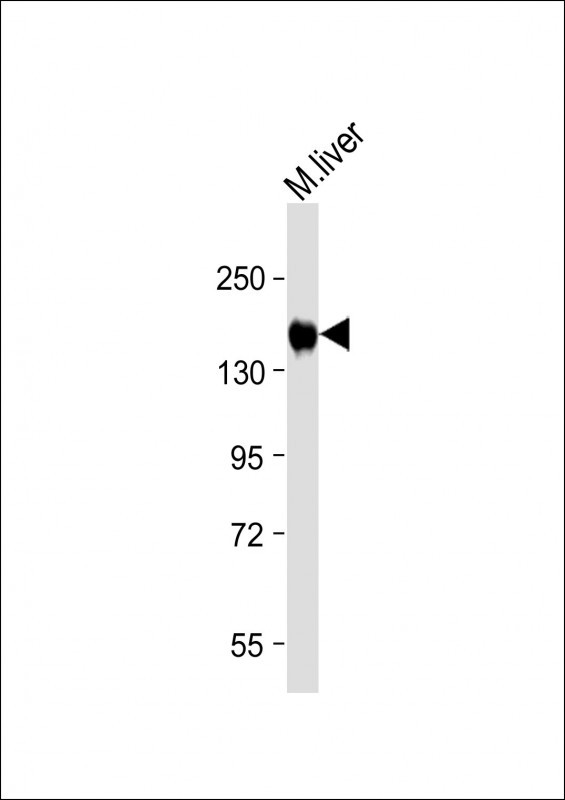
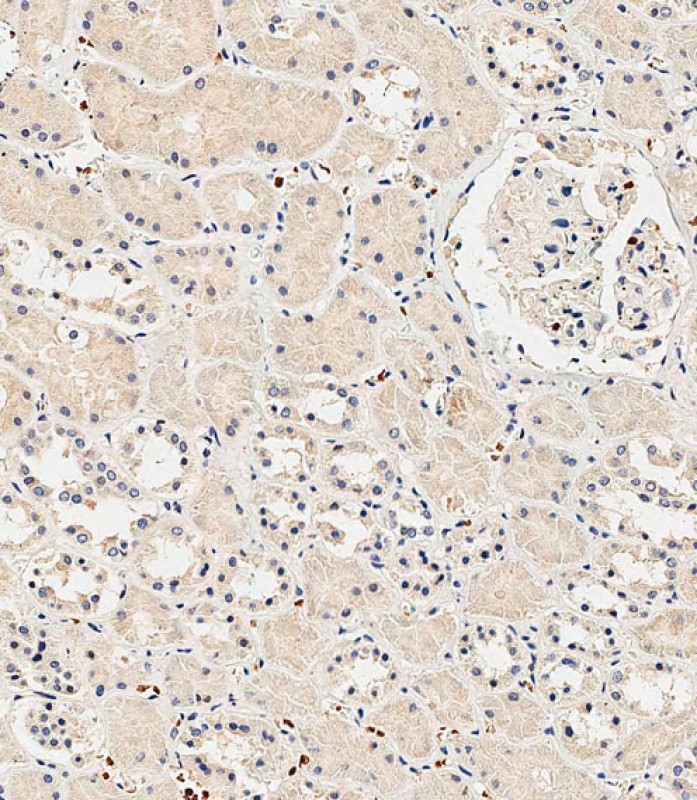
INSR(Insulin Receptor) Antibody (N-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 1
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IHC-P-Leica, WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P06213 |
| Other Accession | P15127, P15208 |
| Reactivity | Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 156333 Da |
| Antigen Region | 28-57 aa |
| Gene ID | 3643 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Insulin receptor, IR, CD220, Insulin receptor subunit alpha, Insulin receptor subunit beta, INSR |
| Target/Specificity | This INSR(Insulin Receptor) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 28-57 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human INSR(Insulin Receptor). |
| Dilution | IHC-P-Leica~~1:500 WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | INSR(Insulin Receptor) Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | INSR |
|---|---|
| Function | Receptor tyrosine kinase which mediates the pleiotropic actions of insulin. Binding of insulin leads to phosphorylation of several intracellular substrates, including, insulin receptor substrates (IRS1, 2, 3, 4), SHC, GAB1, CBL and other signaling intermediates. Each of these phosphorylated proteins serve as docking proteins for other signaling proteins that contain Src-homology-2 domains (SH2 domain) that specifically recognize different phosphotyrosine residues, including the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K and SHP2. Phosphorylation of IRSs proteins lead to the activation of two main signaling pathways: the PI3K-AKT/PKB pathway, which is responsible for most of the metabolic actions of insulin, and the Ras- MAPK pathway, which regulates expression of some genes and cooperates with the PI3K pathway to control cell growth and differentiation. Binding of the SH2 domains of PI3K to phosphotyrosines on IRS1 leads to the activation of PI3K and the generation of phosphatidylinositol-(3, 4, 5)-triphosphate (PIP3), a lipid second messenger, which activates several PIP3-dependent serine/threonine kinases, such as PDPK1 and subsequently AKT/PKB. The net effect of this pathway is to produce a translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 from cytoplasmic vesicles to the cell membrane to facilitate glucose transport. Moreover, upon insulin stimulation, activated AKT/PKB is responsible for: anti-apoptotic effect of insulin by inducing phosphorylation of BAD; regulates the expression of gluconeogenic and lipogenic enzymes by controlling the activity of the winged helix or forkhead (FOX) class of transcription factors. Another pathway regulated by PI3K-AKT/PKB activation is mTORC1 signaling pathway which regulates cell growth and metabolism and integrates signals from insulin. AKT mediates insulin- stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 thereby activating mTORC1 pathway. The Ras/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK pathway is mainly involved in mediating cell growth, survival and cellular differentiation of insulin. Phosphorylated IRS1 recruits GRB2/SOS complex, which triggers the activation of the Ras/RAF/MAP2K/MAPK pathway. In addition to binding insulin, the insulin receptor can bind insulin-like growth factors (IGFI and IGFII). Isoform Short has a higher affinity for IGFII binding. When present in a hybrid receptor with IGF1R, binds IGF1. PubMed:12138094 shows that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Long are activated with a high affinity by IGF1, with low affinity by IGF2 and not significantly activated by insulin, and that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Short are activated by IGF1, IGF2 and insulin. In contrast, PubMed:16831875 shows that hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Long and hybrid receptors composed of IGF1R and INSR isoform Short have similar binding characteristics, both bind IGF1 and have a low affinity for insulin. In adipocytes, inhibits lipolysis (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15208}; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Late endosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15208}. Lysosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15208}. Note=Binding of insulin to INSR induces internalization and lysosomal degradation of the receptor, a means for down-regulating this signaling pathway after stimulation. In the presence of SORL1, internalized INSR molecules are redirected back to the cell surface, thereby preventing their lysosomal catabolism and strengthening insulin signal reception. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15208} |
| Tissue Location | Isoform Long and isoform Short are predominantly expressed in tissue targets of insulin metabolic effects: liver, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle but are also expressed in the peripheral nerve, kidney, pulmonary alveoli, pancreatic acini, placenta vascular endothelium, fibroblasts, monocytes, granulocytes, erythrocytes and skin. Isoform Short is preferentially expressed in fetal cells such as fetal fibroblasts, muscle, liver and kidney. Found as a hybrid receptor with IGF1R in muscle, heart, kidney, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, hepatoma, fibroblasts, spleen and placenta (at protein level). Overexpressed in several tumors, including breast, colon, lung, ovary, and thyroid carcinomas |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
INSR is a receptor that binds insulin and has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. Autophosphorylation activates the kinase activity. This Type I mebrane protein is composed of a tetramer of 2 alpha and 2 beta chains linked by disulfide bonds. The alpha chains contribute to the formation of the ligand-binding domain, while the beta chains carry the kinase domain. After being transported from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus, the single glycosylated precursor is further glycosylated and then cleaved, followed by its transport to the plasma membrane. Defects in INSR are the cause of insulin resistance of various forms, including mild insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus with acanthosis nigricans, minor physical abnormalities and sometimes polycystic ovaries. Insulin resistance associated with acanthosis nigricans, hirsutism and hyperandrogenism is referred to as insulin resistance type A. Defects in INSR are the cause of Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome, also known as Mendenhall syndrome. It is a severe insulin resistance syndrome characterized by insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus with pineal hyperplasia and somatic abnormalities. Typical features include coarse, senile-appearing facies, dental and skin abnormalities, abdominal distension, and phallic enlargement. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. Defects in INSR are the cause of leprechaunism, also known as Donohue syndrome. Leprechaunism represents the most severe form of insulin resistance syndrome, characterized by intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation and death in early infancy. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. Defects in INSR may be associated with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
References
George, S., et al., Endocrinology 144(2):631-637 (2003).
Longo, N., et al., Hum. Mol. Genet. 11(12):1465-1475 (2002).
Hamer, I., et al., Diabetologia 45(5):657-667 (2002).
Osawa, H., et al., Clin. Genet. 59(3):194-197 (2001).
Rique, S., et al., Clin. Genet. 57(1):67-69 (2000).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.