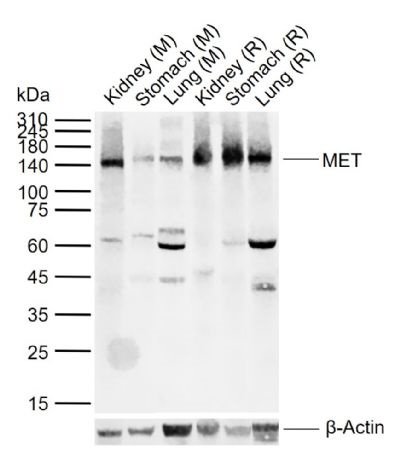
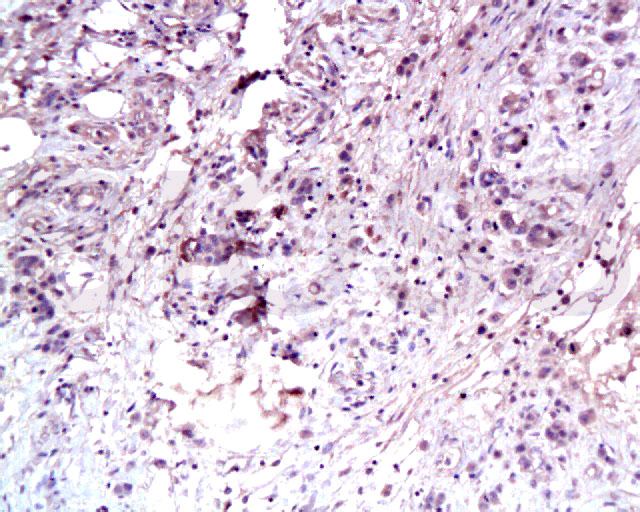
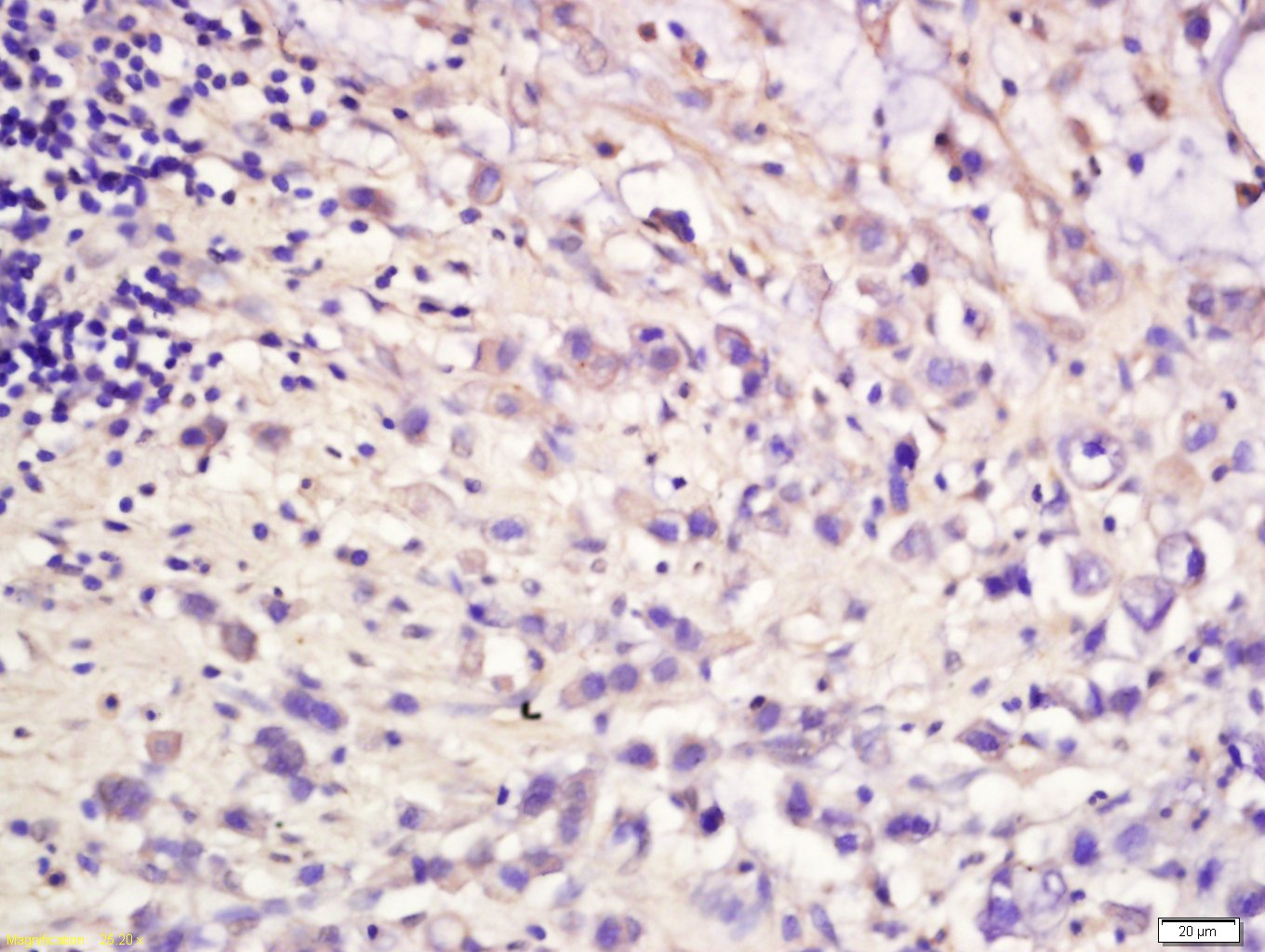
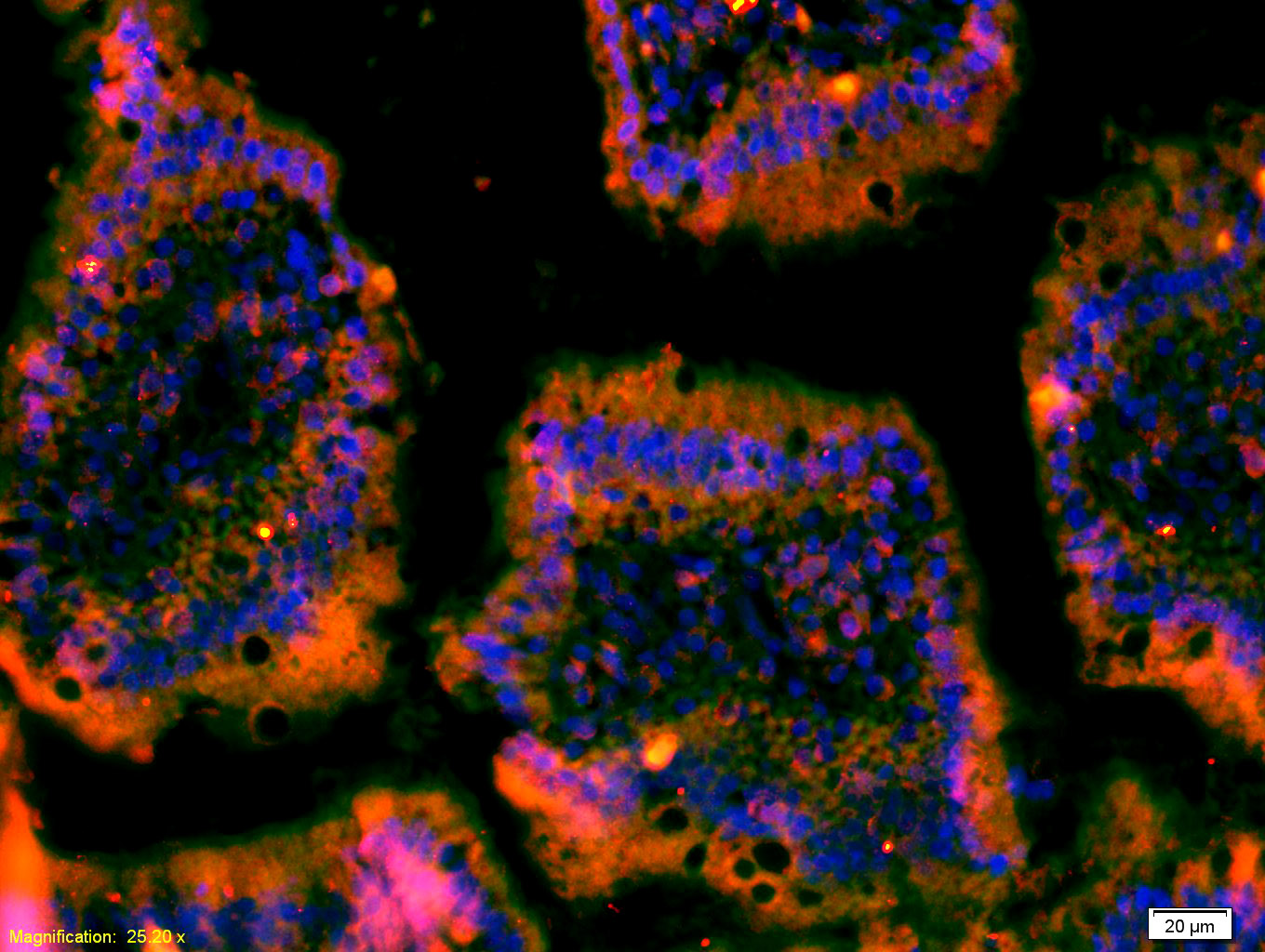
MET Rabbit pAb
MET Rabbit pAb
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P16056 |
| Reactivity | Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 33/123/156 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from mouse MET |
| Epitope Specificity | 621-720/1379 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.Isoform 3: Secreted. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. Contains 3 IPT/TIG domains. Contains 1 protein kinase domain. Contains 1 Sema domain. |
| SUBUNIT | Heterodimer made of an alpha chain (50 kDa) and a beta chain (145 kDa) which are disulfide linked. Binds PLXNB1. Interacts when phosphorylated with downstream effectors including STAT3, PIK3R1, SRC, PCLG1, GRB2 and GAB1. Interacts with SPSB1, SPSB2 and SPSB4 (By similarity). Interacts with INPP5D/SHIP1. When phosphorylated at Tyr-1356, interacts with INPPL1/SHIP2. Interacts with RANBP9 and RANBP10, as well as SPSB1, SPSB2, SPSB3 and SPSB4. SPSB1 binding occurs in the presence and in the absence of HGF, however HGF treatment has a positive effect on this interaction. Interacts with MUC20; prevents interaction with GRB2 and suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell proliferation. Interacts with GRB10. |
| Post-translational modifications | Autophosphorylated in response to ligand binding on Tyr-1234 and Tyr-1235 in the kinase domain leading to further phosphorylation of Tyr-1349 and Tyr-1356 in the C-terminal multifunctional docking site.Dephosphorylated by PTPRJ at Tyr-1349 and Tyr-1365.Ubiquitinated. Ubiquitination by CBL regulates the receptor stability and activity through proteasomal degradation. |
| DISEASE | Note=Activation of MET after rearrangement with the TPR gene produces an oncogenic protein.Note=Defects in MET may be associated with gastric cancer.Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [MIM:114550]: A primary malignant neoplasm of epithelial liver cells. The major risk factors for HCC are chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, prolonged dietary aflatoxin exposure, alcoholic cirrhosis, and cirrhosis due to other causes. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.Renal cell carcinoma papillary (RCCP) [MIM:605074]: A subtype of renal cell carcinoma tending to show a tubulo-papillary architecture formed by numerous, irregular, finger-like projections of connective tissue. Renal cell carcinoma is a heterogeneous group of sporadic or hereditary carcinoma derived from cells of the proximal renal tubular epithelium. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.Note=A common allele in the promoter region of the MET shows genetic association with susceptibility to autism in some families. Functional assays indicate a decrease in MET promoter activity and altered binding of specific transcription factor complexes.Note=MET activating mutations may be involved in the development of a highly malignant, metastatic syndrome known as cancer of unknown primary origin (CUP) or primary occult malignancy. Systemic neoplastic spread is generally a late event in cancer progression. However, in some instances, distant dissemination arises at a very early stage, so that metastases reach clinical relevance before primary lesions. Sometimes, the primary lesions cannot be identified in spite of the progresses in the diagnosis of malignancies. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene encodes a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase family of proteins and the product of the proto-oncogene MET. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate alpha and beta subunits that are linked via disulfide bonds to form the mature receptor. Further processing of the beta subunit results in the formation of the M10 peptide, which has been shown to reduce lung fibrosis. Binding of its ligand, hepatocyte growth factor, induces dimerization and activation of the receptor, which plays a role in cellular survival, embryogenesis, and cellular migration and invasion. Mutations in this gene are associated with papillary renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and various head and neck cancers. Amplification and overexpression of this gene are also associated with multiple human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, May 2016] |
| Other Names | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor, HGF receptor, 2.7.10.1, HGF/SF receptor, Proto-oncogene c-Met, Scatter factor receptor, SF receptor, Tyrosine-protein kinase Met, Met |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | Expressed in normal hepatocytes as well as in epithelial cells lining the stomach, the small and the large intestine. Found also in basal keratinocytes of esophagus and skin. High levels are found in liver, gastrointestinal tract, thyroid and kidney. Also present in the brain. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4), 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 ℃. |
| Name | Met |
|---|---|
| Function | Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis and survival. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces autophosphorylation of MET on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. Following activation by ligand, interacts with the PI3-kinase subunit PIK3R1, PLCG1, SRC, GRB2, STAT3 or the adapter GAB1. Recruitment of these downstream effectors by MET leads to the activation of several signaling cascades including the RAS-ERK, PI3 kinase-AKT, or PLCgamma-PKC. The RAS-ERK activation is associated with the morphogenetic effects while PI3K/AKT coordinates prosurvival effects. During embryonic development, MET signaling plays a role in gastrulation, development and migration of neuronal precursors, angiogenesis and kidney formation. During skeletal muscle development, it is crucial for the migration of muscle progenitor cells and for the proliferation of secondary myoblasts (PubMed:30777867). In adults, participates in wound healing as well as organ regeneration and tissue remodeling. Also promotes differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic cells (By similarity). May regulate cortical bone osteogenesis (PubMed:26637977). |
| Cellular Location | Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.