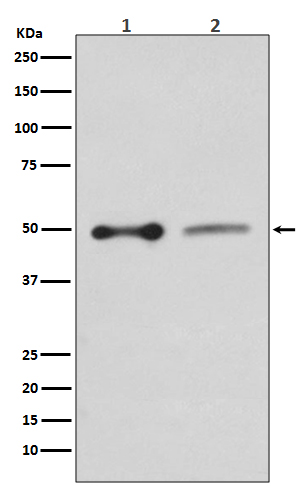
EBP50 Antibody
Rabbit mAb
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O14745 |
| Reactivity | Rat |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Other Names | SLC9A3R1; EBP50; NPHLOP2; NHERF; NHERF-1; NHERF1; |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Calculated MW | 38868 Da |
| Dilution | WB 1:500~1:2000 IHC 1:50~1:200 |
|---|---|
| Purification | Affinity-chromatography |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human EBP50 |
| Description | Scaffold protein that connects plasma membrane proteins with members of the ezrin/moesin/radixin family and thereby helps to link them to the actin cytoskeleton and to regulate their surface expression. Necessary for recycling of internalized ADRB2. Was first known to play a role in the regulation of the activity and subcellular location of SLC9A3. Necessary for cAMP-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of SLC9A3. |
| Storage Condition and Buffer | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. |
| Name | NHERF1 (HGNC:11075) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | NHERF, SLC9A3R1 |
| Function | Scaffold protein that connects plasma membrane proteins with members of the ezrin/moesin/radixin family and thereby helps to link them to the actin cytoskeleton and to regulate their surface expression. Necessary for recycling of internalized ADRB2. Was first known to play a role in the regulation of the activity and subcellular location of SLC9A3. Necessary for cAMP-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of SLC9A3. May enhance Wnt signaling. May participate in HTR4 targeting to microvilli (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of phosphate reabsorption in the renal proximal tubules. Involved in sperm capacitation. May participate in the regulation of the chloride and bicarbonate homeostasis in spermatozoa. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Apical cell membrane. Endomembrane system; Peripheral membrane protein. Cell projection, filopodium. Cell projection, ruffle. Cell projection, microvillus. Note=Translocates from the cytoplasm to the apical cell membrane in a PODXL-dependent manner. Colocalizes with CFTR at the midpiece of sperm tail (By similarity). Colocalizes with actin in microvilli-rich apical regions of the syncytiotrophoblast. Found in microvilli, ruffling membrane and filopodia of HeLa cells. Present in lipid rafts of T-cells. |
| Tissue Location | Detected in liver, kidney, pancreas, prostate, spleen, small intestine and placenta, in particular in the syncytiotrophoblast. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.