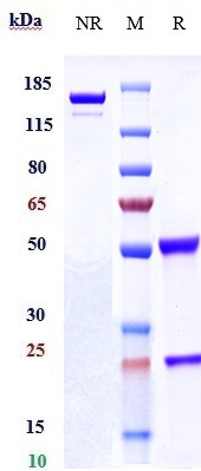
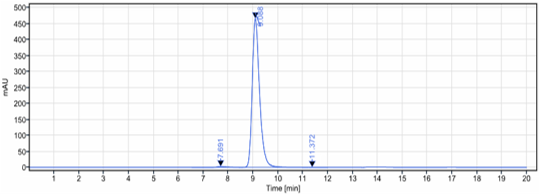
Anti-CLEC12A / CD371 Reference Antibody (tepoditamab)
Recombinant Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| FC, Kinetics, Animal Model |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q5QGZ9 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Calculated MW | 144.73 KDa |
| Target/Specificity | CLEC12A / CD371 |
|---|---|
| Endotoxin | < 0.001EU/ µg,determined by LAL method. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Expression system | CHO Cell |
| Format | Purified monoclonal antibody supplied in PBS, pH6.0, without preservative.This antibody is purified through a protein A column. |
| Name | CLEC12A {ECO:0000303|PubMed:16838277, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:31713} |
|---|---|
| Function | Myeloid inhibitory C-type lectin receptor that acts as a negative regulator of myeloid cell activation (PubMed:14739280, PubMed:15238421, PubMed:16239426, PubMed:34234773, PubMed:38367667, PubMed:38386511, PubMed:39143217). Myeloid cell inhibition is required to limit proinflammatory pathways and protect against excessive inflammation (By similarity). Specifically recognizes and binds various structures, such as neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) or monosodium urate crystals (PubMed:38367667, PubMed:38386511, PubMed:39143217). Also acts as a pattern-recognition receptor for pathogen-associated molecules, such as plasmodium hemozoin or mycobacterial micolic acid (PubMed:31269448, PubMed:36542980). Ligand-binding induces phosphorylation of its ITIM motif, followed by recruitment of tyrosine- protein phosphatases PTPN6 and PTPN11, which counteract tyrosine- protein kinase SYK, thereby preventing myeloid cell activation (PubMed:14739280, PubMed:16239426, PubMed:34234773). Acts as a pattern- recognition receptor for NETs in neutrophils: specifically recognizes DNA in NETs, leading to inhibit neutrophil activation and limit further NET formation (PubMed:39143217). This regulation is essential for controlling key neutrophil responses and limit NET-mediated inflammatory conditions (By similarity). Also recognizes dead cells by acting as a receptor for monosodium urate crystals, leading to down- regulate neutrophil activation (PubMed:38367667, PubMed:38386511). Binding to monosodium urate crystals also promotes the type I interferon response (By similarity). Acts as an inhibitor of natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity (PubMed:15238421). Also acts as an ihibitor of dendritic cell maturation in an IL10-dependent manner (PubMed:16239426). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Note=Ligand binding leads to internalization (PubMed:16239426). Clusters at phagocytic vesicles upon monosodium urate crystal-binding (PubMed:38367667) |
| Tissue Location | Preferentially expressed in lymphoid tissues and immune cells, including natural killer (NK) cells, T-cells, dendritic cells and monocytes or macrophages (PubMed:14739280, PubMed:15238421, PubMed:15548716, PubMed:16239426, PubMed:16838277). Detected in spleen macrophage-rich red pulp and in lymph node (at protein level) (PubMed:16838277). Detected in peripheral blood leukocytes, dendritic cells, bone marrow, monocytes, mononuclear leukocytes and macrophages (PubMed:16838277). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.