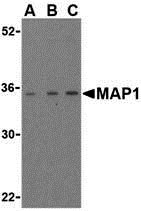
MAP1 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q96BY2 |
| Other Accession | NP_071434, 19923584 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 39513 Da |
| Application Notes | MAP1 antibody can be used for the detection of MAP-1 by Western blot at 1 to 4 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 64112 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | MAP1 Antibody: MAP-1, PNMA4, Modulator of apoptosis 1, Paraneoplastic antigen Ma4, MAP-1, modulator of apoptosis 1 |
| Target/Specificity | MOAP1; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | MAP1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | MAP1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MOAP1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:19366867, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:16658} |
|---|---|
| Function | Retrotransposon-derived protein that forms virion-like capsids (By similarity). Acts as an effector of BAX during apoptosis: enriched at outer mitochondria membrane and associates with BAX upon induction of apoptosis, facilitating BAX-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis (PubMed:11060313, PubMed:16199525). Required for death receptor-dependent apoptosis (PubMed:11060313). When associated with RASSF1, promotes BAX conformational change and translocation to mitochondrial membranes in response to TNF and TNFSF10 stimulation (PubMed:15949439). Also promotes autophagy: promotes phagophore closure via association with ATG8 proteins (PubMed:33783314). Acts as an inhibitor of the NFE2L2/NRF2 pathway via interaction with SQSTM1: interaction promotes dissociation of SQSTM1 inclusion bodies that sequester KEAP1, relieving inactivation of the BCR(KEAP1) complex (PubMed:33393215). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Mitochondrion outer membrane Extracellular vesicle membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ERH6} Note=Forms virion-like extracellular vesicles that are released from cells. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ERH6} |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed, with high levels in heart and brain. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
MAP1 Antibody: Apoptosis plays a major role in normal organism development, tissue homeostasis, and removal of damaged cells. Disruption of this process has been implicated in a variety of diseases such as cancer. Members of the Bcl-2 family are known to be critical regulators of this process. These proteins are characterized by the presence of several conserved motifs termed Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains. A related protein termed MAP-1 has recently been identified. This protein contains a BH3-like domain and induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in mammalian cells when overexpressed. It forms homodimers and associates with Bcl-2 family members such as Bax, Bcl-2, and Bcl-XL in vitro and in vivo. It has been suggested that MAP-1 associates with the tumor suppressor RASSF1A following death receptor activation, allowing a conformational change in Bax that leads to cellular apoptosis.
References
Lockshin RA, Osborne B, and Zakeri Z. Cell death in the third millennium. Cell Death Differ. 2000; 7:2-7.
Cory S, Huang DCS, and Adams JM. The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 2003; 22:8590-607.
Heiser D, Labi V, Erlacher M, et al. The Bcl-2 protein family and its role in the development of neoplastic disease. Exp. Geron. 2004; 39:1125-35.
Tan KO, Tan KML, Chan S-L, et al. MAP-1, a novel proapoptotic protein containing a BH3-like motif that associates with Bax through its Bcl-2 homology domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2001; 276:2802-7.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.