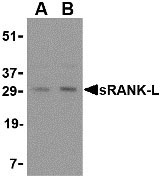
sRANK Ligand Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O14788 |
| Other Accession | NP_003692, 4507595 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 35 kDa |
| Application Notes | sRANK-L antibody can be used for detection of sRANK-L by Western blot at 0.25 - 0.5 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 8600 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | sRANK Ligand Antibody: ODF, OPGL, sOdf, CD254, OPTB2, RANKL, TRANCE, hRANKL2, Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, Osteoclast differentiation factor, ODF, tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11 |
| Target/Specificity | TNFSF11; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Antibody can be stored at 4°C up to one year. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | sRANK Ligand Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | TNFSF11 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | OPGL, RANKL, TRANCE |
| Function | Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF11B/OPG and to TNFRSF11A/RANK. Osteoclast differentiation and activation factor. Augments the ability of dendritic cells to stimulate naive T-cell proliferation. May be an important regulator of interactions between T-cells and dendritic cells and may play a role in the regulation of the T-cell-dependent immune response. May also play an important role in enhanced bone-resorption in humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy (PubMed:22664871). Induces osteoclastogenesis by activating multiple signaling pathways in osteoclast precursor cells, chief among which is induction of long lasting oscillations in the intracellular concentration of Ca (2+) resulting in the activation of NFATC1, which translocates to the nucleus and induces osteoclast-specific gene transcription to allow differentiation of osteoclasts. During osteoclast differentiation, in a TMEM64 and ATP2A2-dependent manner induces activation of CREB1 and mitochondrial ROS generation necessary for proper osteoclast generation (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein [Isoform 2]: Cytoplasm. |
| Tissue Location | Highest in the peripheral lymph nodes, weak in spleen, peripheral blood Leukocytes, bone marrow, heart, placenta, skeletal muscle, stomach and thyroid |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
sRANK Ligand Antibody: The receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANK-L) is a recently discovered member of the TNF-ligand family involved in the regulation of the T cell-dependent immune response, lymph node organogenesis and bone formation. RANK-L exists as both a normal, transmembrane form and a truncated, soluble form (sRANK-L), both of which can stimulate the receptor. Activation of T cells, such as by treatment with interleukin-7, induces RANK-L production and leads to an increase of osteoclast formation and bone loss. Finally, sRANK-L can activate the antiapoptotic kinase Akt through a signaling complex involving Src kinase and TRAF6, suggesting sRANK-L may also play a role in regulating apoptosis. This antibody will recognize both the soluble form and the uncleaved transmembrane form of RANK-L.
References
Wong BR, Rho J, Arron J, et al. TRANCE is a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family that activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase in T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997; 272:25190-4.
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature 1999; 397:315-23.
Weitzmann MN, Cenci S, Rifas L, et al. Interleukin-7 stimulates osteoclast formation by up-regulating the T-cell production of soluble osteoclastogenic cytokines. Blood 2000; 96:1873-8.
Bharti AC, Takada Y, Shishodia S, et al. Evidence that receptor activator of the nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB ligand can suppress cell proliferation and induce apoptosis through activation of a NF-kappaB-independent and TRAF6-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2004; 279:6065-76.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.













 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.