CX3CL1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E, IP |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P78423 |
| Other Accession | AAB50014, 1899259 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 42203 Da |
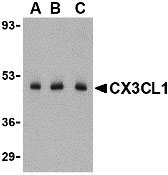
| Application Notes | CX3CL1 antibody can be used for detection of CX3CL1 by Western blot at 0.5 - 2 µg/mL dilution. CX3CL1 is ofen observed migrating at 80 - 100 kDa in SDS-PAGE, presumably due to post-translational modification. |
| Gene ID | 6376 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | CX3CL1 Antibody: NTN, NTT, CXC3, CXC3C, SCYD1, ABCD-3, C3Xkine, fractalkine, neurotactin, FKN, A-152E5.2, Fractalkine, C-X3-C motif chemokine 1, chemokine (C-X3-C motif) ligand 1 |
| Target/Specificity | CX3CL1; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | CX3CL1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | CX3CL1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CX3CL1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:9024663} |
|---|---|
| Function | Chemokine that acts as a ligand for both CX3CR1 and integrins ITGAV:ITGB3 and ITGA4:ITGB1 (PubMed:12055230, PubMed:21829356, PubMed:23125415, PubMed:9782118, PubMed:9931005). The CX3CR1-CX3CL1 signaling exerts distinct functions in different tissue compartments, such as immune response, inflammation, cell adhesion and chemotaxis (PubMed:12055230, PubMed:9024663, PubMed:9177350, PubMed:9782118). Regulates leukocyte adhesion and migration processes at the endothelium (PubMed:9024663, PubMed:9177350). Can activate integrins in both a CX3CR1-dependent and CX3CR1-independent manner (PubMed:23125415, PubMed:24789099). In the presence of CX3CR1, activates integrins by binding to the classical ligand-binding site (site 1) in integrins (PubMed:23125415, PubMed:24789099). In the absence of CX3CR1, binds to a second site (site 2) in integrins which is distinct from site 1 and enhances the binding of other integrin ligands to site 1 (PubMed:23125415, PubMed:24789099). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the seminal plasma, endometrial fluid and follicular fluid (at protein level). Small intestine, colon, testis, prostate, heart, brain, lung, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas. Most abundant in the brain and heart |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
CX3CL1 Antibody: Chemokines are a family of proteins associated with the trafficking of leukocytes in immune surveillance and inflammatory cell recruitment. They are classified based on the positions of key cysteine residues. CX3CL1 is a CX3C chemokine known to induce adhesion and migration of leukocytes mediated by a membrane-bound and soluble form respectively. Recent experiments have shown that CX3CL1 can suppress the production of nitrous oxide, interleukin-6, and TNF-α in activated microglia and neuronal cells, suggesting that it may act as an intrinsic inhibitor against neurotoxicity by activated microglia. Its receptor, CX3CR1, also functions as a co-receptor for HIV-1 and HIV-2 envelope fusion and virus infection, which can be inhibited by CX3CL1.
References
Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, et al. Chemokines and their receptors in the central nervous system. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2001; 22:147-84.
Umehara H, Goda S, Imai T, et al. Fractalkine, a CX3C-chemokine, functions predominantly as an adhesion molecule in monocytic cell line THP-1. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2001; 79:298-302.
Mizuno T, Kawanokuchi J, Numata K, et al. Production and neuroprotective functions of fractalkine in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 2003; 979:65-70.
Combadiere C, Salzwedel K, Smith ED, et al. Identification of CX3CR1. A chemotactic receptor for the human CX3C chemokine fractalkine and a fusion coreceptor for HIV-1. J. Biol. Chem.1998; 273:23799-804.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.