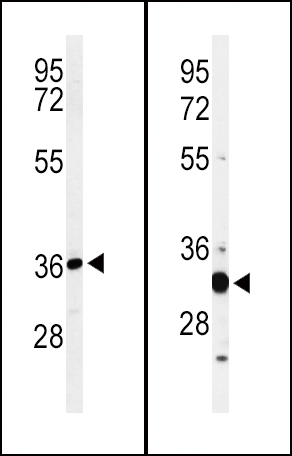
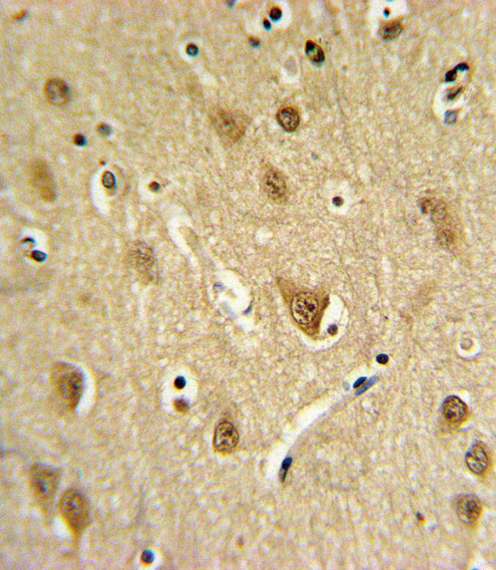
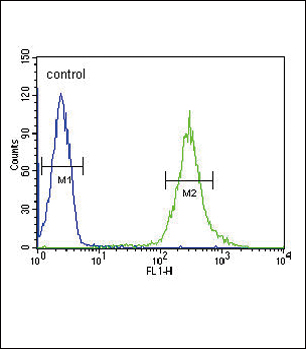
ST8SIA4 Antibody (Center)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 1
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| FC, IHC-P, WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q92187 |
| Other Accession | Q64692, Q6ZXC9 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Predicted | Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 41295 Da |
| Antigen Region | 186-214 aa |
| Gene ID | 7903 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CMP-N-acetylneuraminate-poly-alpha-2, 8-sialyltransferase, 2499-, Alpha-2, 8-sialyltransferase 8D, Polysialyltransferase-1, Sialyltransferase 8D, SIAT8-D, Sialyltransferase St8Sia IV, ST8SiaIV, ST8SIA4, PST, PST1, SIAT8D |
| Target/Specificity | This ST8SIA4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 186-214 amino acids from the Central region of human ST8SIA4. |
| Dilution | FC~~1:10~50 IHC-P~~1:10~50 WB~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | ST8SIA4 Antibody (Center) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ST8SIA4 (HGNC:10871) |
|---|---|
| Function | Catalyzes the transfer of a sialic acid from a CMP-linked sialic acid donor onto a terminal alpha-2,3-, alpha-2,6-, or alpha-2,8- linked sialic acid of an N-linked glycan protein acceptor through alpha-2,8-linkages (PubMed:10766765, PubMed:11279095, PubMed:28810663, PubMed:9774483). Therefore, participates in polysialic acid synthesis on various sialylated N-acetyllactosaminyl oligosaccharides, including NCAM1 N-glycans, FETUB N-glycans and AHSG (PubMed:10766765, PubMed:11279095, PubMed:28810663, PubMed:9774483). It is noteworthy that alpha-2,3-linked sialic acid is apparently a better acceptor than alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid (PubMed:9774483). |
| Cellular Location | Golgi apparatus membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Secreted |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in fetal brain, lung and kidney and in adult heart, spleen and thymus (PubMed:7624364). Present to a lesser extent in adult brain, placenta, lung, large and small intestine and peripheral blood leukocytes (PubMed:7624364) |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the polycondensation of alpha-2,8-linked sialic acid required for the synthesis of polysialic acid, a modulator of the adhesive properties of neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM1). The encoded protein, which is a member of glycosyltransferase family 29, is a type II membrane protein that may be present in the Golgi apparatus.
References
Johnson, M.P., et al. Hum. Genet. 126(5):655-666(2009)
Foley, D.A., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 284(23):15505-15516(2009)
Otowa, T., et al. J. Hum. Genet. 54(2):122-126(2009)
Sonuga-Barke, E.J., et al. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 147B (8), 1359-1368 (2008) :
Schreiber, S.C., et al. Gastroenterology 134(5):1555-1566(2008)
Close, B.E., et al. Glycobiology 11(11):997-1008(2001)
Angata, K., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 276(18):15369-15377(2001)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.














 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.