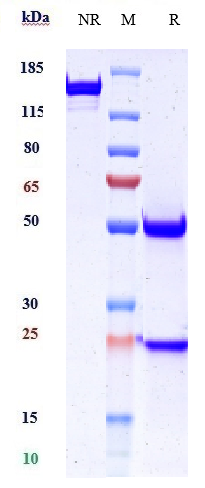
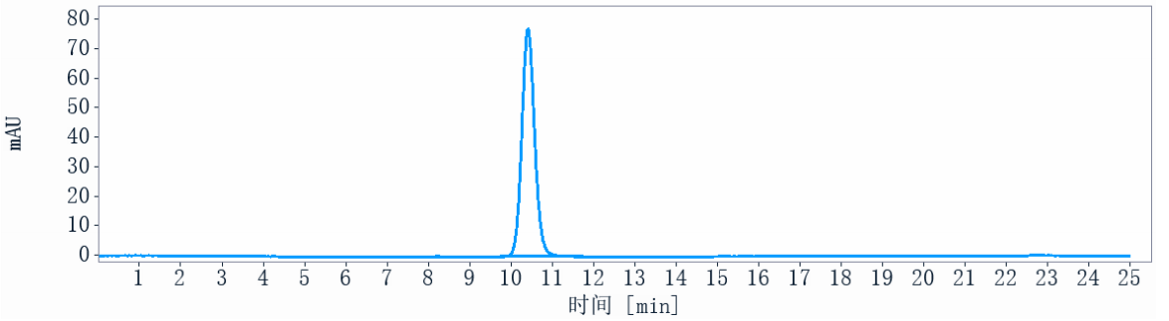
Anti-DSG3 Reference Antibody (Forerunner patent anti-DSG3)
Recombinant Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| FC, Kinetics, Animal Model |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P32926 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Calculated MW | 146.54 KDa |
| Target/Specificity | DSG3 |
|---|---|
| Endotoxin | < 0.001EU/ µg,determined by LAL method. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Expression system | CHO Cell |
| Format | Purified monoclonal antibody supplied in PBS, pH6.0, without preservative.This antibody is purified through a protein A column. |
| Name | DSG3 (HGNC:3050) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CDHF6 |
| Function | A component of desmosome cell-cell junctions which are required for positive regulation of cellular adhesion (PubMed:31835537). Required for adherens and desmosome junction assembly in response to mechanical force in keratinocytes (PubMed:31835537). Required for desmosome-mediated cell-cell adhesion of cells surrounding the telogen hair club and the basal layer of the outer root sheath epithelium, consequently is essential for the anchoring of telogen hairs in the hair follicle (PubMed:9701552). Required for the maintenance of the epithelial barrier via promoting desmosome-mediated intercellular attachment of suprabasal epithelium to basal cells (By similarity). May play a role in the protein stability of the desmosome plaque components DSP, JUP, PKP1, PKP2 and PKP3 (PubMed:22294297). Required for YAP1 localization at the plasma membrane in keratinocytes in response to mechanical strain, via the formation of an interaction complex composed of DSG3, PKP1 and YWHAG (PubMed:31835537). May also be involved in the positive regulation of YAP1 target gene transcription and as a result cell proliferation (PubMed:31835537). Positively regulates cellular contractility and cell junction formation via organization of cortical F-actin bundles and anchoring of actin to tight junctions, in conjunction with RAC1 (PubMed:22796473). The cytoplasmic pool of DSG3 is required for the localization of CDH1 and CTNNB1 at developing adherens junctions, potentially via modulation of SRC activity (PubMed:22294297). Inhibits keratinocyte migration via suppression of p38MAPK signaling, may therefore play a role in moderating wound healing (PubMed:26763450). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell junction, desmosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35902}. Cytoplasm. Cell junction, tight junction. Cell junction |
| Tissue Location | Expressed throughout the basal and spinous layer of the epidermis with weak expression in the granular layer (at protein level) (PubMed:19717567). Expressed in skin and mucosa (at protein level) (PubMed:22294297, PubMed:30528827). Expressed in the basal layer of the outer root sheath of the telogen hair club, specifically at the cell membrane between the apex of the cells and the surrounding hair club (at protein level) (PubMed:9701552). Expression is less abundant between the lateral margins of the outer root sheath basal cells (at protein level) (PubMed:9701552). Also expressed in the tongue, tonsil and esophagus (PubMed:16740002). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.