflammasome, which mediates inflammasome activation in response to defects in membrane integrity, leading to secretion of inflammatory cytokines IL1B and IL18 and pyroptosis (PubMed:16407889, PubMed:18403674, PubMed:18604214, PubMed:23582325, PubMed:25686105, PubMed:27929086, PubMed:28656979, PubMed:28847925, PubMed:30487600, PubMed:30612879, PubMed:31086327, PubMed:31086329, PubMed:31189953, PubMed:33231615, PubMed:34133077, PubMed:34341353, PubMed:34512673, PubMed:36442502). In response to pathogens and other damage-associated signals that affect the integrity of membranes, initiates the formation of the inflammasome polymeric complex composed of NLRP3, CASP1 and PYCARD/ASC (PubMed:16407889, PubMed:18403674, PubMed:27432880, PubMed:28847925, PubMed:31189953, PubMed:33231615, PubMed:34133077, PubMed:34341353, PubMed:36142182, PubMed:36442502). Recruitment of pro-caspase-1 (proCASP1) to the NLRP3 inflammasome promotes caspase-1 (CASP1) activation, which subsequently cleaves and activates inflammatory cytokines IL1B and IL18 and gasdermin-D (GSDMD), promoting cytokine secretion and pyroptosis (PubMed:23582325, PubMed:28847925, PubMed:31189953, PubMed:33231615, PubMed:34133077, PubMed:34341353). Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome is also required for HMGB1 secretion; stimulating inflammatory responses (PubMed:22801494). Under resting conditions, ADP-bound NLRP3 is autoinhibited (PubMed:35114687). NLRP3 activation stimuli include extracellular ATP, nigericin, reactive oxygen species, crystals of monosodium urate or cholesterol, amyloid-beta fibers, environmental or industrial particles and nanoparticles, such as asbestos, silica, aluminum salts, cytosolic dsRNA, etc (PubMed:16407889, PubMed:18403674, PubMed:18604214, PubMed:19414800, PubMed:23871209). Almost all stimuli trigger intracellular K(+) efflux (By similarity). These stimuli lead to membrane perturbation and activation of NLRP3 (By similarity). Upon activation, NLRP3 is transported to microtubule organizing center (MTOC), where it is unlocked by NEK7, leading to its relocalization to dispersed trans-Golgi network (dTGN) vesicle membranes and formation of an active inflammasome complex (PubMed:36442502, PubMed:39173637). Associates with dTGN vesicle membranes by binding to phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) (PubMed:30487600, PubMed:34554188). Shows ATPase activity (PubMed:17483456). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Inflammasome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center. Golgi apparatus membrane. Endoplasmic reticulum {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R4B8}. Mitochondrion. Secreted. Nucleus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R4B8} Note=In macrophages, under resting conditions, mainly located in the cytosol and on membranes of various organelles, such as endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and Golgi: forms an inactive double-ring cage that is primarily localized on membranes (By similarity). Upon activation, NLRP3 is transported to microtubule organizing center (MTOC), where it is unlocked by NEK7, leading to its relocalization to dispersed trans-Golgi network (dTGN) vesicle membranes for the formation of an active inflammasome complex (PubMed:39173637) Recruited to dTGN vesicle membranes by binding to phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) (PubMed:30487600). After the induction of pyroptosis, inflammasome specks are released into the extracellular space where they can further promote IL1B processing and where they can be engulfed by macrophages (PubMed:24952504). Phagocytosis induces lysosomal damage and inflammasome activation in the recipient cells (PubMed:24952504). In the Th2 subset of CD4(+) helper T-cells, mainly located in the nucleus (By similarity). Nuclear localization depends upon KPNA2 (By similarity). In the Th1 subset of CD4(+) helper T-cells, mainly cytoplasmic (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R4B8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24952504, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30487600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:39173637} |
| Tissue Location | Predominantly expressed in macrophages (PubMed:33231615, PubMed:34133077). Also expressed in dendritic cells, B- and T-cells (at protein level) (PubMed:11786556, PubMed:17164409) Expressed in LPS-treated granulocytes, but not in resting cells (at protein level) (PubMed:17164409). Expression in monocytes is very weak (at protein level) (PubMed:17164409). Expressed in stratified non- keratinizing squamous epithelium, including oral, esophageal and ectocervical mucosa and in the Hassall's corpuscles in the thymus Also, detected in the stratified epithelium covering the bladder and ureter (transitional mucosa) (at protein level) (PubMed:17164409) Expressed in lung epithelial cells (at protein level) (PubMed:23229815). Expressed in chondrocytes (PubMed:12032915) Expressed at low levels in resting osteoblasts (PubMed:17907925) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
As the sensor component of the NLRP3 inflammasome, plays a crucial role in innate immunity and inflammation. In response to pathogens and other damage-associated signals, initiates the formation of the inflammasome polymeric complex, made of NLRP3, PYCARD and CASP1 (and possibly CASP4 and CASP5). Recruitment of proCASP1 to the inflammasome promotes its activation and CASP1- catalyzed IL1B and IL18 maturation and secretion in the extracellular milieu (PubMed:28847925). Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome is also required for HMGB1 secretion (PubMed:22801494). The active cytokines and HMGB1 stimulate inflammatory responses. Inflammasomes can also induce pyroptosis, an inflammatory form of programmed cell death. Under resting conditions, NLRP3 is autoinhibited. NLRP3 activation stimuli include extracellular ATP, reactive oxygen species, K(+) efflux, crystals of monosodium urate or cholesterol, amyloid-beta fibers, environmental or industrial particles and nanoparticles, cytosolic dsRNA, etc. However, it is unclear what constitutes the direct NLRP3 activator. Activation in presence of cytosolic dsRNA is mediated by DHX33 (PubMed:23871209). Independently of inflammasome activation, regulates the differentiation of T helper 2 (Th2) cells and has a role in Th2 cell-dependent asthma and tumor growth (By similarity). During Th2 differentiation, required for optimal IRF4 binding to IL4 promoter and for IRF4-dependent IL4 transcription. Binds to the consensus DNA sequence 5'-GRRGGNRGAG- 3'. May also participate in the transcription of IL5, IL13, GATA3, CCR3, CCR4 and MAF (By similarity).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.