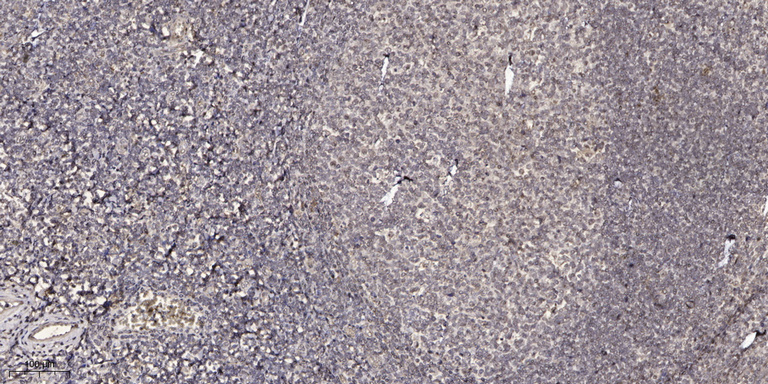
CJ099 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
CJ099 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| IHC, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q6UWK7 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Human |
| Host | Polyclonal, Rabbit,IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 9173 Da |
| Gene ID | 387695 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Protein GPR15LG, Antimicrobial peptide with 57 amino acid residues, AP-57, Antimicrobial peptide-57, Colon-derived SUSD2 binding factor, CSBF, Protein GPR15 ligand {ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:31428}, Protein GPR15L, Secreted protein C10orf99, GPR15LG (HGNC:31428), C10orf99, GPR15L |
| Dilution | IHC~~1:100~500 IF~~1:50~200 |
| Storage Conditions | -20℃ |
| Name | GPR15LG (HGNC:31428) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | C10orf99, GPR15L |
| Function | Highly cationic protein that has multiple functions. Acts as a chemotactic factor that mediates lymphocytes recruitment to epithelia through binding and activation of the G-protein coupled receptor GPR15 (PubMed:28900043, PubMed:28936214). May be a tumor suppressor; together with SUSD2 has a growth inhibitory effect on colon cancer cells which includes G1 cell cycle arrest (PubMed:25351403). May regulate keratinocyte proliferation (PubMed:29872130). In addition, through activation of Mas-related G protein-coupled receptors (MRGPRs) contributes to pruritogenesis by activating itch-selective sensory neurons and mast cells degranulation (PubMed:35704588). |
| Cellular Location | Secreted |
| Tissue Location | Expressed at high levels in colon, and cervix and at moderate level in tonsil (PubMed:25585381, PubMed:28900043). Highly reduced expression in primary colon cancer tissues compared with that in adjacent tissues (PubMed:25351403). Highest levels of expression detected in stomach and colon; expressed in epithelium of skin and esophagus, and in some tumor and/or tumor adjacent tissues (TAT), including TAT of esophagus cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) tissues (at protein level) (PubMed:25585381) Highly expressed by inflammatory differentiated keratinocytese (PubMed:35704588). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.